Central Zone, Tigray
Central Zone
ዞባ ማእኸላይ | |
|---|---|
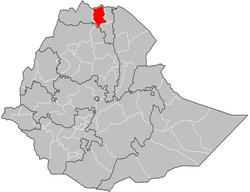 Central Tigray location in Ethiopia | |
| Country | |
| Region | |
| Largest city | Axum |
| Area | |
• Total | 22,133.87 km2 (8,545.93 sq mi) |
| Population (2012 est.) | |
• Total | 1,412,339 |
| • Density | 64/km2 (170/sq mi) |
The Central Zone (Tigrinya: ዞባ ማእከላይ, romanized: Zobā Māʼékalāy) is a zone in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Towns and cities in the Central Zone include Axum and Adwa, as well as the historically significant village of Yeha and the town of Tembien Abiyi Adi. The Central Zone is bordered on the east by the Eastern Zone, on the south by South Eastern Zone, on the west by North Western Zone and on the north by Eritrea.
Demographics
[edit]
Based on the 2007 Census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia (CSA), this Zone has a total population of 1,245,824, of whom 613,797 are men and 632,027 women; 176,453 or 14.16% are urban inhabitants. The largest ethnic group reported in the Central Zone was the Tigrayan (99.37%); all other ethnic groups made up 0.63% of the population. Tigrinya is spoken as a first language by 99.4; the remaining 0.6% spoke all other primary languages reported. 97.82% of the population said they were Orthodox Christians, and 2.07% were Muslim.[1]
The 1994 national census reported a total population for the zone of 943,850, of whom 464,633 were men and 479,217 women; 91,058 or 9.6% of its population were urban dwellers. The Zone is predominantly Tigrayan, at 99.6% of the population, while 0.11% were Agaw, 0.096% Amhara, and all other ethnic groups 0.12%. Tigrinya was spoken as a first language by 99.67% of the inhabitants. 98.41% of the population said they were Orthodox Christians, and 1.55% were Muslim. Concerning education in the Zone, 9.64% of the population were considered literate; 10.62% of children aged 7–12 were in primary school, while a negligible number of the children aged 13–14 were in junior secondary school, and 0.14% of children aged 15–18 were in senior secondary school. Concerning sanitary conditions, about 25% of the urban and 5.6% of all houses had access to safe drinking water at the time of the census; about 2.5% of the urban and 6% of the total had toilet facilities.[2]
According to a May 24, 2004 World Bank memorandum, 13% of the inhabitants of the Central Zone have access to electricity, this zone has a road density of 29.0 kilometers per 1000 square kilometers, the average rural household has 0.8 hectare of land (compared to the national average of 1.01 hectare of land and a regional average of 0.51)[3] and the equivalent of 0.8 heads of livestock. 17% of the population is in non-farm related jobs, compared to the national average of 25% and a regional average of 28%. 74% of all eligible children are enrolled in primary school, and 28% in secondary schools. 78% of the zone is exposed to malaria, and none to Tsetse fly. The memorandum gave this zone a drought risk rating of 616.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Census 2007 Tables: Tigray Region Archived November 14, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, Tables 2.1, 3.1, 3.2, 3.4.
- ^ The 1994 Population and Housing Census of Ethiopia: Tigray Region Archived December 7, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, vol. 1, part 1: Tables 2.1, 2.11, 2.14
- ^ Comparative national and regional figures comes from another World Bank publication, Klaus Deininger et al. "Tenure Security and Land Related Investment", WP-2991 Archived 2007-03-10 at the Wayback Machine (accessed 23 March 2006).
- ^ World Bank, Four Ethiopias: A Regional Characterization (accessed 23 March 2006).
