Hyperlipidemia
| Hyperlipidemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hyperlipoproteinemia, hyperlipidaemia[1] |
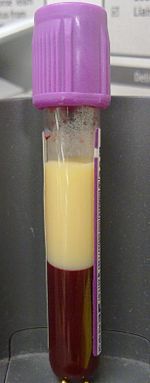 | |
| A 4-ml sample of hyperlipidemic blood in a vacutainer with EDTA. Left to settle for four hours without centrifugation, the lipids separated into the top fraction. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Differential diagnosis | Hypertriglyceridemia |
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally high levels of any or all lipids (e.g. fats, triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids) or lipoproteins in the blood.[2] The term hyperlipidemia refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding.[3] Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels.[3]
Lipids (water-insoluble molecules) are transported in a protein capsule.[4] The size of that capsule, or lipoprotein, determines its density.[4] The lipoprotein density and type of apolipoproteins it contains determines the fate of the particle and its influence on metabolism.
Hyperlipidemias are divided into primary and secondary subtypes. Primary hyperlipidemia is usually due to genetic causes (such as a mutation in a receptor protein), while secondary hyperlipidemia arises due to other underlying causes such as diabetes. Lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities are common in the general population and are regarded as modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease due to their influence on atherosclerosis.[5] In addition, some forms may predispose to acute pancreatitis.
Signs and Symptoms
[edit]Hyperlipidemia, on its own, is typically asymptomatic. However, further sequelae of hyperlipidemia may lead to consequences, and, therefore, symptoms. Increased lipids in the blood results in the formation of plaques in blood vessels, leading to a condition called atherosclerosis.[6] If the buildup of lipids is in the coronary arteries, then this may lead to a heart attack, due to the lack of blood perfusion to the heart muscle. If the buildup happens in the brain, then this may lead to a stroke.
Some physical exams findings suggestive of hyperlipidemia are xanthomas, which are yellow "bumps" found on the skin, on the arms, legs, or trunk. Xanthelasmas are similar deposits of fat under the skin, but these appear on the eyelids.[7]
Causes
[edit]The major causes of hyperlipidemia are either genetic or lifestyle causes. Individuals with a genetic predisposition for hyperlipidemia or a family history are more at risk for this disease. However, unhealthy habits can lead to secondary hyperlipidemia:[6] A diet heavy in trans fats or saturated fats, contained in red meats and dairy, can lead to secondary hyperlipidemia. Not getting enough exercise can also be a risk factor. Stress and alcohol can lead to elevated levels of cholesterol. Smoking damages blood vessels, contributing to atherosclerosis and lowers HDL (good cholesterol) levels.[8] An increase in age also increases the risk of hyperlipidemia.

Classification
[edit]Hyperlipidemias may basically be classified as either familial (also called primary[9]) when caused by specific genetic abnormalities or acquired (also called secondary)[9] when resulting from another underlying disorder that leads to alterations in plasma lipid and lipoprotein metabolism.[9] Also, hyperlipidemia may be idiopathic, that is, without a known cause.[10]
Hyperlipidemias are also classified according to which types of lipids are elevated, that is hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia or both in combined hyperlipidemia. Elevated levels of Lipoprotein(a) may also be classified as a form of hyperlipidemia.[11]

Familial (primary)
[edit]Familial hyperlipidemias are classified according to the Fredrickson classification, which is based on the pattern of lipoproteins on electrophoresis or ultracentrifugation.[12] It was later adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO).[13] It does not directly account for HDL, and it does not distinguish among the different genes that may be partially responsible for some of these conditions.[citation needed]
| Hyperlipo- proteinemia |
OMIM | Synonyms | Defect | Increased lipoprotein | Main symptoms | Treatment | Serum appearance | Estimated prevalence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I | a | 238600 | Buerger-Gruetz syndrome or familial hyperchylomicronemia | Decreased lipoprotein lipase (LPL) | Chylomicrons | Acute pancreatitis, lipemia retinalis, eruptive skin xanthomas, hepatosplenomegaly | Diet control | Creamy top layer | One in 1,000,000[14] |
| b | 207750 | Familial apoprotein CII deficiency | Altered ApoC2 | ||||||
| c | 118830 | LPL inhibitor in blood | |||||||
| Type II | a | 143890 | Familial hypercholesterolemia | LDL receptor deficiency | LDL | Xanthelasma, arcus senilis, tendon xanthomas | Bile acid sequestrants, statins, niacin | Clear | One in 500 for heterozygotes |
| b | 144250 | Familial combined hyperlipidemia | Decreased LDL receptor and increased ApoB | LDL and VLDL | Statins, niacin, fibrate | Turbid | One in 100 | ||
| Type III | 107741 | Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia | Defect in Apo E 2 synthesis | IDL | Tuberoeruptive xanthomas and palmar xanthomas | Fibrate, statins | Turbid | One in 10,000[15] | |
| Type IV | 144600 | Familial hypertriglyceridemia | Increased VLDL production and decreased elimination | VLDL | Can cause pancreatitis at high triglyceride levels | Fibrate, niacin, statins | Turbid | One in 100 | |
| Type V | 144650 | Increased VLDL production and decreased LPL | VLDL and chylomicrons | Niacin, fibrate | Creamy top layer and turbid bottom | ||||

Type I
[edit]Type I hyperlipoproteinemia exists in several forms:
- Lipoprotein lipase deficiency (type Ia), due to a deficiency of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) or altered apolipoprotein C2, resulting in elevated chylomicrons, the particles that transfer fatty acids from the digestive tract to the liver
- Familial apoprotein CII deficiency (type Ib),[17][18] a condition caused by a lack of lipoprotein lipase activator.[19]: 533
- Chylomicronemia due to circulating inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase (type Ic)[20]
Type I hyperlipoproteinemia usually presents in childhood with eruptive xanthomata and abdominal colic. Complications include retinal vein occlusion, acute pancreatitis, steatosis, and organomegaly, and lipemia retinalis.
Type II
[edit]Hyperlipoproteinemia type II is further classified into types IIa and IIb, depending mainly on whether elevation in the triglyceride level occurs in addition to LDL cholesterol.
Type IIa
[edit]This may be sporadic (due to dietary factors), polygenic, or truly familial as a result of a mutation either in the LDL receptor gene on chromosome 19 (0.2% of the population) or the ApoB gene (0.2%). The familial form is characterized by tendon xanthoma, xanthelasma, and premature cardiovascular disease. The incidence of this disease is about one in 500 for heterozygotes, and one in 1,000,000 for homozygotes.[21]
HLPIIa is a rare genetic disorder characterized by increased levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood due to the lack of uptake (no Apo B receptors) of LDL particles. This pathology, however, is the second-most common disorder of the various hyperlipoproteinemias, with individuals with a heterozygotic predisposition of one in every 500 and individuals with homozygotic predisposition of one in every million. These individuals may present with a unique set of physical characteristics such as xanthelasmas (yellow deposits of fat underneath the skin often presenting in the nasal portion of the eye), tendon and tuberous xanthomas, arcus juvenilis (the graying of the eye often characterized in older individuals), arterial bruits, claudication, and of course atherosclerosis. Laboratory findings for these individuals are significant for total serum cholesterol levels two to three times greater than normal, as well as increased LDL cholesterol, but their triglycerides and VLDL values fall in the normal ranges.[22]
To manage persons with HLPIIa, drastic measures may need to be taken, especially if their HDL cholesterol levels are less than 30 mg/dL and their LDL levels are greater than 160 mg/dL. A proper diet for these individuals requires a decrease in total fat to less than 30% of total calories with a ratio of monounsaturated:polyunsaturated:saturated fat of 1:1:1. Cholesterol should be reduced to less than 300 mg/day, thus the avoidance of animal products and to increase fiber intake to more than 20 g/day with 6g of soluble fiber/day.[23] Exercise should be promoted, as it can increase HDL. The overall prognosis for these individuals is in the worst-case scenario if uncontrolled and untreated individuals may die before the age of 20, but if one seeks a prudent diet with correct medical intervention, the individual may see an increased incidence of xanthomas with each decade, and Achilles tendinitis and accelerated atherosclerosis will occur.[24]
