Portal:North America
The North America Portal

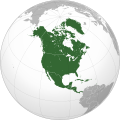
North America is a continent in the Northern and Western Hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes the Bahamas, Bermuda, Canada, the Caribbean, Central America, Clipperton Island, Greenland, Mexico, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the United States.
North America covers an area of about 24,709,000 square kilometers (9,540,000 square miles), representing approximately 16.5% of the Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. As of 2021[update], North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In human geography, the terms "North America" and "North American" can refer to Canada, the United States, Mexico, and Greenland or, alternatively, Canada, Greenland and the US (Mexico being classified as part of Latin America) or simply Canada and the US (Greenland being classified as either Arctic or European (due to its political status as a part of Denmark) and Mexico classified as Latin American).
It is unknown with certainty how and when first human populations first reached North America. People were known to live in the Americas at least 20,000 years ago, but various evidence points to possibly earlier dates. The Paleo-Indian period in North America followed the Last Glacial Period, and lasted until about 10,000 years ago when the Archaic period began. The classic stage followed the Archaic period, and lasted from approximately the 6th to 13th centuries. Beginning in 1000 AD, the Norse were the first Europeans to begin exploring and ultimately colonizing areas of North America.
In 1492, the exploratory voyages of Christopher Columbus led to a transatlantic exchange, including migrations of European settlers during the Age of Discovery and the early modern period. Present-day cultural and ethnic patterns reflect interactions between European colonists, indigenous peoples, enslaved Africans, immigrants from Europe, Asia, and descendants of these respective groups. (Full article...)

The Panic of 1907, also known as the 1907 Bankers' Panic or Knickerbocker Crisis, was a financial crisis that took place in the United States over a three-week period starting in mid-October, when the New York Stock Exchange suddenly fell almost 50% from its peak the previous year. The panic occurred during a time of economic recession, and there were numerous runs affecting banks and trust companies. The 1907 panic eventually spread throughout the nation when many state and local banks and businesses entered bankruptcy. The primary causes of the run included a retraction of market liquidity by a number of New York City banks and a loss of confidence among depositors, exacerbated by unregulated side bets at bucket shops.
The panic was triggered by the failed attempt in October 1907 to corner the market on stock of the United Copper Company. When the bid failed, banks that had lent money to the cornering scheme suffered runs that later spread to affiliated banks and trusts, leading a week later to the downfall of the Knickerbocker Trust Company, New York City's third-largest trust. The collapse of the Knickerbocker spread fear throughout the city's trusts as regional banks withdrew reserves from New York City banks. The panic then extended across the nation as vast numbers of people withdrew deposits from their regional banks, causing the 8th-largest decline in U.S. stock market history. (Full article...)

Joseph Georges Gonzague Vézina (/ˈvɛzɪnə/; French: [ʒɔʁʒ vezina]; January 21, 1887 – March 27, 1926) was a Canadian professional ice hockey goaltender who played seven seasons in the National Hockey Association (NHA) and nine in the National Hockey League (NHL), all with the Montreal Canadiens. After being signed by the Canadiens in 1910, Vézina played in 327 consecutive regular season games and a further 39 playoff games, before leaving early during a game in 1925 due to illness. Vézina was diagnosed with tuberculosis, and died on March 27, 1926.
The only goaltender to play for the Canadiens between 1910 and 1925, Vézina helped the team win the Stanley Cup in 1916 and 1924, while reaching the Stanley Cup Finals three more times. Nicknamed the "Chicoutimi Cucumber" for his calm composure while in goal, Vézina allowed the fewest goals in the league seven times in his career: four times in the NHA and three times in the NHL. In 1918, Vézina became the first NHL goaltender to both record a shutout and earn an assist on a goal. At the start of the 1926–27 NHL season, the Canadiens donated the Vezina Trophy to the NHL as an award to the goaltender who allowed the fewest goals during the season. Since 1981, the award has been given to the most outstanding goaltender as determined by a vote of NHL general managers. In Vézina's hometown of Chicoutimi, the sports arena is named the Centre Georges-Vézina in his honour. When the Hockey Hall of Fame opened in 1945, Vézina was one of the original nine inductees, and in 2017 the NHL included him on their list of the 100 greatest players in league history. (Full article...)

The Central American squirrel monkey (Saimiri oerstedii), also known as the red-backed squirrel monkey, is a squirrel monkey species from the Pacific coast of Costa Rica and Panama. It is restricted to the northwestern tip of Panama near the border with Costa Rica, and the central and southern Pacific coast of Costa Rica, primarily in Manuel Antonio and Corcovado National Parks.
It is a small monkey with an orange back and a distinctive white and black facial mask. It has an omnivorous diet, eating fruits, other plant materials, invertebrates and some small vertebrates. In turn, it has a number of predators, including raptors, cats and snakes. It lives in large groups that typically contain between 20 and 75 monkeys. It has one of the most egalitarian social structures of all monkeys. Females do not form dominance hierarchies, and males do so only at breeding season. Females become sexually mature at 2+1⁄2 years, and males at 4 to 5 years. Sexually mature females leave the natal group, but males can remain with their natal group their entire life. The Central American squirrel monkey can live for more than 15 years. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ...that in 1869 the Spanish colonial authorities banned Baseball in Cuba because Cubans began to prefer baseball to viewing bullfights, the Spaniards' national sport?
- ... that Vermont coppers (pictured) were the currency used in Vermont before it became a U.S. state in 1791?
- ...that Navassa Island off the west coast of Haiti is claimed by the United States as an unorganized unincorporated territory?
- ... that the First Mexican Empire was the official name of independent Mexico under a monarchical regime from 1822 to 1823?
- ... that the book The Complex: How the Military Invades Our Everyday Lives explores U.S. military expenditures on items including Southern catfish restaurants and Dunkin' Donuts?
Selected panorama

Topics
Categories
List articles
Related portals
Northern America
Central America
Caribbean
WikiProjects
 North America
North America-
 Canada
Canada -
 Greenland
Greenland -
 Mexico
Mexico -
 Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon -
 United States
United States  Central America
Central America-
 Belize
Belize -
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica -
 El Salvador
El Salvador -
 Guatemala
Guatemala -
 Honduras
Honduras -
 Nicaragua
Nicaragua -
 Panama
Panama  Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica Caribbean
Caribbean-
 Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda -
 Bahamas
Bahamas -
 Barbados
Barbados -
 Bermuda
Bermuda -
 Cuba
Cuba -
 Dominica
Dominica -
 Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic -
 Grenada
Grenada -
 Haiti
Haiti -
 Jamaica
Jamaica -
 Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico -
 Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis -
 Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia -
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines -
 Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus