Astatine
| Astatine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈæstətiːn, -tɪn/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | unknown, probably metallic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mass number | [210] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Astatine in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 85 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 17 (halogens) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid (predicted) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 8.91–8.95 g/cm3 (estimated)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar volume | 23.6 cm3/mol (estimated)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | common: −1, +1 +3,[2] +5,[2] +7[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | from decay | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) (predicted)[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-68-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | from Ancient Greek ἄστατος (ástatos) 'unstable' | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Dale R. Corson, Kenneth Ross MacKenzie, Emilio Segrè (1940) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isotopes of astatine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Astatine is a chemical element; it has symbol At and atomic number 85. It is the rarest naturally occurring element in the Earth's crust, occurring only as the decay product of various heavier elements. All of astatine's isotopes are short-lived; the most stable is astatine-210, with a half-life of 8.1 hours. Consequently, a solid sample of the element has never been seen, because any macroscopic specimen would be immediately vaporized by the heat of its radioactivity.
The bulk properties of astatine are not known with certainty. Many of them have been estimated from its position on the periodic table as a heavier analog of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine, the four stable halogens. However, astatine also falls roughly along the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, and some metallic behavior has also been observed and predicted for it. Astatine is likely to have a dark or lustrous appearance and may be a semiconductor or possibly a metal. Chemically, several anionic species of astatine are known and most of its compounds resemble those of iodine, but it also sometimes displays metallic characteristics and shows some similarities to silver.
The first synthesis of astatine was in 1940 by Dale R. Corson, Kenneth Ross MacKenzie, and Emilio G. Segrè at the University of California, Berkeley. They named it from the Ancient Greek ἄστατος (astatos) 'unstable'. Four isotopes of astatine were subsequently found to be naturally occurring, although much less than one gram is present at any given time in the Earth's crust. Neither the most stable isotope, astatine-210, nor the medically useful astatine-211 occur naturally; they are usually produced by bombarding bismuth-209 with alpha particles.
Characteristics
[edit]Astatine is an extremely radioactive element; all its isotopes have half-lives of 8.1 hours or less, decaying into other astatine isotopes, bismuth, polonium, or radon. Most of its isotopes are very unstable, with half-lives of seconds or less. Of the first 101 elements in the periodic table, only francium is less stable, and all the astatine isotopes more stable than the longest-lived francium isotopes (205–211At) are in any case synthetic and do not occur in nature.[6]
The bulk properties of astatine are not known with any certainty.[7] Research is limited by its short half-life, which prevents the creation of weighable quantities.[8] A visible piece of astatine would immediately vaporize itself because of the heat generated by its intense radioactivity.[9] It remains to be seen if, with sufficient cooling, a macroscopic quantity of astatine could be deposited as a thin film.[4] Astatine is usually classified as either a nonmetal or a metalloid;[10][11] metal formation has also been predicted.[4][12]
Physical
[edit]Most of the physical properties of astatine have been estimated (by interpolation or extrapolation), using theoretically or empirically derived methods.[13] For example, halogens get darker with increasing atomic weight – fluorine is nearly colorless, chlorine is yellow-green, bromine is red-brown, and iodine is dark gray/violet. Astatine is sometimes described as probably being a black solid (assuming it follows this trend), or as having a metallic appearance (if it is a metalloid or a metal).[14][15][16]
Astatine sublimes less readily than iodine, having a lower vapor pressure.[8] Even so, half of a given quantity of astatine will vaporize in approximately an hour if put on a clean glass surface at room temperature.[a] The absorption spectrum of astatine in the middle ultraviolet region has lines at 224.401 and 216.225 nm, suggestive of 6p to 7s transitions.[18][19]
The structure of solid astatine is unknown.[20] As an analog of iodine it may have an orthorhombic crystalline structure composed of diatomic astatine molecules, and be a semiconductor (with a band gap of 0.7 eV).[21][22] Alternatively, if condensed astatine forms a metallic phase, as has been predicted, it may have a monatomic face-centered cubic structure; in this structure, it may well be a superconductor, like the similar high-pressure phase of iodine.[4] Metallic astatine is expected to have a density of 8.91–8.95 g/cm3.[1]
Evidence for (or against) the existence of diatomic astatine (At2) is sparse and inconclusive.[23][24][25][26][27] Some sources state that it does not exist, or at least has never been observed,[28][29] while other sources assert or imply its existence.[30][31][32] Despite this controversy, many properties of diatomic astatine have been predicted;[33] for example, its bond length would be 300±10 pm, dissociation energy <50 kJ/mol,[34] and heat of vaporization (∆Hvap) 54.39 kJ/mol.[35] Many values have been predicted for the melting and boiling points of astatine, but only for At2.[36]
Chemical
[edit]The chemistry of astatine is "clouded by the extremely low concentrations at which astatine experiments have been conducted, and the possibility of reactions with impurities, walls and filters, or radioactivity by-products, and other unwanted nano-scale interactions".[21] Many of its apparent chemical properties have been observed using tracer studies on extremely dilute astatine solutions,[32][37] typically less than 10−10 mol·L−1.[38] Some properties, such as anion formation, align with other halogens.[8] Astatine has some metallic characteristics as well, such as plating onto a cathode,[b] and coprecipitating with metal sulfides in hydrochloric acid.[40] It forms complexes with EDTA, a metal chelating agent,[41] and is capable of acting as a metal in antibody radiolabeling; in some respects, astatine in the +1 state is akin to silver in the same state. Most of the organic chemistry of astatine is, however, analogous to that of iodine.[42] It has been suggested that astatine can form a stable monatomic cation in aqueous solution.[40][43]
Astatine has an electronegativity of 2.2 on the revised Pauling scale – lower than that of iodine (2.66) and the same as hydrogen. In hydrogen astatide (HAt), the negative charge is predicted to be on the hydrogen atom, implying that this compound could be referred to as astatine hydride according to certain nomenclatures.[44][45][46][47] That would be consistent with the electronegativity of astatine on the Allred–Rochow scale (1.9) being less than that of hydrogen (2.2).[48][c] However, official IUPAC stoichiometric nomenclature is based on an idealized convention of determining the relative electronegativities of the elements by the mere virtue of their position within the periodic table. According to this convention, astatine is handled as though it is more electronegative than hydrogen, irrespective of its true electronegativity. The electron affinity of astatine, at 233 kJ mol−1, is 21% less than that of iodine.[50] In comparison, the value of Cl (349) is 6.4% higher than F (328); Br (325) is 6.9% less than Cl; and I (295) is 9.2% less than Br. The marked reduction for At was predicted as being due to spin–orbit interactions.[38] The first ionization energy of astatine is about 899 kJ mol−1, which continues the trend of decreasing first ionization energies down the halogen group (fluorine, 1681; chlorine, 1251; bromine, 1140; iodine, 1008).[3]
Compounds
[edit]Less reactive than iodine, astatine is the least reactive of the halogens;[51] the chemical properties of tennessine, the next-heavier group 17 element, have not yet been investigated, however.[52] Astatine compounds have been synthesized in nano-scale amounts and studied as intensively as possible before their radioactive disintegration. The reactions involved have been typically tested with dilute solutions of astatine mixed with larger amounts of iodine. Acting as a carrier, the iodine ensures there is sufficient material for laboratory techniques (such as filtration and precipitation) to work.[53][54][d] Like iodine, astatine has been shown to adopt odd-numbered oxidation states ranging from −1 to +7.[57]