Type IIb
[edit]The high VLDL levels are due to overproduction of substrates, including triglycerides, acetyl-CoA, and an increase in B-100 synthesis. They may also be caused by the decreased clearance of LDL. Prevalence in the population is 10%.[25]
- Familial combined hyperlipoproteinemia (FCH)
- Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency (often called Cholesteryl ester storage disease)
- Secondary combined hyperlipoproteinemia (usually in the context of metabolic syndrome, for which it is a diagnostic criterion)
Type III
[edit]This form is due to high chylomicrons and IDL (intermediate density lipoprotein). Also known as broad beta disease or dysbetalipoproteinemia, the most common cause for this form is the presence of ApoE E2/E2 genotype. It is due to cholesterol-rich VLDL (β-VLDL). Its prevalence has been estimated to be approximately 1 in 10,000.[15]
It is associated with hypercholesterolemia (typically 8–12 mmol/L), hypertriglyceridemia (typically 5–20 mmol/L), a normal ApoB concentration, and two types of skin signs (palmar xanthomata or orange discoloration of skin creases, and tuberoeruptive xanthomata on the elbows and knees). It is characterized by the early onset of cardiovascular disease and peripheral vascular disease. Remnant hyperlipidemia occurs as a result of abnormal function of the ApoE receptor, which is normally required for clearance of chylomicron remnants and IDL from the circulation. The receptor defect causes levels of chylomicron remnants and IDL to be higher than normal in the blood stream. The receptor defect is an autosomal recessive mutation or polymorphism.[26]
Type IV
[edit]Familial hypertriglyceridemia is an autosomal dominant condition occurring in approximately 1% of the population.[27] This form is due to high triglyceride level. Other lipoprotein levels are typically within the normal reference range or slightly increased.[28] Treatment include diet control, fibrates and niacins. Although statins are typically the first line treatment for hyperlipidemias, fibrates are actually better at reducing elevated triglyceride levels and are considered first line.[29]
Type V
[edit]Hyperlipoproteinemia type V, also known as mixed hyperlipoproteinemia familial or mixed hyperlipidemia,[30] is very similar to type I, but with high VLDL in addition to chylomicrons.
It is also associated with glucose intolerance and hyperuricemia.[31]
In medicine, combined hyperlipidemia (or -aemia) (also known as "multiple-type hyperlipoproteinemia") is a commonly occurring form of hypercholesterolemia (elevated cholesterol levels) characterized by increased LDL and triglyceride concentrations, often accompanied by decreased HDL.[32] On lipoprotein electrophoresis (a test now rarely performed) it shows as a hyperlipoproteinemia type IIB. It is the most common inherited lipid disorder, occurring in about one in 200 persons. In fact, almost one in five individuals who develop coronary heart disease before the age of 60 has this disorder. The elevated triglyceride levels (>5 mmol/L) are generally due to an increase in very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), a class of lipoprotein prone to cause atherosclerosis.[33]
Both conditions are treated with fibrate drugs, which act on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), specifically PPARα, to decrease free fatty acid production. Statin drugs, especially the synthetic statins (atorvastatin and rosuvastatin) can decrease LDL levels by increasing hepatic reuptake of LDL due to increased LDL-receptor expression.
Unclassified familial forms
[edit]These unclassified forms are extremely rare:
Acquired (secondary)
[edit]Acquired hyperlipidemias (also called secondary dyslipoproteinemias) often mimic primary forms of hyperlipidemia and can have similar consequences.[9] They may result in increased risk of premature atherosclerosis or, when associated with marked hypertriglyceridemia, may lead to pancreatitis and other complications of the chylomicronemia syndrome.[9] The most common causes of acquired hyperlipidemia are:
- Diabetes mellitus[9]
- Use of drugs such as thiazide diuretics,[9] beta blockers,[9] and estrogens[9]
Other conditions leading to acquired hyperlipidemia include:
- Hypothyroidism[9]
- Kidney failure[9]
- Nephrotic syndrome[9]
- Alcohol consumption[9]
- Some rare endocrine disorders[9] and metabolic disorders[9]
Treatment of the underlying condition, when possible, or discontinuation of the offending drugs usually leads to an improvement in the hyperlipidemia.
Another acquired cause of hyperlipidemia, although not always included in this category, is postprandial hyperlipidemia, a normal increase following ingestion of food.[32][34]
Screening/Diagnosis
[edit]Adults 20 years and older should have the cholesterol checked every four to six years.[35] Serum level of Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL) cholesterol, High Density Lipoproteins (HDL) Cholesterol, and triglycerides are commonly tested in primary care setting using a lipid panel.[36] Quantitative levels of lipoproteins and triglycerides contribute toward cardiovascular disease risk stratification via models/calculators such as Framingham Risk Score, ACC/AHA Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Estimator, and/or Reynolds Risk Scores. These models/calculators may also take into account of family history (heart disease and/or high blood cholesterol), age, gender, Body-Mass-Index, medical history (diabetes, high cholesterol, heart disease), high sensitivity CRP levels, coronary artery calcium score, and ankle-brachial index.[37] The cardiovascular stratification further determines what medical intervention may be necessary to decrease the risk of future cardiovascular disease.[38]
Total cholesterol
[edit]The combined quantity of LDL and HDL. A total cholesterol of higher than 240 mg/dL is abnormal, but medical intervention is determined by the breakdown of LDL and HDL levels.[39]
LDL cholesterol
[edit]LDL, commonly known as "bad cholesterol", is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease.[40][41] LDL cholesterol transports cholesterol particles throughout the body, and can build up in the walls of the arteries, making them hard and narrow.[42] LDL cholesterol is produced naturally by the body, but eating a diet high in saturated fat, trans fats, and cholesterol can increase LDL levels.[43] Elevated LDL levels are associated with diabetes, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, and atherosclerosis. In a fasting lipid panel, a LDL greater than 160 mg/dL is abnormal.[37][39]
HDL cholesterol
[edit]HDL, also known as "good cholesterol", is associated with decreased risk of cardiovascular disease.[41] HDL cholesterol carries cholesterol from other parts of the body back to the liver and then removes the cholesterol from the body.[44] It can be affected by acquired or genetic factors, including tobacco use, obesity, inactivity, hypertriglyceridemia, diabetes, high carbohydrate diet, medication side effects (beta-blockers, androgenic steroids, corticosteroids, progestogens, thiazide diuretics, retinoic acid derivatives, oral estrogens, etc.) and genetic abnormalities (mutations ApoA-I, LCAT, ABC1).[37] Low level is defined as less than 40 mg/dL.[39][45]
Triglycerides
[edit]Triglyceride level is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease and/or metabolic syndrome.[37] Food intake prior to testing may cause elevated levels, up to 20%. Normal level is defined as less than 150 mg/dL.[46] Borderline high is defined as 150 to 199 mg/dL.[46] High level is between 200 and 499 mg/dL.[46] Greater than 500 mg/dL is defined as very high,[46] and is associated with pancreatitis and requires medical treatment.[47]
Screening age
[edit]Health organizations does not have a consensus on the age to begin screening for hyperlipidemia.[37] The CDC recommends cholesterol screenings once between ages 9 and 11, once again between 17 and 21, and every 4 to 6 years in adulthood.[48] Doctors may recommend more frequent screenings for people with a family history of early heart attacks, heart disease, or if a child has obesity or diabetes.[48] USPSTF recommends men older than 35 and women older than 45 to be screened.[49][50] NCE-ATP III recommends all adults older than 20 to be screened as it may lead potential lifestyle modification that can reduce risks of other diseases.[51] However, screening should be done for those with known CHD or risk-equivalent conditions (e.g. Acute Coronary Syndrome, history of heart attacks, Stable or Unstable angina, Transient ischemic attacks, Peripheral arterial disease of atherosclerotic origins, coronary or other arterial revascularization).[37]
Screening frequency
[edit]Adults 20 years and older should have the cholesterol checked every four to six years,[35] and most screening guidelines recommends testing every 5 years.[37] USPSTF recommends increased frequency for people with elevated risk of CHD, which may be determined using cardiovascular disease risk scores.[50]
Management
[edit]Management of hyperlipidemia includes maintenance of a normal body weight, increased physical activity, and decreased consumption of refined carbohydrates and simple sugars.[52] Prescription drugs may be used to treat some people having significant risk factors,[52] such as cardiovascular disease, LDL cholesterol greater than 190 mg/dL or diabetes. Common medication therapy is a statin.[52][53]
Lifestyle Modification
[edit]The first step in managing hyperlipidemia should be lifestyle modification, which, if not proven to be effective, can be used in conjunction with medical management. One diet that was specifically developed to help lower cholesterol levels is called the TLC diet (therapeutic lifestyle changes diet). This was created by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute in 1985 and combines physical activity, diet, and weight management to help lower cholesterol levels.[54]
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
[edit]Competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase, such as lovastatin, atorvastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin, and pitavastatin, inhibit the synthesis of mevalonate, a precursor molecule to cholesterol.[55] This medication class is especially effective at decreasing elevated LDL cholesterol.[55] Major side effects include elevated transaminases and myopathy.[55]
Fibric acid derivatives
[edit]Fibric acid derivatives, such as gemfibrozil and fenofibrate, function by increasing the lipolysis in adipose tissue via activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α.[55] They decrease VLDL – very low density lipoprotein – and LDL in some people.[55] Major side effects include rashes, GI upset, myopathy, or increased transaminases.[55] Fibrates may be prescribed in conjunction with statins to further reduce cholesterol if monotherapy is not successful; however, the combination of statins and fibrates may increase myopathy.[56]
Niacin
[edit]Niacin, or vitamin B3 has a mechanism of action that is poorly understood, however it has been shown to decrease LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and increase HDL cholesterol.[55] The most common side effect is flushing secondary to skin vasodilation.[55] This effect is mediated by prostaglandins and can be decreased by taking concurrent aspirin.[55]
Bile acid binding resins
[edit]Bile acid binding resins, such as colestipol, cholestyramine, and colesevelam, function by binding bile acids, increasing their excretion.[55] They are useful for decreasing LDL cholesterol.[55] The most common side effects include bloating and diarrhea.[55]
Sterol absorption inhibitors
[edit]Inhibitors of intestinal sterol absorption, such as ezetimibe, function by decreasing the absorption of cholesterol in the GI tract by targeting NPC1L1, a transport protein in the gastrointestinal wall.[55] This results in decreased LDL cholesterol.[55]
PCSK9 inhibitors
[edit]PCSK9 inhibitors are a newer drug class, approved by the FDA in 2015, which inhibit the liver-made enzyme (PCSK9), which typically breaks down LDL receptors.[57][58] LDL receptors function to remove cholesterol from the bloodstream. Thus, by inhibiting the enzyme (PCSK9) that breaks down LDL receptors, more LDL receptors are available to lower lipids in the bloodstream.[59] PCSK9 inhibitors are usually prescribed as adjunct therapy to first-line statins. Side effects can include flu-like symptoms and pain/swelling at the injection site.[60]
Prognosis
[edit]Relation to cardiovascular disease
[edit]Hyperlipidemia predisposes a person to atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of lipids, cholesterol, calcium, fibrous plaques within the walls of arteries.[61] This accumulation narrows the blood vessel and reduces blood flow and oxygen to muscles of the heart.[61][62] Over time fatty deposits can build up, hardening and narrowing the arteries until organs and tissues don't receive enough blood to properly function.[62] If arteries that supply the heart with blood are affected, a person might have angina (chest pain).[42] Complete blockage of the artery causes infarction of the myocardial cells, also known as heart attack.[63] Fatty buildup in the arteries can also lead to stroke, if a blood clot blocks blood flow to the brain.[42]
Prevention
[edit]Quitting smoking, lowering intake of saturated fat and alcohol, losing excess body weight, and eating a low-salt diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce blood cholesterol.[42][35][46]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Youngson RM (2005). "Hyperlipidaemia". Collins Dictionary of Medicine.
