NAND gate
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
| A | B | A NAND B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
In digital electronics, a NAND gate (Negated AND or NOT AND) is a logic gate which produces an output that is false only if all its inputs are true; thus its output is complement to that of the AND gate. A LOW (0) output results only if both the inputs to the gate are HIGH (1); if one or both inputs are LOW (0), a HIGH (1) output results. It is made using transistors.
The NAND gate is significant because any boolean function can be implemented by using a combination of NAND gates. This property is called functional completeness.
Digital systems employing certain logic circuits take advantage of NAND's functional completeness.
The function NAND(a1, a2, ..., an) is logically equivalent to NOT(a1 AND a2 AND ... AND an).
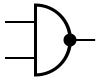
Symbols
There are three symbols for NAND gates: the MIL/ANSI symbol, the IEC symbol and the deprecated DIN symbol sometimes found on old schematics. For more information see logic gate symbols.

|

|
|
| MIL/ANSI Symbol | IEC Symbol | DIN Symbol |
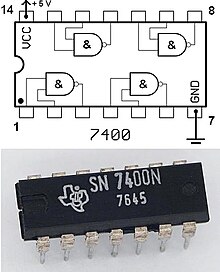
Hardware description and pinout
NAND gates are basic logic gates, and as such they are recognised in TTL and CMOS ICs.
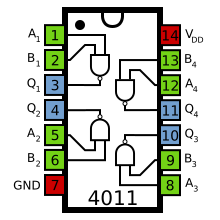
CMOS version
The standard, 4000 series, CMOS IC is the 4011, which includes four independent, two-input, NAND gates.
Availability
These devices are available from most semiconductor manufacturers such as Fairchild Semiconductor, Philips or Texas Instruments. These are usually available in both through-hole DIL and SOIC format. Datasheets are readily available in most datasheet databases.
The standard 2-, 3-, 4- and 8-input NAND gates are available:
- CMOS
- 4011: Quad 2-input NAND gate
- 4023: Triple 3-input NAND gate
- 4012: Dual 4-input NAND gate
- 4068: Mono 8-input NAND gate
- TTL
- 7400: Quad 2-input NAND gate
- 7410: Triple 3-input NAND gate
- 7420: Dual 4-input NAND gate
- 7430: Mono 8-input NAND gate
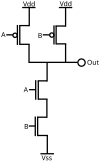
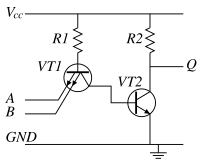
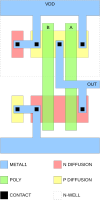
Implementations
The NAND gate has the property of functional completeness. That is, any other logic function (AND, OR, etc.) can be implemented using only NAND gates.[1] An entire processor can be created using NAND gates alone. In TTL ICs using multiple-emitter transistors, it also requires fewer transistors than a NOR gate.
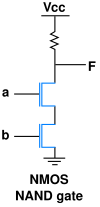 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Alternatives
If no specific NAND gates are available, one can be made from NOR gates, because NAND and NOR gates are considered the "universal gates", meaning that they can be used to make all the others.[1]
| NOR construction |
|---|

|
See also
- AND gate
- OR gate
- NOT gate
- NOR gate
- XOR gate
- XNOR gate
- Boolean algebra (logic)
- Logic gates
- NAND logic
- Digital electronics