Only a few compounds with metals have been reported, in the form of astatides of sodium,[9] palladium, silver, thallium, and lead.[58] Some characteristic properties of silver and sodium astatide, and the other hypothetical alkali and alkaline earth astatides, have been estimated by extrapolation from other metal halides.[59]

The formation of an astatine compound with hydrogen – usually referred to as hydrogen astatide – was noted by the pioneers of astatine chemistry.[60] As mentioned, there are grounds for instead referring to this compound as astatine hydride. It is easily oxidized; acidification by dilute nitric acid gives the At0 or At+ forms, and the subsequent addition of silver(I) may only partially, at best, precipitate astatine as silver(I) astatide (AgAt). Iodine, in contrast, is not oxidized, and precipitates readily as silver(I) iodide.[8][61]
Astatine is known to bind to boron,[62] carbon, and nitrogen.[63] Various boron cage compounds have been prepared with At–B bonds, these being more stable than At–C bonds.[64] Astatine can replace a hydrogen atom in benzene to form astatobenzene C6H5At; this may be oxidized to C6H5AtCl2 by chlorine. By treating this compound with an alkaline solution of hypochlorite, C6H5AtO2 can be produced.[65] The dipyridine-astatine(I) cation, [At(C5H5N)2]+, forms ionic compounds with perchlorate[63] (a non-coordinating anion[66]) and with nitrate, [At(C5H5N)2]NO3.[63] This cation exists as a coordination complex in which two dative covalent bonds separately link the astatine(I) centre with each of the pyridine rings via their nitrogen atoms.[63]
With oxygen, there is evidence of the species AtO− and AtO+ in aqueous solution, formed by the reaction of astatine with an oxidant such as elemental bromine or (in the last case) by sodium persulfate in a solution of perchloric acid.[8][67] The species previously thought to be AtO−2 has since been determined to be AtO(OH)−2, a hydrolysis product of AtO+ (another such hydrolysis product being AtOOH).[68] The well characterized AtO−3 anion can be obtained by, for example, the oxidation of astatine with potassium hypochlorite in a solution of potassium hydroxide.[65][69] Preparation of lanthanum triastatate La(AtO3)3, following the oxidation of astatine by a hot Na2S2O8 solution, has been reported.[70] Further oxidation of AtO−3, such as by xenon difluoride (in a hot alkaline solution) or periodate (in a neutral or alkaline solution), yields the perastatate ion AtO−4; this is only stable in neutral or alkaline solutions.[71] Astatine is also thought to be capable of forming cations in salts with oxyanions such as iodate or dichromate; this is based on the observation that, in acidic solutions, monovalent or intermediate positive states of astatine coprecipitate with the insoluble salts of metal cations such as silver(I) iodate or thallium(I) dichromate.[65][72]
Astatine may form bonds to the other chalcogens; these include S7At+ and At(CSN)−2 with sulfur, a coordination selenourea compound with selenium, and an astatine–tellurium colloid with tellurium.[73]
Astatine is known to react with its lighter homologs iodine, bromine, and chlorine in the vapor state; these reactions produce diatomic interhalogen compounds with formulas AtI, AtBr, and AtCl.[55] The first two compounds may also be produced in water – astatine reacts with iodine/iodide solution to form AtI, whereas AtBr requires (aside from astatine) an iodine/iodine monobromide/bromide solution. The excess of iodides or bromides may lead to AtBr−2 and AtI−2 ions,[55] or in a chloride solution, they may produce species like AtCl−2 or AtBrCl− via equilibrium reactions with the chlorides.[56] Oxidation of the element with dichromate (in nitric acid solution) showed that adding chloride turned the astatine into a molecule likely to be either AtCl or AtOCl. Similarly, AtOCl−2 or AtCl−2 may be produced.[55] The polyhalides PdAtI2, CsAtI2, TlAtI2,[74][75][76] and PbAtI[77] are known or presumed to have been precipitated. In a plasma ion source mass spectrometer, the ions [AtI]+, [AtBr]+, and [AtCl]+ have been formed by introducing lighter halogen vapors into a helium-filled cell containing astatine, supporting the existence of stable neutral molecules in the plasma ion state.[55] No astatine fluorides have been discovered yet. Their absence has been speculatively attributed to the extreme reactivity of such compounds, including the reaction of an initially formed fluoride with the walls of the glass container to form a non-volatile product.[e] Thus, although the synthesis of an astatine fluoride is thought to be possible, it may require a liquid halogen fluoride solvent, as has already been used for the characterization of radon fluoride.[55][71]
History
[edit]In 1869, when Dmitri Mendeleev published his periodic table, the space under iodine was empty; after Niels Bohr established the physical basis of the classification of chemical elements, it was suggested that the fifth halogen belonged there. Before its officially recognized discovery, it was called "eka-iodine" (from Sanskrit eka – "one") to imply it was one space under iodine (in the same manner as eka-silicon, eka-boron, and others).[81] Scientists tried to find it in nature; given its extreme rarity, these attempts resulted in several false discoveries.[82]
The first claimed discovery of eka-iodine was made by Fred Allison and his associates at the Alabama Polytechnic Institute (now Auburn University) in 1931. The discoverers named element 85 "alabamine", and assigned it the symbol Ab, designations that were used for a few years.[83][84][85] In 1934, H. G. MacPherson of University of California, Berkeley disproved Allison's method and the validity of his discovery.[86] There was another claim in 1937, by the chemist Rajendralal De. Working in Dacca in British India (now Dhaka in Bangladesh), he chose the name "dakin" for element 85, which he claimed to have isolated as the thorium series equivalent of radium F (polonium-210) in the radium series.[87] The properties he reported for dakin do not correspond to those of astatine,[87] and astatine's radioactivity would have prevented him from handling it in the quantities he claimed.[88] Moreover, astatine is not found in the thorium series, and the true identity of dakin is not known.[87]
In 1936, the team of Romanian physicist Horia Hulubei and French physicist Yvette Cauchois claimed to have discovered element 85 by observing its X-ray emission lines. In 1939, they published another paper which supported and extended previous data. In 1944, Hulubei published a summary of data he had obtained up to that time, claiming it was supported by the work of other researchers. He chose the name "dor", presumably from the Romanian for "longing" [for peace], as World War II had started five years earlier. As Hulubei was writing in French, a language which does not accommodate the "ine" suffix, dor would likely have been rendered in English as "dorine", had it been adopted. In 1947, Hulubei's claim was effectively rejected by the Austrian chemist Friedrich Paneth, who would later chair the IUPAC committee responsible for recognition of new elements. Even though Hulubei's samples did contain astatine-218, his means to detect it were too weak, by current standards, to enable correct identification; moreover, he could not perform chemical tests on the element.[88] He had also been involved in an earlier false claim as to the discovery of element 87 (francium) and this is thought to have caused other researchers to downplay his work.[89]

In 1940, the Swiss chemist Walter Minder announced the discovery of element 85 as the beta decay product of radium A (polonium-218), choosing the name "helvetium" (from Helvetia, the Latin name of Switzerland). Berta Karlik and Traude Bernert were unsuccessful in reproducing his experiments, and subsequently attributed Minder's results to contamination of his radon stream (radon-222 is the parent isotope of polonium-218).[90][f] In 1942, Minder, in collaboration with the English scientist Alice Leigh-Smith, announced the discovery of another isotope of element 85, presumed to be the product of thorium A (polonium-216) beta decay. They named this substance "anglo-helvetium",[91] but Karlik and Bernert were again unable to reproduce these results.[53]
Later in 1940, Dale R. Corson, Kenneth Ross MacKenzie, and Emilio Segrè isolated the element at the University of California, Berkeley. Instead of searching for the element in nature, the scientists created it by bombarding bismuth-209 with alpha particles in a cyclotron (particle accelerator) to produce, after emission of two neutrons, astatine-211.[92] The discoverers, however, did not immediately suggest a name for the element. The reason for this was that at the time, an element created synthetically in "invisible quantities" that had not yet been discovered in nature was not seen as a completely valid one; in addition, chemists were reluctant to recognize radioactive isotopes as legitimately as stable ones.[93] In 1943, astatine was found as a product of two naturally occurring decay chains by Berta Karlik and Traude Bernert, first in the so-called uranium series, and then in the actinium series.[94][95] (Since then, astatine was also found in a third decay chain, the neptunium series.[96]) Friedrich Paneth in 1946 called to finally recognize synthetic elements, quoting, among other reasons, recent confirmation of their natural occurrence, and proposed that the discoverers of the newly discovered unnamed elements name these elements. In early 1947, Nature published the discoverers' suggestions; a letter from Corson, MacKenzie, and Segrè suggested the name "astatine"[93] coming from the Ancient Greek αστατος (astatos) meaning 'unstable', because of its propensity for radioactive decay, with the ending "-ine", found in the names of the four previously discovered halogens. The name was also chosen to continue the tradition of the four stable halogens, where the name referred to a property of the element.[97]
Corson and his colleagues classified astatine as a metal on the basis of its analytical chemistry.[98] Subsequent investigators reported iodine-like,[99][100] cationic,[101][102] or amphoteric behavior.[103][53] In a 2003 retrospective, Corson wrote that "some of the properties [of astatine] are similar to iodine ... it also exhibits metallic properties, more like its metallic neighbors Po and Bi."[97]
Isotopes
[edit]| Mass number |
Half-life[6] | Probability of alpha decay[6] |
Alpha- decay half-life |
|---|---|---|---|
| 207 | 1.80 h | 8.6% | 20.9 h |
| 208 | 1.63 h | 0.55% | 12.3 d |
| 209 | 5.41 h | 4.1% | 5.5 d |
| 210 | 8.1 h | 0.175% | 193 d |
| 211 | 7.21 h | 41.8% | 17.2 h |
| 212 | 0.31 s | ≈100% | 0.31 s |
| 213 | 125 ns | 100% | 125 ns |
| 214 | 558 ns | 100% | 558 ns |
| 219 | 56 s | 97% | 58 s |
| 220 | 3.71 min | 8% | 46.4 min |
| 221 | 2.3 min | experimentally alpha-stable |
∞ |
There are 41 known isotopes of astatine, with mass numbers of 188 and 190–229.[104][105] Theoretical modeling suggests that about 37 more isotopes could exist.[104] No stable or long-lived astatine isotope has been observed, nor is one expected to exist.[106]
Astatine's alpha decay energies follow the same trend as for other heavy elements.[106] Lighter astatine isotopes have quite high energies of alpha decay, which become lower as the nuclei become heavier. Astatine-211 has a significantly higher energy than the previous isotope, because it has a nucleus with 126 neutrons, and 126 is a magic number corresponding to a filled neutron shell. Despite having a similar half-life to the previous isotope (8.1 hours for astatine-210 and 7.2 hours for astatine-211), the alpha decay probability is much higher for the latter: 41.81% against only 0.18%.[6][h] The two following isotopes release even more energy, with astatine-213 releasing the most energy. For this reason, it is the shortest-lived astatine isotope.[106] Even though heavier astatine isotopes release less energy, no long-lived astatine isotope exists, because of the increasing role of beta decay (electron emission).[106] This decay mode is especially important for astatine; as early as 1950 it was postulated that all isotopes of the element undergo beta decay,[107] though nuclear mass measurements indicate that 215At is in fact beta-stable, as it has the lowest mass of all isobars with A = 215.[6] Astatine-210 and most of the lighter isotopes exhibit beta plus decay (positron emission), astatine-217 and heavier isotopes except astatine-218 exhibit beta minus decay, while astatine-211 undergoes electron capture.[5]
The most stable isotope is astatine-210, which has a half-life of 8.1 hours. The primary decay mode is beta plus, to the relatively long-lived (in comparison to astatine isotopes) alpha emitter polonium-210. In total, only five isotopes have half-lives exceeding one hour (astatine-207 to -211). The least stable ground state isotope is astatine-213, with a half-life of 125 nanoseconds. It undergoes alpha decay to the extremely long-lived bismuth-209.[6]
Astatine has 24 known nuclear isomers, which are nuclei with one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) in an excited state. A nuclear isomer may also be called a "meta-state", meaning the system has more internal energy than the "ground state" (the state with the lowest possible internal energy), making the former likely to decay into the latter. There may be more than one isomer for each isotope. The most stable of these nuclear isomers is astatine-202m1,[i] which has a half-life of about 3 minutes, longer than those of all the ground states bar those of isotopes 203–211 and 220. The least stable is astatine-213m1; its half-life of 110 nanoseconds is shorter than 125 nanoseconds for astatine-213, the shortest-lived ground state.[5]
Natural occurrence
[edit]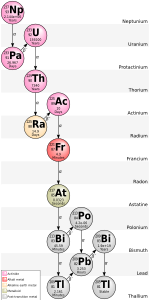
Astatine is the rarest naturally occurring element.[j] The total amount of astatine in the Earth's crust (quoted mass 2.36 × 1025 grams)[108] is estimated by some to be less than one gram at any given time.[8] Other sources estimate the amount of ephemeral astatine, present on earth at any given moment, to be up to one ounce[109] (about 28 grams).
Any astatine present at the formation of the Earth has long since disappeared; the four naturally occurring isotopes (astatine-215, -217, -218 and -219)[110] are instead continuously produced as a result of the decay of radioactive thorium and uranium ores, and trace quantities of neptunium-237. The landmass of North and South America combined, to a depth of 16 kilometers (10 miles), contains only about one trillion astatine-215 atoms at any given time (around 3.5 × 10−10 grams).[111] Astatine-217 is produced via the radioactive decay of neptunium-237. Primordial remnants of the latter isotope—due to its relatively short half-life of 2.14 million years—are no longer present on Earth. However, trace amounts occur naturally as a product of transmutation reactions in uranium ores.[112] Astatine-218 was the first astatine isotope discovered in nature.[113] Astatine-219, with a half-life of 56 seconds, is the longest lived of the naturally occurring isotopes.[6]
Isotopes of astatine are sometimes not listed as naturally occurring because of misconceptions[103] that there are no such isotopes,[114] or discrepancies in the literature. Astatine-216 has been counted as a naturally occurring isotope but reports of its observation[115] (which were described as doubtful) have not been confirmed.[116]
Synthesis
[edit]Formation
[edit]| Reaction[k] | Energy of alpha particle | |
|---|---|---|
| Threshold energy | Maximum production | |
| 209 83Bi + 4 2He → 211 85At + 2 1 0n |
20.7 MeV[117] | 30[118]–31 MeV[117] |
| 209 83Bi + 4 2He → 210 85At + 3 1 0n |
28.4[119]–28.6 MeV[117][120] | 37 MeV[117] |
| 209 83Bi + 4 2He → 209 85At + 4 1 0n |
35.9 MeV[120] | |

Astatine was first produced by bombarding bismuth-209 with energetic alpha particles, and this is still the major route used to create the relatively long-lived isotopes astatine-209 through astatine-211. Astatine is only produced in minuscule quantities, with modern techniques allowing production runs of up to 6.6 gigabecquerels[119] (about 86 nanograms or 2.47×1014 atoms). Synthesis of greater quantities of astatine using this method is constrained by the limited availability of suitable cyclotrons and the prospect of melting the target.[119][122][l] Solvent radiolysis due to the cumulative effect of astatine decay[124] is a related problem. With cryogenic technology, microgram quantities of astatine might be able to be generated via proton irradiation of thorium or uranium to yield radon-211, in turn decaying to astatine-211. Contamination with astatine-210 is expected to be a drawback of this method.[125]
The most important isotope is astatine-211, the only one in commercial use. To produce the bismuth target, the metal is sputtered onto a gold, copper, or aluminium surface at 50 to 100 milligrams per square centimeter. Bismuth oxide can be used instead; this is forcibly fused with a copper plate.[126] The target is kept under a chemically neutral nitrogen atmosphere,[127] and is cooled with water to prevent premature astatine vaporization.[126] In a particle accelerator, such as a cyclotron,[128] alpha particles are collided with the bismuth. Even though only one bismuth isotope is used (bismuth-209), the reaction may occur in three possible ways, producing astatine-209, astatine-210, or astatine-211. Although higher energies can produce more astatine-211, it will produce unwanted astatine-210 that decays to toxic polonium-210 as well. Instead, the maximum energy of the particle accelerator is set to be below or slightly above the threshold of astatine-210 production, in order to maximize the production of astatine-211 while keeping the amount of astatine-210 at an acceptable level.[119][118]
Separation methods
[edit]Since astatine is the main product of the synthesis, after its formation it must only be separated from the target and any significant contaminants. Several methods are available, "but they generally follow one of two approaches—dry distillation or [wet] acid treatment of the target followed by solvent extraction." The methods summarized below are modern adaptations of older procedures, as reviewed by Kugler and Keller.[129][m] Pre-1985 techniques more often addressed the elimination of co-produced toxic polonium; this requirement is now mitigated by capping the energy of the cyclotron irradiation beam.[119]
Dry
[edit]The astatine-containing cyclotron target is heated to a temperature of around 650 °C. The astatine volatilizes and is condensed in (typically) a cold trap. Higher temperatures of up to around 850 °C may increase the yield, at the risk of bismuth contamination from concurrent volatilization. Redistilling the condensate may be required to minimize the presence of bismuth[131] (as bismuth can interfere with astatine labeling reactions). The astatine is recovered from the trap using one or more low concentration solvents such as sodium hydroxide, methanol or chloroform. Astatine yields of up to around 80% may be achieved. Dry separation is the method most commonly used to produce a chemically useful form of astatine.[122][132]
Wet
[edit]The irradiated bismuth (or sometimes bismuth trioxide) target is first dissolved in, for example, concentrated nitric or perchloric acid. Following this first step, the acid can be distilled away to leave behind a white residue that contains both bismuth and the desired astatine product. This residue is then dissolved in a concentrated acid, such as hydrochloric acid. Astatine is extracted from this acid using an organic solvent such as dibutyl ether, diisopropyl ether (DIPE), or thiosemicarbazide. Using liquid-liquid extraction, the astatine product can be repeatedly washed with an acid, such as HCl, and extracted into the organic solvent layer. A separation yield of 93% using nitric acid has been reported, falling to 72% by the time purification procedures were completed (distillation of nitric acid, purging residual nitrogen oxides, and redissolving bismuth nitrate to enable liquid–liquid extraction).[133][134] Wet methods involve "multiple radioactivity handling steps" and have not been considered well suited for isolating larger quantities of astatine. However, wet extraction methods are being examined for use in production of larger quantities of astatine-211, as it is thought that wet extraction methods can provide more consistency.[134] They can enable the production of astatine in a specific oxidation state and may have greater applicability in experimental radiochemistry.[119]
Uses and precautions
[edit]| Agent | Applications |
|---|---|
| [211At]astatine-tellurium colloids | Compartmental tumors |
| 6-[211At]astato-2-methyl-1,4-naphtaquinol diphosphate | Adenocarcinomas |
| 211At-labeled methylene blue | Melanomas |
| Meta-[211At]astatobenzyl guanidine | Neuroendocrine tumors |
| 5-[211At]astato-2'-deoxyuridine | Various |
| 211At-labeled biotin conjugates | Various pretargeting |
| 211At-labeled octreotide | Somatostatin receptor |
| 211At-labeled monoclonal antibodies and fragments | Various |
| 211At-labeled bisphosphonates | Bone metastases |
Newly formed astatine-211 is the subject of ongoing research in nuclear medicine.[135] It must be used quickly as it decays with a half-life of 7.2 hours; this is long enough to permit multistep labeling strategies. Astatine-211 has potential for targeted alpha-particle therapy, since it decays either via emission of an alpha particle (to bismuth-207),[136] or via electron capture (to an extremely short-lived nuclide, polonium-211, which undergoes further alpha decay), very quickly reaching its stable granddaughter lead-207. Polonium X-rays emitted as a result of the electron capture branch, in the range of 77–92 keV, enable the tracking of astatine in animals and patients.[135] Although astatine-210 has a slightly longer half-life, it is wholly unsuitable because it usually undergoes beta plus decay to the extremely toxic polonium-210.[137]
The principal medicinal difference between astatine-211 and iodine-131 (a radioactive iodine isotope also used in medicine) is that iodine-131 emits high-energy beta particles, and astatine does not. Beta particles have much greater penetrating power through tissues than do the much heavier alpha particles. An average alpha particle released by astatine-211 can travel up to 70 μm through surrounding tissues; an average-energy beta particle emitted by iodine-131 can travel nearly 30 times as far, to about 2 mm.[126] The short half-life and limited penetrating power of alpha radiation through tissues offers advantages in situations where the "tumor burden is low and/or malignant cell populations are located in close proximity to essential normal tissues."[119] Significant morbidity in cell culture models of human cancers has been achieved with from one to ten astatine-211 atoms bound per cell.[138]
Astatine ... [is] miserable to make and hell to work with.[139]
Several obstacles have been encountered in the development of astatine-based radiopharmaceuticals for cancer treatment. World War II delayed research for close to a decade. Results of early experiments indicated that a cancer-selective carrier would need to be developed and it was not until the 1970s that monoclonal antibodies became available for this purpose. Unlike iodine, astatine shows a tendency to dehalogenate from molecular carriers such as these, particularly at sp3 carbon sites[n] (less so from sp2 sites). Given the toxicity of astatine accumulated and retained in the body, this emphasized the need to ensure it remained attached to its host molecule. While astatine carriers that are slowly metabolized can be assessed for their efficacy, more rapidly metabolized carriers remain a significant obstacle to the evaluation of astatine in nuclear medicine. Mitigating the effects of astatine-induced radiolysis of labeling chemistry and carrier molecules is another area requiring further development. A practical application for astatine as a cancer treatment would potentially be suitable for a "staggering" number of patients; production of astatine in the quantities that would be required remains an issue.[125][140][o]
Animal studies show that astatine, similarly to iodine—although to a lesser extent, perhaps because of its slightly more metallic nature[109]—is preferentially (and dangerously) concentrated in the thyroid gland. Unlike iodine, astatine also shows a tendency to be taken up by the lungs and spleen, possibly because of in-body oxidation of At– to At+.[42] If administered in the form of a radiocolloid it tends to concentrate in the liver. Experiments in rats and monkeys suggest that astatine-211 causes much greater damage to the thyroid gland than does iodine-131, with repetitive injection of the nuclide resulting in necrosis and cell dysplasia within the gland.[141] Early research suggested that injection of astatine into female rodents caused morphological changes in breast tissue;[142] this conclusion remained controversial for many years. General agreement was later reached that this was likely caused by the effect of breast tissue irradiation combined with hormonal changes due to irradiation of the ovaries.[139] Trace amounts of astatine can be handled safely in fume hoods if they are well-aerated; biological uptake of the element must be avoided.[29]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ This half-vaporization period grows to 16 hours if it is instead put on a gold or platinum surface; this may be caused by poorly understood interactions between astatine and these noble metals.[17]
- ^ It is also possible that this is sorption on a cathode.[39]
- ^ The algorithm used to generate the Allred-Rochow scale fails in the case of hydrogen, providing a value that is close to that of oxygen (3.5). Hydrogen is instead assigned a value of 2.2. Despite this shortcoming, the Allred-Rochow scale has achieved a relatively high degree of acceptance.[49]
- ^ Iodine can act as a carrier despite it reacting with astatine in water because these reactions require iodide (I−), not (only) I2.[55][56]
- ^ An initial attempt to fluoridate astatine using chlorine trifluoride resulted in formation of a product which became stuck to the glass. Chlorine monofluoride, chlorine, and tetrafluorosilane were formed. The authors called the effect "puzzling", admitting they had expected formation of a volatile fluoride.[78] Ten years later, the compound was predicted to be non-volatile, out of line with the lighter halogens but similar to radon fluoride;[79] by this time, the latter had been shown to be ionic.[80]
- ^ In other words, some other substance was undergoing beta decay (to a different end element), not polonium-218.