- ^ "Hyperlipidemia". The Free Dictionary. citing: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. Saunders. 2007. and The American Heritage Medical Dictionary. Houghton Mifflin Company. 2007. ISBN 978-0618824359.
- ^ a b "Hyperlipidemia | Society for Vascular Surgery". vascular.org. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ a b Hall JE (2016). Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology. Elsevier. ISBN 978-1455770052. OCLC 932195756.
- ^ Lilly L (2015). Pathophysiology of heart disease : a collaborative project of medical students and faculty. Wolters Kluwer. ISBN 978-1496308696. OCLC 1052840871.
- ^ a b https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21656-hyperlipidemia.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Xanthoma Information | Mount Sinai - New York". Mount Sinai Health System. Retrieved 2024-11-13.
- ^ CDC (2024-05-20). "Risk Factors for High Cholesterol". Cholesterol. Retrieved 2024-11-27.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Chait A, Brunzell JD (June 1990). "Acquired hyperlipidemia (secondary dyslipoproteinemias)". Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. 19 (2): 259–278. doi:10.1016/S0889-8529(18)30324-4. PMID 2192873.
- ^ Rozynkowa D, Paluszak J, Borowczyk T, Rakowski W (1967). "Idiopathic hyperlipidemia; search for a metabolic defect and its familial origin". Pol Med J. 6 (2): 429–35. PMID 6030652.
- ^ "MedlinePlus page for Lipoprotein #CITENNLM". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ Fredrickson DS, Lees RS (March 1965). "A system for phenotyping hyperlipoproteinemia". Circulation. 31 (3): 321–327. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.31.3.321. PMID 14262568.
- ^ Beaumont, JL; Carlson, LA; Cooper, GR; Fejfar, Z; Fredrickson, DS; Strasser, T (1970). "Classification of hyperlipidaemias and hyperlipoproteinaemias". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 43 (6): 891–915. PMC 2427808. PMID 4930042.
- ^ "Hyperlipoproteinemia, Type I". Centre for Arab Genomic Studies. 6 March 2007. Archived from the original on 27 March 2012.
About 1:1,000,000 people are affected with Hyperlipoproteinemia type I worldwide with a higher prevalence in some regions of Canada.
- ^ a b Fung M, Hill J, Cook D, Frohlich J (June 2011). "Case series of type III hyperlipoproteinemia in children". BMJ Case Reports. 2011: bcr0220113895. doi:10.1136/bcr.02.2011.3895. PMC 3116222. PMID 22691586.
- ^ "New Product Bulletin on Crestor® (rosuvastatin)". American Pharmacists Association. Archived from the original on 2011-09-27.
- ^ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): Apolipoprotein C-II Deficency - 207750
- ^ Yamamura T, Sudo H, Ishikawa K, Yamamoto A (September 1979). "Familial type I hyperlipoproteinemia caused by apolipoprotein C-II deficiency". Atherosclerosis. 34 (1): 53–65. doi:10.1016/0021-9150(79)90106-0. hdl:11094/32883. PMID 227429.
- ^ James WD, Berger TG, et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ^ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): Chylomicronemia, Familial, Due to Circulating Inhibitor of Lipoprotein Lipase - 118830
- ^ Cuchel, M.; Bruckert, E.; Ginsberg, H. N.; Raal, F. J.; Santos, R. D.; Hegele, R. A.; Kuivenhoven, J. A.; Nordestgaard, B. G.; Descamps, O. S.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Watts, G. F.; Averna, M.; Boileau, C.; Boren, J. (2014-08-02). "Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: new insights and guidance for clinicians to improve detection and clinical management. A position paper from the Consensus Panel on Familial Hypercholesterolaemia of the European Atherosclerosis Society". European Heart Journal. 35 (32): 2146–2157. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehu274. ISSN 0195-668X. PMC 4139706. PMID 25053660.
