Moctezuma II
| Moctezuma II Motecuhzoma Xocoyotl | |
|---|---|
| Tlatoani of Tenochtitlan | |
 Moctezuma II in the Codex Mendoza | |
| Reign | 1502–1520 |
| Predecessor | Ahuitzotl |
| Successor | Cuitláhuac |
| Issue | Tecuichpo Another daughter Chimalpopoca Taltecatzin |
| Father | Axayacatl |
Moctezuma (c. 1466 – June 1520), also known by a number of variant spellings including Montezuma, Moteuczoma, Motecuhzoma and referred to in full by early Nahuatl texts as Motecuhzoma Xocoyotzin[N.B. 1] and similar, was the ninth tlatoani or ruler of Tenochtitlan, reigning from 1502 to 1520. It was during Moctezuma's reign that the episode known as the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire began.
The portrayal of Moctezuma in history has mostly been colored by his role as ruler of a defeated nation, and many sources describe him as weak-willed and indecisive. The biases of some historical sources make it difficult to understand his actions during the Spanish invasion.[1]
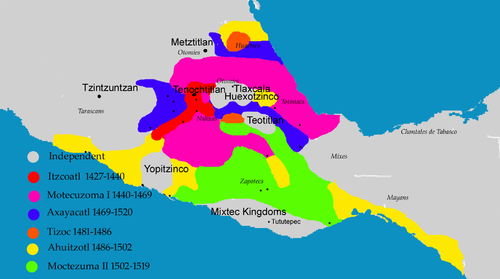
During his reign the Aztec Empire reached its maximal size. Through warfare, Moctezuma II expanded the territory as far south as Xoconosco in Chiapas and the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, and incorporated the Zapotec and Yopi people into the empire.[2] He changed the previous meritocratic system of social hierarchy and widened the divide between pipiltin (nobles) and macehualtin (commoners) by prohibiting commoners from working in the royal palaces.[2] The famous Stone of Tizoc, a sacrificial stone decorated with carvings representing Tizoc, Moctezuma's predecessor as tlatoani, was also elaborated during his rule.[citation needed]
He had eight daughters, including Tecuichpo —also known as Doña Isabel Moctezuma— and eleven sons, among them Chimalpopoca (not to be confused with the previous huey tlatoani) and Tlaltecatzin.[3]
Name
The Nahuatl pronunciation of his name is [motekʷˈsoːma]. It is a compound of a noun meaning "lord and forever almighty" and a verb meaning "to frown in anger", and so is interpreted as "he is one who frowns like a lord"[4] or "he who is angry in a noble manner."[5]
His name glyph, shown in the upper left corner of the image from the Codex Mendoza above, was composed of a diadem (xiuhuitzolli) on straight hair with an attached earspool, a separate nosepiece and a speech scroll.[6]
Regnal number
The use of a regnal number is only for modern distinction from the first Moctezuma, referred to as Moctezuma I, because even if the latter was the great-grandparent of the former, there was no dynastic succession among the Aztecs.[1] The Aztec chronicles called him Motecuhzoma Xocoyotzin, while the first was called Motecuhzoma Ilhuicamina or Huehuemotecuhzoma ("Old Moctezuma"). Xocoyotzin (IPA: [ʃokoˈjotsin]) means "honored young one".[citation needed]
The sources of Moctezuma's biography
The descriptions of the life of Moctezuma are full of contradictions, and thus nothing is known for certain about his personality and rule.
Bernal Díaz del Castillo

The first hand account of Bernal Díaz del Castillo's True History of the Conquest of New Spain paints a portrait of a noble leader who struggles to maintain order in his kingdom after he is taken prisoner by Cortés. In his first description of Moctezuma, Díaz del Castillo writes:
"The Great Montezuma was about forty years old, of good height, well proportioned, spare and slight, and not very dark, though of the usual Indian complexion. He did not wear his hair long but just over his ears, and he had a short black beard, well-shaped and thin. His face was rather long and cheerful, he had fine eyes, and in his appearance and manner could express geniality or, when necessary, a serious composure. He was very neat and clean, and took a bath every afternoon. He had many women as his mistresses, the daughters of chieftains, but two legitimate wives who were Caciques[N.B. 2] in their own right, and only some of his servants knew of it. He was quite free from sodomy. The clothes he wore one day he did not wear again till three or four days later. He had a guard of two hundred chieftains lodged in rooms beside his own, only some of whom were permitted to speak to him." (Díaz del Castillo 1568/1963: 224–25)
When Moctezuma was allegedly killed by being stoned to death by his own people "Cortes and all of us captains and soldiers wept for him, and there was no one among us that knew him and had dealings with him who did not mourn him as if he were our father, which was not surprising, since he was so good. It was stated that he had reigned for seventeen years, and was the best king they ever had in Mexico, and that he had personally triumphed in three wars against countries he had subjugated. I have spoken of the sorrow we all felt when we saw that Montezuma was dead. We even blamed the Mercederian friar for not having persuaded him to become a Christian." (Díaz del Castillo 1568/1963: 294)[7]
Bernardino de Sahagún
The Florentine Codex, made by Bernardino de Sahagún and his native informants of Tenochtitlan-subjugated Tlatelolco, generally portrays Tlatelolco and Tlatelolcan rulers in a favorable light relative to the Tenocha, and Moctezuma in particular is depicted unfavorably as a weak-willed, superstitious, and indulgent ruler (Restall 2003). Historian James Lockhart suggests that the people needed to have a scapegoat for the Aztec defeat, and Moctezuma naturally fell into that role.[8]
Hernán Cortés
Unlike Bernal Díaz, who was remembering his memories many years after the fact, Cortés wrote his Cartas de relación (Letters from Mexico) in the moment in order to justify his actions to the Spanish Crown. His prose is characterized by simple descriptions and explanations, along with frequent personal addresses to the King. In his Second Letter, Cortés describes his first encounter with Moctezuma thus:
"Mutezuma [sic] came to greet us and with him some two hundred lords, all barefoot and dressed in a different costume, but also very rich in their way and more so than the others. They came in two columns, pressed very close to the walls of the street, which is very wide and beautiful and so straight that you can see from one end to the other. Mutezuma came down the middle of this street with two chiefs, one on his right hand and the other on his left. And they were all dressed alike except that Mutezuma wore sandals whereas the others went barefoot; and they held his arm on either side." (Translation: Anthony Pagden 1986:84)[9]
Cortés' truthfulness and motives have been called into question by many scholars. Anthony Pagden[10] and Eulalia Guzman (Relaciones de Hernan Cortes 1958:279)[11] have pointed the Biblical messages that Cortés seems to ascribe to Moctezuma's retelling of the legend of Quetzalcoatl as a vengeful Messiah who would return to rule over the Mexica. Pagden has written that "There is no preconquest tradition which places Quetzalcoatl in this role, and it seems possible therefore that it was elaborated by Sahagún and Motolinía from informants who themselves had partially lost contact with their traditional tribal histories" (Pagden 1986:467)
Fernando Alvarado Tezozómoc
Fernando Alvarado Tezozómoc, who wrote the Crónica Mexicayotl, was a grandson of Moctezuma II and his chronicle mostly relates the genealogy of the Aztec rulers. He describes Moctezuma's issue and counts that Moctezuma had nineteen children – eleven sons and eight daughters.[12]
Depiction in early post-conquest literature

Some of the Aztec stories about Moctezuma describe him as being fearful of the Spanish newcomers, and some sources, such as the Florentine codex, comment that the Aztecs believed the Spaniards to be gods and Cortés to be the returned god Quetzalcoatl. The veracity of this claim is difficult to ascertain, but recently ethnohistorians specialising in early Spanish/Nahua relations have discarded it as post-conquest mythicalisation.[13]
Much of the idea of Cortés being seen as a deity can be traced back to the Florentine Codex written down some 50 years after the conquest. In the codex's description of the first meeting between Moctezuma and Cortés, the Aztec ruler is described as giving a prepared speech in classical oratorial Nahuatl, a speech which as described verbatim in the codex (written by Sahagún's Tlatelolcan informants who were probably not eyewitnesses of the meeting) included such prostrate declarations of divine or near-divine admiration as, "You have graciously come on earth, you have graciously approached your water, your high place of Mexico, you have come down to your mat, your throne, which I have briefly kept for you, I who used to keep it for you," and, "You have graciously arrived, you have known pain, you have known weariness, now come on earth, take your rest, enter into your palace, rest your limbs; may our lords come on earth." Matthew Restall argues that Moctezuma politely offering his throne to Cortés (if indeed he did ever give the speech as reported) may well have been meant as the exactly opposite of what it was taken to mean: politeness in Aztec culture was a way to assert dominance and show superiority.[14] This speech has been a factor in fostering the belief that Moctezuma was addressing Cortés as the returning god Quetzalcoatl. Other parties have also propagated the idea that the Native Americans believed the conquistadors to be gods: most notably the historians of the Franciscan order such as Fray Gerónimo de Mendieta.[15] Some Franciscan priests held millenarian beliefs and the natives taking the Spanish conquerors for gods was an idea that went well with this theology.[16] Bernardino de Sahagún, who compiled the Florentine Codex, was also a Franciscan priest.