- ^ In the table, "alpha decay half-life" refers to the half-life if decay modes other than alpha are omitted.
- ^ This means that, if decay modes other than alpha are omitted, then astatine-210 has an alpha decay half-life of 4,628.6 hours (128.9 days) and astatine-211 has one of only 17.2 hours (0.7 days). Therefore, astatine-211 is very much less stable toward alpha decay than astatine-210.
- ^ "m1" means that this state of the isotope is the next possible one above – with an energy greater than – the ground state. "m2" and similar designations refer to further higher energy states. The number may be dropped if there is only one well-established meta state, such as astatine-216m. Other designation techniques are sometimes used.
- ^ Emsley[9] states that this title has been lost to berkelium, "a few atoms of which can be produced in very-highly concentrated uranium-bearing deposits"; however, his assertion is not corroborated by any primary source.
- ^ A nuclide is commonly denoted by a symbol of the chemical element this nuclide belongs to, preceded by a non-spaced superscript mass number and a subscript atomic number of the nuclide located directly under the mass number. (Neutrons may be considered as nuclei with the atomic mass of 1 and the atomic charge of 0, with the symbol being n.) With the atomic number omitted, it is also sometimes used as a designation of an isotope of an element in isotope-related chemistry.
- ^ See however Nagatsu et al.[123] who encapsulate the bismuth target in a thin aluminium foil and place it in a niobium holder capable of holding molten bismuth.
- ^ See also Lavrukhina and Pozdnyakov.[130]
- ^ In other words, where carbon's one s atomic orbital and three p orbitals hybridize to give four new orbitals shaped as intermediates between the original s and p orbitals.
- ^ "Unfortunately, the conundrum confronting the ... field is that commercial supply of 211At awaits the demonstration of clinical efficacy; however, the demonstration of clinical efficacy requires a reliable supply of 211At."[119]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Arblaster, JW, ed. (2018). Selected Values of the Crystallographic Properties of Elements. Materials Park, Ohio: ASM International. p. 604. ISBN 978-1-62708-154-2.
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b Rothe, S.; Andreyev, A. N.; Antalic, S.; Borschevsky, A.; Capponi, L.; Cocolios, T. E.; De Witte, H.; Eliav, E.; et al. (2013). "Measurement of the First Ionization Potential of Astatine by Laser Ionization Spectroscopy". Nature Communications. 4: 1–6. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4E1835R. doi:10.1038/ncomms2819. PMC 3674244. PMID 23673620.
- ^ a b c d Hermann, A.; Hoffmann, R.; Ashcroft, N. W. (2013). "Condensed Astatine: Monatomic and Metallic". Physical Review Letters. 111 (11): 116404-1 – 116404-5. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.111k6404H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.116404. PMID 24074111.
- ^ a b c Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ a b c d e f g Audi, Georges; Bersillon, Olivier; Blachot, Jean; Wapstra, Aaldert Hendrik (2003). "The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties". Nuclear Physics A. 729: 3–128. Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729....3A. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 2002, p. 795.
- ^ a b c d e f Wiberg, N., ed. (2001). Holleman-Wiberg: Inorganic Chemistry. Translation of 101st German edition by M. Eagleson and W. D. Brewer, English language editor B. J. Aylett. Academic Press. p. 423. ISBN 978-0-12-352651-9.
- ^ a b c Emsley, J. (2011). Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements (New ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 57–58. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- ^ Kotz, J. C.; Treichel, P. M.; Townsend, J. (2011). Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity (8th ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-8400-4828-8.
- ^ Jahn, T. P. (2010). MIPS and Their Role in the Exchange of Metalloids. Vol. 679. Springer. p. 41. ISBN 978-1-4419-6314-7.
- ^ Siekierski, S.; Burgess, J. (2002). Concise Chemistry of the Elements. Horwood. pp. 65, 122. ISBN 978-1-898563-71-6.
- ^ Maddock, A. G. (1956). "Astatine". Supplement to Mellor's Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry, Supplement II, Part 1, (F, Cl, Br, I, At). Longmans, Green & Co. (Ltd.). pp. 1064–1079.
- ^ Garrett, A. B.; Richardson, J. B.; Kiefer, A. S. (1961). Chemistry: A First Course in Modern Chemistry. Ginn. p. 313.
- ^ Seaborg, G. T. (2015). "Transuranium element". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 24 February 2015.
- ^ Oon, H. L. (2007). Chemistry Expression: An Inquiry Approach. John Wiley and Sons. p. 300. ISBN 978-981-271-162-5.
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 251.
- ^ McLaughlin, R. (1964). "Absorption Spectrum of Astatine". Journal of the Optical Society of America. 54 (8): 965–967. Bibcode:1964JOSA...54..965M. doi:10.1364/JOSA.54.000965.
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 235.
- ^ Donohue, J. (1982). The Structures of the Elements. Robert E. Krieger. p. 400. ISBN 978-0-89874-230-5.
- ^ a b Vernon, R. (2013). "Which Elements are Metalloids?". Journal of Chemical Education. 90 (12): 1703–1707 (1704). Bibcode:2013JChEd..90.1703V. doi:10.1021/ed3008457.
- ^ Batsanov, S. S. (1972). "Quantitative characteristics of bond metallicity in crystals". Journal of Structural Chemistry. 12 (5): 809–813. Bibcode:1972JStCh..12..809B. doi:10.1007/BF00743349. ISSN 0022-4766. S2CID 96816296.
- ^ Merinis, J.; Legoux, G.; Bouissières, G. (1972). "Etude de la formation en phase gazeuse de composés interhalogénés d'astate par thermochromatographie" [Study of the gas-phase formation of interhalogen compounds of astatine by thermochromatography]. Radiochemical and Radioanalytical Letters (in French). 11 (1): 59–64.
- ^ Takahashi, N.; Otozai, K. (1986). "The Mechanism of the Reaction of Elementary Astatine with Organic Solvents". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 103 (1): 1–9. Bibcode:1986JRNC..103....1T. doi:10.1007/BF02165358. S2CID 93572282.
- ^ Takahashi, N.; Yano, D.; Baba, H. (1992). "Chemical Behavior of Astatine Molecules". Proceedings of the International Conference on Evolution in Beam Applications, Takasaki, Japan, 5–8 November 1991. pp. 536–539.
- ^ Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, p. 21.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 110, 116, 210–211, 224.
- ^ Meyers, R. A. (2001). "Halogen Chemistry". Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (3rd ed.). Academic Press. pp. 197–222 (202). ISBN 978-0-12-227410-7.
- ^ a b Keller, C.; Wolf, W.; Shani, J. (2011). "Radionuclides, 2. Radioactive Elements and Artificial Radionuclides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Vol. 31. pp. 89–117 (96). doi:10.1002/14356007.o22_o15. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- ^ Otozai, K.; Takahashi, N. (1982). "Estimation Chemical Form Boiling Point Elementary Astatine by Radio Gas Chromatography". Radiochimica Acta. 31 (3–4): 201–203. doi:10.1524/ract.1982.31.34.201. S2CID 100363889.
- ^ Zumdahl, S. S.; Zumdahl, S. A. (2008). Chemistry (8th ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 56. ISBN 978-0-547-12532-9.
