Oxetene
Appearance
(Redirected from Oxete)
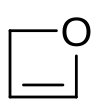
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2H-Oxete | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-Oxacyclobut-2-ene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 4652799 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O | |
| Molar mass | 56.06326 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Oxetene is an unsaturated heterocycle. The compound is unstable[citation needed] and has been synthesized.[1] Compared to oxetane, the saturated compound, oxetene is destabilized because the double bond increases the ring strain.[citation needed] Synthesis of some substituted derivatives has been reported.[2][3]
Oxetene is less studied than oxetane, a related compound that is the base of a number of organic molecules.[2]
Synthesis
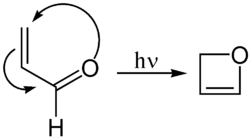
[edit]Oxetene can be synthesised by the photochemical cyclization of acrolein:[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Friedrich, Louis; Lam, Yuk-Sun (1981). "Syntheses and reactions of 3-phenyloxete and the parent unsubstituted oxete". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 46 (2): 306–311. doi:10.1021/jo00315a016.
- ^ a b Longchar, M.; Bora, U.; Boruah, R. C.; Sandhu, J. S. (2002). "A Convenient Synthesis of Oxetene Via [2+2]Cycloaddition Reaction Under Microwave Irradiation". Synthetic Communications. 32 (23): 3611. doi:10.1081/SCC-120014973.
- ^ Martino, Philip C.; Shevlin, Philip B. (1980). "Oxetene: Synthesis and energetics of electrocyclic ring opening". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 102 (16): 5429. doi:10.1021/ja00536a069.
- ^ Kikuchi O. (1981). "A classification of the photochemical electrocyclic reactions of heteroatom conjugated systems". Tetrahedron Lett. 22 (9): 859–862. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(81)80015-9.