Mythical accounts of omens and Moctezuma's superstition
Bernardino de Sahagún (1499–1590) mentions eight events, occurring prior to the arrival of the Spanish, which were interpreted as signs of a possible disaster, e.g. a comet, the burning of a temple, a crying ghostly woman, and others. Some speculate that the Aztecs were particularly susceptible to such ideas of doom and disaster because the particular year in which the Spanish arrived coincided with a "tying of years" ceremony at the end of a 52-year cycle in the Aztec calendar, which in Aztec belief was linked to changes, rebirth and dangerous events. The belief of the Aztecs being rendered passive by their own superstition is referred to by Matthew Restall as part of "The Myth of Native Desolation" to which he dedicates chapter 6 in his book Seven Myths of the Spanish Conquest.[17] These legends are likely a part of the post-conquest rationalisation by the Aztecs of their defeat, and serve to show Moctezuma as indecisive, vain, and superstitious, and ultimately the cause of the fall of the Aztec Empire.[8]
Ethnohistorian Susan Gillespie has argued that the Nahua understanding of history as repeating itself in cycles also led to a subsequent rationalisation of the events of the conquests. In this interpretation the description of Moctezuma, the final ruler of the Aztec Empire, was tailored to fit the role of earlier rulers of ending dynasties - for example Quetzalcoatl, the mythical last ruler of the Toltecs.[18] In any case it is more than likely that the description of Moctezuma in post-conquest sources was largely coloured by his role as a monumental closing figure of Aztec history.[citation needed]
Contact with the Spanish
First interactions with the Spanish

In 1517, Moctezuma received the first reports of Europeans landing on the east coast of his empire; this was the expedition of Juan de Grijalva who had landed on San Juan de Ulúa, which although within Totonac territory was under the auspices of the Aztec Empire. Moctezuma ordered that he be kept informed of any new sightings of foreigners at the coast and posted extra watch guards to accomplish this. (Díaz del Castillo 1963: 220).
When Cortés arrived in 1519, Moctezuma was immediately informed and he sent emissaries to meet the newcomers, one of them known to be an Aztec noble named Tentlil in the Nahuatl language but referred to in the writings of Cortés and Bernal Díaz del Castillo as "Tendile". As the Spaniards approached Tenochtitlan they made an alliance with the Tlaxcalteca, who were enemies of the Aztec Triple Alliance, and they helped instigate revolt in many towns under Aztec dominion. Moctezuma was aware of this and he sent gifts to the Spaniards, probably in order to show his superiority to the Spaniards and Tlaxcalteca.[19]
On November 8, 1519, Moctezuma met Cortés on the causeway leading into Tenochtitlan and the two leaders exchanged gifts. Moctezuma gave Cortés the gift of an Aztec calendar, one disc of crafted gold and another of silver. Cortés later melted these down for their material value (Díaz del Castillo 1963: 216–19).
Host and prisoner of the Spaniards
Moctezuma brought Cortés to his palace where the Spaniards lived as his guests for several months. Moctezuma continued to govern his empire and even undertook conquests of new territory during the Spaniards' stay at Tenochtitlan.[citation needed]
At some time during that period Moctezuma became a prisoner in his own house. Exactly why this happened is not clear from the extant sources. The Aztec nobility reportedly became increasingly displeased with the large Spanish army staying in Tenochtitlan, and Moctezuma told Cortés that it would be best if they left. Shortly thereafter Cortés left to fight Pánfilo de Narváez and during his absence the massacre in the main temple turned the tense situation between the Spaniards and Aztecs into direct hostilities, and Moctezuma became a hostage used by the Spaniards to assure their security.[N.B. 3]
Death

In the subsequent battles with the Spaniards after Cortés' return, Moctezuma was killed. The details of his death are unknown: different versions of his demise are given by different sources.
In his Historia, Bernal Díaz del Castillo states that on July 1, 1520, the Spanish forced Moctezuma to appear on the balcony of his palace, appealing to his countrymen to retreat. The people were appalled by their emperor's complicity and pelted him with rocks and darts. He died a short time after that. Bernal Díaz gives this account:
Barely was [the emperor's speech to his subjects] finished when a sudden shower of stones and darts descended. Our men who had been shielding Montezuma had momentarily neglected their duty when they saw the attack cease while he spoke to his chiefs. Montezuma was hit by three stones, one on the head, one on the arm, and one on the leg; and though they begged him to have his wounds dressed and eat some food and spoke very kindly to him, he refused. Then quite unexpectedly we were told that he was dead.[20]
Cortés similarly reported that Moctezuma died wounded by a stone thrown by his countrymen. On the other hand, the indigenous accounts claim that Moctezuma was killed by the Spanish prior to their leaving the city. [citation needed]
Some modern scholars, such as Matthew Restall (2003), prefer the indigenous accounts over the Spanish ones. They surmise that the Spanish killed Moctezuma once his inability to pacify the Aztec people had made him useless.[citation needed]
Aftermath
The Spaniards were forced to flee the city and they took refuge in Tlaxcala, and signed a treaty with them to conquer Tenochtitlan, offering to the Tlaxcalans freedom from any kind of tribute and the control of Tenochtitlan.[citation needed]
Moctezuma was then succeeded by his brother Cuitláhuac, who died shortly after during a smallpox epidemic. He was succeeded by his adolescent nephew, Cuauhtémoc. During the siege of the city, the sons of Moctezuma were murdered by the Aztec, possibly because they wanted to surrender. By the following year, the Aztec empire had entirely succumbed to the Spanish.[citation needed]
Following the conquest, Moctezuma's daughter Techichpotzin was considered the heiress to the king's wealth following Spanish customs and given the name "Isabel". She was married to different conquistadors who laid claim to the heritage of the Aztec emperor. [citation needed]
Descendants in Mexico and the Spanish nobility
Several lines of descendants exist in Mexico and Spain through Moctezuma II's son and daughters, notably Tlacahuepan Ihualicahuaca, or Pedro Moctezuma and Tecuichpo Ixcaxochitzin, or Isabel Moctezuma.
The grandson of Moctezuma II, Pedro's son, Ihuitemotzin, baptized as Diego Luis de Moctezuma, was brought to Spain by King Philip II. There he married Francisca de la Cueva de Valenzuela.[21] In 1627, their son Pedro Tesifón de Moctezuma was given the title of 1st Count of Moctezuma de Tultengo, and thus became part of the Spanish nobility. The title was later designated as "Count of Moctezuma de Tultengo". In 1766, the holder of the title became a Grandee of Spain. In 1865 (coincidentally during the Second Mexican Empire) the title, which was held by Antonio María Moctezuma-Marcilla de Teruel y Navarro, 14th Count of Moctezuma de Tultengo, was elevated to that of a Duke, thus becoming "Duke of Moctezuma", with "de Tultengo" being again added in 1992 by Juan Carlos I.
Another of Moctezuma's daughters, Princess Xipaguacin Moctezuma, married Juan de Grau, Baron of Toleriu, one of Cortés's senior officers, who took her back to Spain with an entourage of Mexica where she died in the Mountain village of Toleriu, near Andorra, in 1537.[citation needed] There are many descendants of this House of Grau-Moctezuma de Toleriu in Spain today.