- ^ a b Housecroft, C. E.; Sharpe, A. G. (2008). Inorganic chemistry (3rd ed.). Pearson Education. p. 533. ISBN 978-0-13-175553-6.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 116.
- ^ Burgers, Peter C.; Zeneyedpour, Lona; Luider, Theo M.; Holmes, John L. (2024). "Estimation of thermodynamic and physicochemical properties of the alkali astatides: On the bond strength of molecular astatine (At2) and the hydration enthalpy of astatide (At−)". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 59 (4): e5010. doi:10.1002/jms.5010. ISSN 1076-5174. PMID 38488842.
- ^ Glushko, V. P.; Medvedev, V. A.; Bergma, G. A. (1966). Termicheskie Konstanty Veshchestv (in Russian). Vol. 1. Nakua. p. 65.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 116–117.
- ^ Smith, A.; Ehret, W. F. (1960). College chemistry. Appleton-Century-Crofts. p. 457.
- ^ a b Champion, J.; Seydou, M.; Sabatié-Gogova, A.; Renault, E.; Montavon, G.; Galland, N. (2011). "Assessment of an Effective Quasirelativistic Methodology Designed to Study Astatine Chemistry in Aqueous Solution". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 13 (33): 14984–14992 (14984). Bibcode:2011PCCP...1314984C. doi:10.1039/C1CP20512A. PMID 21769335.
- ^ Milanov, M.; Doberenz, V.; Khalkin, V. A.; Marinov, A. (1984). "Chemical Properties of Positive Singly Charged Astatine Ion in Aqueous Solution". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 83 (2): 291–299. Bibcode:1984JRNC...83..291M. doi:10.1007/BF02037143. S2CID 97361684.
- ^ a b Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 234.
- ^ Milesz, S.; Jovchev, M.; Schumann, D.; Khalkin, V. A. (1988). "The EDTA Complexes of Astatine". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 127 (3): 193–198. Bibcode:1988JRNC..127..193M. doi:10.1007/BF02164864. S2CID 93032218.
- ^ a b Guérard, F.; Gestin, J.-F.; Brechbiel, M. W. (2013). "Production of [211At]-Astatinated Radiopharmaceuticals and Applications in Targeted α-Particle Therapy". Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals. 28 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1089/cbr.2012.1292. PMC 3545490. PMID 23075373.
- ^ Champion, J.; Alliot, C.; Renault, E.; Mokili, B. M.; Chérel, M.; Galland, N.; Montavon, G. (2010). "Astatine Standard Redox Potentials and Speciation in Acidic Medium". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 114 (1): 576–582 (581). Bibcode:2010JPCA..114..576C. doi:10.1021/jp9077008. PMID 20014840. S2CID 15738065.
- ^ Dolg, M.; Kuchle, W.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H.; Schwerdtfeger, P. (1991). "Ab Initio Pseudopotentials for Hg to Rn: II. Molecular Calculations on the Hydrides of Hg to At and the Fluorides of Rn". Molecular Physics. 74 (6): 1265–1285 (1265, 1270, 1282). Bibcode:1991MolPh..74.1265D. doi:10.1080/00268979100102951.
- ^ Saue, T.; Faegri, K.; Gropen, O. (1996). "Relativistic Effects on the Bonding of Heavy and Superheavy Hydrogen Halides". Chemical Physics Letters. 263 (3–4): 360–366 (361–362). Bibcode:1996CPL...263..360S. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(96)01250-X.
- ^ Barysz, M. (2010). Relativistic Methods for Chemists. Springer. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-4020-9974-8.
- ^ Thayer, J. S. (2005). "Relativistic Effects and the Chemistry of the Heaviest Main-group elements". Journal of Chemical Education. 82 (11): 1721–1727 (1725). Bibcode:2005JChEd..82.1721T. doi:10.1021/ed082p1721.
- ^ Wulfsberg, G. (2000). Inorganic Chemistry. University Science Books. p. 37. ISBN 978-1-891389-01-6.
- ^ Smith, D. W. (1990). Inorganic Substances: A Prelude to the Study of Descriptive Inorganic Chemistry. Cambridge University Press. p. 135. ISBN 978-0-521-33738-0.
- ^ Leimbach, D.; Sundberg, J.; Yangyang, G.; et al. (February 2020). "The electron affinity of astatine". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 3824. arXiv:2002.11418. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.3824L. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17599-2. PMC 7393155. PMID 32733029.
- ^ Anders, E. (1959). "Technetium and astatine chemistry". Annual Review of Nuclear Science. 9: 203–220. Bibcode:1959ARNPS...9..203A. doi:10.1146/annurev.ns.09.120159.001223. (subscription required)
- ^ "Superheavy Element 117 Confirmed – On the Way to the "Island of Stability"". GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research. Archived from the original on 3 August 2018. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ a b c Nefedov, V. D.; Norseev, Yu. V.; Toropova, M. A.; Khalkin, Vladimir A. (1968). "Astatine". Russian Chemical Reviews. 37 (2): 87–98. Bibcode:1968RuCRv..37...87N. doi:10.1070/RC1968v037n02ABEH001603. S2CID 250775410. (subscription required)
- ^ Aten, A. H. W. Jr.; Doorgeest, T.; Hollstein, U.; Moeken, H. P. (1952). "Section 5: Radiochemical Methods. Analytical Chemistry of Astatine". Analyst. 77 (920): 774–777. Bibcode:1952Ana....77..774A. doi:10.1039/AN9527700774. (subscription required)
- ^ a b c d e f Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, p. 31.
- ^ a b Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, p. 38.
- ^ Chatterjee, Sayandev; Czerwinski, Kenneth R.; Fitzgerald, Hilary A.; Lakes, Andrew L.; Liao, Zuolei; Ludwig, Russell C.; McBride, Katie M.; Vlasenko, Vladislav P. (2020). "Novel Platforms for Drug Delivery Applications". Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials. Woodhead Publishing. Subchapter 16.4.2: Redox behavior. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-91376-8.00012-4.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 213–214.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 214–218.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 211.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 109–110, 129, 213.
- ^ Davidson, M. (2000). Contemporary boron chemistry. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-85404-835-9.
- ^ a b c d Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, p. 276.
- ^ Elgqvist, J.; Hultborn, R.; Lindegren, S.; Palm, S. (2011). "Ovarian cancer: background and clinical perspectives". In Speer, S. (ed.). Targeted Radionuclide Therapy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 380–396 (383). ISBN 978-0-7817-9693-4.
- ^ a b c Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, pp. 190–191.
- ^ Brookhart, M.; Grant, B.; Volpe, A. F. (1992). "[(3,5-(CF3)2C6H3)4B]-[H(OEt2)2]+: a convenient reagent for generation and stabilization of cationic, highly electrophilic organometallic complexes". Organometallics. 11 (11): 3920–3922. doi:10.1021/om00059a071.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 111.
- ^ Sergentu, Dumitru-Claudiu; Teze, David; Sabatié-Gogova, Andréa; Alliot, Cyrille; Guo, Ning; Bassel, Fadel; Da Silva, Isidro; Deniaud, David; Maurice, Rémi; Champion, Julie; Galland, Nicolas; Montavon, Gilles (2016). "Advances on the Determination of the Astatine Pourbaix Diagram: Predomination of AtO(OH)2− over At− in Basic Conditions". Chem. Eur. J. 22 (9): 2964–71. doi:10.1002/chem.201504403. PMID 26773333.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 222.
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 238.
- ^ a b Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 112, 192–193.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 219.
- ^ Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, pp. 192–193.
- ^ Zuckerman & Hagen 1990, p. 212.
- ^ Brinkman, G. A.; Aten, H. W. (1963). "Decomposition of Caesium Diiodo Astatate (I), (CsAtI2)". Radiochimica Acta. 2 (1): 48. doi:10.1524/ract.1963.2.1.48. S2CID 99398848.