- ^ Burnett, John R.; Hooper, Amanda J.; Hegele, Robert A. (1993), Adam, Margaret P.; Feldman, Jerry; Mirzaa, Ghayda M.; Pagon, Roberta A. (eds.), "APOB-Related Familial Hypobetalipoproteinemia", GeneReviews®, Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle, PMID 33983694, retrieved 2024-11-14
- ^ Harada-Shiba, Mariko; Ohta, Takao; Ohtake, Akira; Ogura, Masatsune; Dobashi, Kazushige; Nohara, Atsushi; Yamashita, Shizuya; Yokote, Koutaro; Joint Working Group by Japan Pediatric Society and Japan Atherosclerosis Society for Making Guidance of Pediatric Familial Hypercholesterolemia (2018-06-01). "Guidance for Pediatric Familial Hypercholesterolemia 2017". Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis. 25 (6): 539–553. doi:10.5551/jat.CR002. ISSN 1880-3873. PMC 6005224. PMID 29415907.
- ^ "High cholesterol - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org. Retrieved 2024-11-14.
- ^ Feingold, Kenneth R. (2000), Feingold, Kenneth R.; Anawalt, Bradley; Blackman, Marc R.; Boyce, Alison (eds.), "Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins", Endotext, South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc., PMID 26247089, retrieved 2024-11-14
- ^ Melnik, Bodo (2020), Plewig, Gerd; French, Lars; Ruzicka, Thomas; Kaufmann, Roland (eds.), "Disorders of Lipid Metabolism", Braun-Falco´s Dermatology, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 1–18, doi:10.1007/978-3-662-58713-3_89-1, ISBN 978-3-662-58713-3, retrieved 2024-11-14
- ^ Boman H, Hazzard WR, AlbersJJ, et ah Frequency of monogenic forms of hyperlipidemia in a normal population. AmJ ttum Genet 27:19A,1975. [1]
- ^ Goyal, Amandeep; Cusick, Austin S.; Reilly, Elizabeth (2024), "Familial Hypertriglyceridemia", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 32310484, retrieved 2024-11-14
- ^ Oh, Robert C.; Trivette, Evan T.; Westerfield, Katie L. (2020-09-15). "Management of Hypertriglyceridemia: Common Questions and Answers". American Family Physician. 102 (6): 347–354. ISSN 1532-0650.
- ^ "Medical Definition Search For 'Type 5 Hyperlipidemia". medilexicon. Retrieved 1 November 2013.
- ^ "Hyperlipoproteinemia Type 5 - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2024-11-14.
- ^ a b "Hyperlipidemia". The Free Dictionary. Citing: Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary (3rd ed.). Elsevier. 2007.
- ^ Padda, Inderbir S.; Fabian, Daniel; Johal, Gurpreet S. (2024), "Familial Combined Hyperlipidemia", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 37276316, retrieved 2024-11-14
- ^ Ansar S, Koska J, Reaven PD (July 2011). "Postprandial hyperlipidemia, endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk: focus on incretins". Cardiovascular Diabetology. 10: 61. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-10-61. PMC 3184260. PMID 21736746.
- ^ a b c "What Your Cholesterol Levels Mean". www.goredforwomen.org. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ "Cholesterol testing and results: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ a b c d e f g Kopin L, Lowenstein C (December 2017). "Dyslipidemia". Annals of Internal Medicine. 167 (11): ITC81 – ITC96. doi:10.7326/AITC201712050. PMID 29204622.
- ^ US Preventive Services Task Force (2022-08-23). "Statin Use for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement". JAMA. 328 (8): 746–753. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.13044. ISSN 0098-7484. PMID 35997723.
- ^ a b c "ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference" (PDF). National Heart, Lungs, and Blood Institute. Retrieved November 7, 2019.
- ^ Pirahanchi Y, Huecker MR (2019), "Biochemistry, LDL Cholesterol", StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30137845, retrieved 2019-11-06
- ^ a b CDC (2017-10-31). "LDL and HDL Cholesterol: "Bad" and "Good" Cholesterol". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2019-11-07.
- ^ a b c d "High cholesterol – Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ "Cholesterol and Heart Disease". www.goredforwomen.org. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ "HDL: The "Good" Cholesterol". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ Information, National Center for Biotechnology (2017-09-07). High cholesterol: Overview. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG).