Other holders of Spanish noble titles that descend from the Aztec emperor include Dukes of Ahumada, Counts of Miravalle, Duke of Abrantes, Condes de la Enjarada, Condes de Alba de Yeltes[citation needed], and Dukes of Atrisco.[22] The Dukes of Alba also descend from these lines.[citation needed] Many Spanish families without noble titles also descend from the numerous branches of the families of the children of Moctezuma II.
Descendants of these families included General Jerónimo Girón-Moctezuma, 3rd Marquis de las Amarilas, a 9th generation descendant of Moctezuma II, who was commander of the Spanish forces at the Battle of Fort Charlotte, and his grandson, Francisco Javier Girón y Ezpeleta, 2nd duque de Ahumada and 5th marqués de las Amarillas who was the founder of the Guardia Civil in Spain.[23]
Native American mythology and folklore
Many Native American peoples are reported to worship deities named after the Aztec ruler, and often a part of the myth is that someday the deified Moctezuma shall return to vindicate his people. In Mexico the modern day Pames, the Otomi, Tepehua[disambiguation needed], Totonac and Nahua peoples are reported to worship earth deities named after Moctezuma.[24] The name also appears in Tzotzil Maya ritual in Zinacantán where dancers dressed as a raingod are called "Moctezumas"[25]
A mythological figure of the Tohono O'odham[26] people of Northern Mexico and some Pueblo people of New Mexico and Arizona by the name Montezuma, can possibly be traced back to the Aztec ruler.[citation needed]
Hubert Howe Bancroft, writing in the 19th century (Native Races, Volume #3), speculated that the name of the historical Aztec Emperor Moctezuma had been used to refer to a combination of different cultural heroes who were united under the name of a particularly salient representative of Native American identity.
Symbol of indigenous leadership
As a symbol of resistance towards Spanish the name of Moctezuma has been invoked in several indigenous rebellions.[citation needed]
One such example was the rebellion of the Virgin Cult in Chiapas in 1721, where the followers of the Virgin Mary rebelled against the Spanish after having been told by an apparition of the virgin that Moctezuma would be resuscitated to assist them against their Spanish oppressors. In the Quisteil rebellion of the Yucatec Maya in 1761 the rebel leader Jacinto Canek reportedly called himself "Little Montezuma".[27]
References in modern culture

- The Mexican emperor is the title character in several 18th-century operas, some entitled Motezuma, for example those by Antonio Vivaldi (1733), Josef Mysliveček (1771), and some with other names, such as a Montezuma by Carl Heinrich Graun (1755) and by Niccolò Antonio Zingarelli (1781). He is also the subject of Roger Sessions' opera Montezuma (1963), and the protagonist in the modern opera La conquista (2005) by Italian composer Lorenzo Ferrero where his part is written in the Nahuatl language.
- Montezuma's Revenge is the colloquial term for any episodes of travelers' diarrhea or other sicknesses contracted by tourists visiting Mexico.
- The Mexico City Metro system has a station named Metro Moctezuma in honour of the tlatoani.
- Montezuma Castle and Montezuma Well, 13th century Indian ruins in central Arizona, were named by 19th century American pioneers who mistakenly thought they were built by the Aztecs.
- The conquest of the Aztecs is recounted in a song by Neil Young called "Cortez the Killer" from the album Zuma, a tribute to Moctezuma who appears in the song as a wise and benevolent ruler.
- In the game Age of Empires II The Conquerors you can play as the Aztecs and Moctezuma is featured in the storyline. The ending is altered from history, with the Aztecs driving back the Spaniards at the final siege of Tenochtitlan.
- In the Civilization line of games Montezuma is the leader of the Aztec empire and can be controlled by the player.
- In the game Where in Time is Carmen Sandiego? produced in 1997, Montezuma is present on the twelfth level. He is the leader of the Aztecs and the player must help him to complete his headdress.
See also
Notes
- ^ Template:Lang-nci-IPA
- ^ Cacique is a hispanicized word of Caribbean origins, meaning "hereditary lord/chief" or "(military) leader". After first encountering the term and office in the Caribbean, conquest-era writers such as Díaz often used it to describe indigenous rulers generally.