- ^ Zuckerman & Hagen 1990, p. 60.
- ^ Zuckerman & Hagen 1989, p. 426.
- ^ Appelman, E. H.; Sloth, E. N.; Studier, M. H. (1966). "Observation of Astatine Compounds by Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry". Inorganic Chemistry. 5 (5): 766–769. doi:10.1021/ic50039a016.
- ^ Pitzer, K. S. (1975). "Fluorides of Radon and Element 118". Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications. 5 (18): 760b–761. doi:10.1039/C3975000760B.
- ^ Bartlett, N.; Sladky, F. O. (1973). "The Chemistry of Krypton, Xenon and Radon". In Bailar, J. C.; Emeléus, H. J.; Nyholm, R.; et al. (eds.). Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 1. Pergamon. pp. 213–330. ISBN 978-0-08-017275-0.
- ^ Ball, P. (2002). The Ingredients: A Guided Tour of the Elements. Oxford University Press. pp. 100–102. ISBN 978-0-19-284100-1.
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, pp. 227–228.
- ^ Allison, F.; Murphy, E. J.; Bishop, E. R.; Sommer, A. L. (1931). "Evidence of the Detection of Element 85 in Certain Substances". Physical Review. 37 (9): 1178–1180. Bibcode:1931PhRv...37.1178A. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.37.1178. (subscription required)
- ^ "Alabamine & Virginium". Time. 15 February 1932. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007.
- ^ Trimble, R. F. (1975). "What Happened to Alabamine, Virginium, and Illinium?". Journal of Chemical Education. 52 (9): 585. Bibcode:1975JChEd..52..585T. doi:10.1021/ed052p585. (subscription required)
- ^ MacPherson, H. G. (1934). "An Investigation of the Magneto-optic Method of Chemical Analysis". Physical Review. 47 (4): 310–315. Bibcode:1935PhRv...47..310M. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.47.310.
- ^ a b c Mellor, J. W. (1965). A Comprehensive Treatise on Inorganic and Theoretical Chemistry. Longmans, Green. p. 1066. OCLC 13842122.
- ^ a b Burdette, S. C.; Thornton, B. F. (2010). "Finding Eka-Iodine: Discovery Priority in Modern Times" (PDF). Bulletin for the History of Chemistry. 35: 86–96. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ Scerri, E. (2013). A Tale of 7 Elements (Google Play ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 188–190, 206. ISBN 978-0-19-539131-2.
- ^ Karlik, B.; Bernert, T. (1942). "Über Eine Vermutete β-Strahlung des Radium A und die Natürliche Existenz des Elementes 85" [About a Suspected β-radiation of Radium A, and the Natural Existence of the Element 85]. Naturwissenschaften (in German). 30 (44–45): 685–686. Bibcode:1942NW.....30..685K. doi:10.1007/BF01487965. S2CID 6667655. (subscription required)
- ^ Leigh-Smith, A.; Minder, W. (1942). "Experimental Evidence of the Existence of Element 85 in the Thorium Family". Nature. 150 (3817): 767–768. Bibcode:1942Natur.150..767L. doi:10.1038/150767a0. S2CID 4121704. (subscription required)
- ^ Corson, MacKenzie & Segrè 1940.
- ^ a b Davis, Helen Miles (1959). The Chemical Elements (PDF) (2nd ed.). Science Service, Ballantine Books. p. 29. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 August 2017. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
- ^ Karlik, B.; Bernert, T. (1943). "Eine Neue Natürliche α-Strahlung" [A New Natural α-radiation]. Naturwissenschaften (in German). 31 (25–26): 298–299. Bibcode:1943NW.....31..298K. doi:10.1007/BF01475613. S2CID 38193384. (subscription required)
- ^ Karlik, B.; Bernert, T. (1943). "Das Element 85 in den Natürlichen Zerfallsreihen" [The Element 85 in the Natural Decay Chains]. Zeitschrift für Physik (in German). 123 (1–2): 51–72. Bibcode:1944ZPhy..123...51K. doi:10.1007/BF01375144. S2CID 123906708. (subscription required)
- ^ Lederer, C. M.; Hollander, J. M.; Perlman, I. (1967). Table of Isotopes (6th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 1–657.
- ^ a b Corson, D. R. (2003). "Astatine". Chemical & Engineering News. 81 (36): 158. doi:10.1021/cen-v081n036.p158.
- ^ Corson, MacKenzie & Segrè 1940, pp. 672, 677.
- ^ Hamilton, J. G.; Soley, M. H. (1940). "A Comparison of the Metabolism of Iodine and of Element 85 (Eka-Iodine)". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 26 (8): 483–489. Bibcode:1940PNAS...26..483H. doi:10.1073/pnas.26.8.483. PMC 1078214. PMID 16588388.
- ^ Neumann, H. M. (1957). "Solvent Distribution Studies of the Chemistry of Astatine". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 4 (5–6): 349–353. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(57)80018-9.
- ^ Johnson, G. L.; Leininger, R. F.; Segrè, E. (1949). "Chemical Properties of Astatine. I". Journal of Chemical Physics. 17 (1): 1–10. Bibcode:1949JChPh..17....1J. doi:10.1063/1.1747034. hdl:2027/mdp.39015086446914. S2CID 95324453.
- ^ Dreyer, I.; Dreyer, R.; Chalkin, V. A. (1979). "Cations of Astatine in Aqueous Solutions; Production and some Characteristics". Radiochemical and Radioanalytical Letters (in German). 36 (6): 389–398.
- ^ a b Aten, A. H. W. Jr. (1964). The Chemistry of Astatine. Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry. Vol. 6. pp. 207–223. doi:10.1016/S0065-2792(08)60227-7. ISBN 978-0-12-023606-0.
- ^ a b Fry, C.; Thoennessen, M. (2013). "Discovery of the astatine, radon, francium, and radium isotopes". Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables. 09 (5): 497–519. arXiv:1205.5841. Bibcode:2013ADNDT..99..497F. doi:10.1016/j.adt.2012.05.003. S2CID 12590893.
- ^ Kokkonen, Henna. "Decay properties of the new isotopes 188At and 190At" (PDF). University of Jyväskylä. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ a b c d Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 229.
- ^ Rankama, K. (1956). Isotope Geology (2nd ed.). Pergamon Press. p. 403. ISBN 978-0-470-70800-2.
- ^ Lide, D. R., ed. (2004). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (85th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 14–10. ISBN 978-0-8493-0485-9.
- ^ a b Stwertka, Albert. A Guide to the Elements, Oxford University Press, 1996, p. 193. ISBN 0-19-508083-1
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 228–229.
- ^ Asimov, I. (1957). Only a Trillion. Abelard-Schuman. p. 24.
- ^ Kolthoff, I. M.; Elving, P. J., eds. (1964). Treatise on Analytical Chemistry. Part II: Analytical Chemistry of the Elements. Vol. 4. New York: Interscience Encyclopedia. p. 487.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 4.
- ^ Maiti, M.; Lahiri, S. (2011). "Production cross section of At radionuclides from 7Li+natPb and 9Be+natTl reactions". Physical Review C. 84 (6): 07601–07604 (07601). arXiv:1109.6413. Bibcode:2011PhRvC..84f7601M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.84.067601. S2CID 115321713.
- ^ Greenwood & Earnshaw 2002, p. 796.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 5.
- ^ a b c d Hermanne, A.; Tárkányi, F.; Takács, S.; Szücs, Z.; Shubin, Yu.N.; Dityuk, A.I. (2005). "Experimental study of the cross-sections of α-particle induced reactions on 209Bi". Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 63 (1). Elsevier BV: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2005.01.015. ISSN 0969-8043.