- ^ a b c d e "Can triglycerides affect my heart health?". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ Pejic RN, Lee DT (2006-05-01). "Hypertriglyceridemia". Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine. 19 (3): 310–316. doi:10.3122/jabfm.19.3.310. PMID 16672684.
- ^ a b CDC (2018-09-07). "Cholesterol Screenings". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Davidson KW, Epling JW, García FA, et al. (August 2016). "Screening for Lipid Disorders in Children and Adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement". JAMA. 316 (6): 625–633. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.9852. PMID 27532917.
- ^ a b "Final Update Summary: Lipid Disorders in Adults (Cholesterol, Dyslipidemia): Screening". US Preventive Services Task Force. Archived from the original on 2019-09-05. Retrieved 2019-11-07.
- ^ Grundy SM. "Then and Now: ATP III vs. IV". American College of Cardiology. Retrieved 2019-11-07.
- ^ a b c Michos ED, McEvoy JW, Blumenthal RS (October 2019). Jarcho JA (ed.). "Lipid Management for the Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease". The New England Journal of Medicine. 381 (16): 1557–1567. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1806939. PMID 31618541. S2CID 204756336.
- ^ Harrison TR (1951). "Principles of Internal Medicine". Southern Medical Journal. 44 (1): 79. doi:10.1097/00007611-195101000-00027. ISSN 0038-4348.
- ^ "Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes (TLC) To Lower Cholesterol | NHLBI, NIH". www.nhlbi.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-11-13.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Katzung BG (2017). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology; 14th Edition. McGraw-Hill Education / Medical. ISBN 978-1259641152. OCLC 1048625746.
- ^ Jacobson, Terry A.; Zimmerman, Franklin H. (January 2006). "Fibrates in combination with statins in the management of dyslipidemia". Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich, Conn.). 8 (1): 35–41, quiz 42–43. doi:10.1111/j.1524-6175.2005.05278.x. ISSN 1524-6175. PMC 8112375. PMID 16407687.
- ^ Hess, Paul L.; Kennedy, Kevin; Cowherd, Michael; Virani, Salim S.; Masoudi, Frederick A.; Navar, Ann Marie; Yeh, Robert W.; Ho, P. Michael; Maddox, Thomas M. (January 2018). "Implications of the FDA approval of PCSK9 inhibitors and FOURIER results for contemporary cardiovascular practice: An NCDR Research to Practice (R2P) project". American Heart Journal. 195: 151–152. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2017.09.004. ISSN 1097-6744. PMC 5961484. PMID 29224643.
- ^ MD, Alyson Kelley-Hedgepeth (2020-06-08). "Are statins enough? When to consider PCSK9 inhibitors". Harvard Health. Retrieved 2024-11-14.
- ^ Pokhrel, Binod; Pellegrini, Mark V.; Levine, Steven N. (2024), "PCSK9 Inhibitors", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 28846236, retrieved 2024-11-14
- ^ Gürgöze, Muhammed T.; Muller-Hansma, Annemarie H.G.; Schreuder, Michelle M.; Galema-Boers, Annette M.H.; Boersma, Eric; Roeters van Lennep, Jeanine E. (February 2019). "Adverse Events Associated With PCSK 9 Inhibitors: A Real-World Experience". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 105 (2): 496–504. doi:10.1002/cpt.1193. ISSN 0009-9236. PMC 6704355. PMID 30053327.
- ^ a b Linton MF, Yancey PG, Davies SS, Jerome WG, Linton EF, Song WL, Doran AC, Vickers KC (2000). Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G (eds.). "The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis". Endotext. MDText.com, Inc. PMID 26844337. Retrieved 2019-11-07.
- ^ a b "Arteriosclerosis / atherosclerosis – Symptoms and causes". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved 2020-04-30.
- ^ Bergheanu SC, Bodde MC, Jukema JW (April 2017). "Pathophysiology and treatment of atherosclerosis : Current view and future perspective on lipoprotein modification treatment". Netherlands Heart Journal. 25 (4): 231–242. doi:10.1007/s12471-017-0959-2. PMC 5355390. PMID 28194698.