- ^ See the account of Moctezuma's captivity, as given in Díaz del Castillo (1963, pp. 245–299).
References
- ^ a b Williamson, Edwin (1992). The Penguin history of Latin America. New York: Penguin Books. p. 18. ISBN 0-14-012559-0. OCLC 29998568.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ a b Hassig, Ross (1988). Aztec warfare: imperial expansion and political control. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 231. ISBN 0-8061-2121-1. OCLC 17106411.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ González-Obregón, Luis (1992). Las Calles de México (1st ed.). Ciudad de México, DF: Editorial Porrúa. ISBN 968-452-299-1.
- ^ Andrews, J. Richard (2003) [1975]. Introduction to Classical Nahuatl. Revised Edition. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. p. 599.
- ^ Brinton, Daniel G. (1890). Ancient Nahuatl Poetry.
- ^ British Museum Exhibition Guide for Moctezuma: Aztec Ruler (2009)
- ^ The Conquest of New Spain. Bernal Díaz del Castillo. Translated by J.M. Cohen, New York: Penguin, 1963.
- ^ a b Lockhart 1993, pp. 17–19
- ^ Hernan Cortes: Letters from Mexico. Translated by Anthony Pagden. New Haven, CT: Yale UP, 1986.
- ^ Hernan Cortes: Letters from Mexico. Translated by Anthony Pagden. New Haven, CT: Yale UP, 1986:467.
- ^ Guzman, Eulalia. Relaciones de Hernan Cortes a Carlos V sobre la invasion de Anáhuac. Vol. I. Mexico, 1958.
- ^ Tezozomoc, Fernando Alvarado, 1992 (1949), Crónica Mexicayotl, Translated by Adrián León, UNAM, México
- ^ Restall 2003, chapter 6
- ^ Restall, 2003, p. 97
- ^ Martínez 1980
- ^ Phelan 1956
- ^ Restall, 2003, chapter 6
- ^ Gillespie, 1989, Chapter 5.
- ^ Restall, Matthew. Seven Myths of the Spanish Conquest. Oxford University Press (2003), ISBN 0-19-516077-0
- ^ Díaz del Castillo (1963, p. 294)
- ^ "Project MUSE". Muse.jhu.edu. Retrieved 16 November 2009.
- ^ http://books.google.com/books?id=UIeezdj79F8C&printsec=frontcover&dq=chipman+moctezuma+children&hl=en&ei=UHo9TPzdOoSosQOMvrXaCg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CCgQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=Atrisco%20miravalle&f=false
- ^ "A Descendant of Moctezuma at the Battle of Mobile, 1780". Book-smith.tripod.com. 4 January 2001. Retrieved 16 November 2009. [dead link]
- ^ Gillespie 1989:165–66
- ^ Bricker,1981:138–9
- ^ Another telling of the Tohono O'odham legend, dated to 1883
- ^ Bricker,1981:73
Bibliography
- González-Obregón, Luis (1992). Las Calles de México (1st ed.). Ciudad de México, DF: Editorial Porrúa. ISBN 968-452-299-1.
- Lockhart, James (ed. and trans.) (1993);We People Here: Nahuatl Accounts of the Conquest of Mexico. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Martínez, Jose Luis (1980). "Gerónimo de Mendieta". Estudios de Cultura Nahuatl, UNAM, Mexico. 14: 131–197.
- Phelan, John Leddy (1970) [1956]. The Millennial Kingdom of the Franciscans in the New World: A Study of the Writings of Gerónimo de Mendieta (1525–1604) (2nd edition, revised ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-01404-9. OCLC 88926.
- Townsend, Richard F. (2000). The Aztecs (2nd edition, revised ed.). London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-28132-7. OCLC 43337963.
- Weaver, Muriel Porter (1993). The Aztecs, Maya, and Their Predecessors: Archaeology of Mesoamerica (3rd ed.). San Diego, CA: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-739065-0. OCLC 25832740.
External links
- A reconstructed portrait of Motecuhzoma Xocoyotzin, based on historical sources, in a contemporary style.