- ^ a b Gyehong, G.; Chun, K.; Park, S. H.; Kim, B. (2014). "Production of α-particle emitting 211At using 45 MeV α-beam". Physics in Medicine and Biology. 59 (11): 2849–2860. Bibcode:2014PMB....59.2849K. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/59/11/2849. PMID 24819557. S2CID 21973246.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Zalutsky, M. R.; Pruszynski, M. (2011). "Astatine-211: Production and Availability". Current Radiopharmaceuticals. 4 (3): 177–185. doi:10.2174/1874471011104030177. PMC 3503149. PMID 22201707.
- ^ a b Maiti, Moumita; Lahiri, Susanta; Kumar, Deepak; Choudhury, Dibyasree (2017). "Separation of no-carrier-added astatine radionuclides from α-particle irradiated lead bismuth eutectic target: A classical method". Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 127. Elsevier BV: 227–230. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.06.020. ISSN 0969-8043.
- ^ Naka, Sadahiro; Ooe, Kazuhiro; Shirakami, Yoshifumi; Kurimoto, Kenta; Sakai, Toshihiro; Takahashi, Kazuhiro; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Wang, Yang; Haba, Hiromitsu; Kato, Hiroki; Tomiyama, Noriyuki; Watabe, Tadashi (15 April 2024). "Production of [211At]NaAt solution under GMP compliance for investigator-initiated clinical trial". EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry. 9 (1). doi:10.1186/s41181-024-00257-z. ISSN 2365-421X. PMC 11018728. PMID 38619655.
- ^ a b Larsen, R. H.; Wieland, B. W.; Zalutsky, M. R. J. (1996). "Evaluation of an Internal Cyclotron Target for the Production of 211At via the 209Bi (α,2n)211At reaction". Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 47 (2): 135–143. Bibcode:1996AppRI..47..135L. doi:10.1016/0969-8043(95)00285-5. PMID 8852627.
- ^ Nagatsu, K.; Minegishi, K. H.; Fukada, M.; Suzuki, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Zhang, M. (2014). "Production of 211At by a vertical beam irradiation method". Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 94: 363–371. Bibcode:2014AppRI..94..363N. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2014.09.012. PMID 25439168.
- ^ Barbet, J.; Bourgeois, M.; Chatal, J. (2014). "Cyclotron-Based Radiopharmaceuticals for Nuclear Medicine Therapy". In R. P.; Baum (eds.). Therapeutic Nuclear Medicine. Springer. pp. 95–104 (99). ISBN 978-3-540-36718-5.
- ^ a b Wilbur, D. S. (2001). "Overcoming the Obstacles to Clinical Evaluation of 211At-Labeled Radiopharmaceuticals". The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 42 (10): 1516–1518. PMID 11585866.
- ^ a b c Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, p. 233.
- ^ Gopalan, R. (2009). Inorganic Chemistry for Undergraduates. Universities Press. p. 547. ISBN 978-81-7371-660-7.
- ^ Stigbrand, T.; Carlsson, J.; Adams, G. P. (2008). Targeted Radionuclide Tumor Therapy: Biological Aspects. Springer. p. 150. ISBN 978-1-4020-8695-3.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, pp. 95–106, 133–139.
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, pp. 243–253.
- ^ Kugler & Keller 1985, p. 97.
- ^ Lindegren, S.; Bäck, T.; Jensen, H. J. (2001). "Dry-distillation of Astatine-211 from Irradiated Bismuth Targets: A Time-saving Procedure with High Recovery Yields". Applied Radiation and Isotopes. 55 (2): 157–160. Bibcode:2001AppRI..55..157L. doi:10.1016/S0969-8043(01)00044-6. PMID 11393754.
- ^ Yordanov, A. T.; Pozzi, O.; Carlin, S.; Akabani, G. J.; Wieland, B.; Zalutsky, M. R. (2005). "Wet Harvesting of No-carrier-added 211At from an Irradiated 209Bi Target for Radiopharmaceutical Applications". Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 262 (3): 593–599. Bibcode:2005JRNC..262..593Y. doi:10.1007/s10967-005-0481-7. S2CID 93179195.
- ^ a b Balkin, Ethan; Hamlin, Donald; Gagnon, Katherine; Chyan, Ming-Kuan; Pal, Sujit; Watanabe, Shigeki; Wilbur, D. (18 September 2013). "Evaluation of a Wet Chemistry Method for Isolation of Cyclotron Produced [211At]Astatine". Applied Sciences. 3 (3): 636–655. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.383.1903. doi:10.3390/app3030636. ISSN 2076-3417.
- ^ a b c Vértes, Nagy & Klencsár 2003, p. 337.
- ^ Zalutsky, Michael; Vaidyanathan, Ganesan (1 September 2000). "Astatine-211-Labeled Radiotherapeutics An Emerging Approach to Targeted Alpha-Particle Radiotherapy". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 6 (14): 1433–1455. doi:10.2174/1381612003399275. PMID 10903402.
- ^ Wilbur, D. Scott (20 February 2013). "Enigmatic astatine". Nature Chemistry. 5 (3): 246. Bibcode:2013NatCh...5..246W. doi:10.1038/nchem.1580. PMID 23422568.
- ^ Vértes, Nagy & Klencsár 2003, p. 338.
- ^ a b Fisher, D. (1995). "Oral History of Dr. Patricia Wallace Durbin, PhD". Human Radiation Studies: Remembering the Early Years. United States Department of Energy, Office of Human Radiation Experiments. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ Vaidyanathan, G.; Zalutsky, M. R. (2008). "Astatine Radiopharmaceuticals: Prospects and Problems". Current Radiopharmaceuticals. 1 (3): 177–196. doi:10.2174/1874471010801030177. PMC 2818997. PMID 20150978.
- ^ Lavrukhina & Pozdnyakov 1970, pp. 232–233.
- ^ Odell, T. T. Jr.; Upton, A. C. (2013) [Softcover reprint of the hardcover 1st edition 1961]. "Late Effects of Internally Deposited Radioisotopes". In Schwiegk, H.; Turba, F. (eds.). Radioactive Isotopes in Physiology Diagnostics and Therapy [Radioaktive Isotope in Physiologie Diagnostik Und Therapie]. Springer-Verlag. pp. 375–392 (385). ISBN 978-3-642-49477-2.
Bibliography
[edit]- Corson, D. R.; MacKenzie, K. R.; Segrè, E. (1940). "Artificially Radioactive Element 85". Physical Review. 58 (8): 672–678. Bibcode:1940PhRv...58..672C. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.58.672. (subscription required)
- Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (2002). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3365-9.
- Kugler, H. K.; Keller, C. (1985). 'At, Astatine', System No. 8a. Gmelin Handbook of Inorganic and Organometallic Chemistry. Vol. 8 (8th ed.). Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-3-540-93516-2.
- Lavrukhina, Avgusta Konstantinovna; Pozdnyakov, Aleksandr Aleksandrovich (1970). Analytical Chemistry of Technetium, Promethium, Astatine, and Francium. Translated by R. Kondor. Ann Arbor–Humphrey Science Publishers. ISBN 978-0-250-39923-9.
- Scerri, Eric (2013). A Tale of Seven Elements. Oxford University Press, ISBN 9780195391312.
- Vértes, A.; Nagy, S.; Klencsár, Z. (2003). Handbook of Nuclear Chemistry. Vol. 4. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-1316-4.
- Zuckerman, J. J.; Hagen, A. P. (1989). Inorganic Reactions and Methods, Volume 3, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 1). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-18656-4.
- Zuckerman, J. J.; Hagen, A. P. (1990). Inorganic Reactions and Methods, Volume 4, The Formation of Bonds to Halogens (Part 2). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-18657-1.
External links
[edit]- Astatine at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
- Astatine: Halogen or Metal?


