1920 United States presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 49.2%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
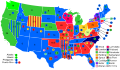
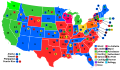
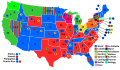
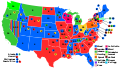
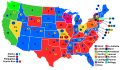
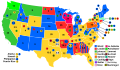
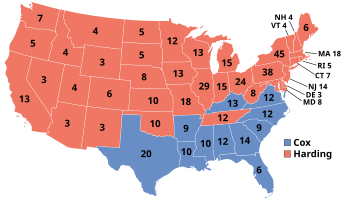 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Harding/Coolidge, blue denotes those won by Cox/Roosevelt. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

In the United States presidential election held on November 2, 1920 Republican senator Warren G. Harding of Ohio defeated Democratic governor James M. Cox of Ohio. It was the first election held after the end of the First World War, and the first election after the ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment which gave equal votes to men and women. It was the third presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state (the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1940, 1944, and 2016), and the last time that the state was not New York. It was the first presidential election to have its results broadcast by radio.[2]
Incumbent Democratic president Woodrow Wilson privately hoped for a third term, despite his severe physical and mental disabilities, but he had very little support. Former president Theodore Roosevelt had been the frontrunner for the Republican nomination, but he died in 1919 without leaving an obvious heir to his progressive legacy. The major parties turned to littleknown dark horse candidates from the state of Ohio, a swing state with a large number of electoral votes. Cox won on the 44th ballot at the 1920 Democratic National Convention, defeating William Gibbs McAdoo (Wilson's son-in-law), A. Mitchell Palmer, and several other candidates. Harding emerged as a compromise candidate between the conservative and progressive wings of the Republican party, and he clinched his nomination on the tenth ballot at the 1920 Republican National Convention.
The election was dominated by the American social and political environment in the aftermath of World War I, which was marked by a hostile response to certain aspects of Wilson's foreign policy and a massive reaction against the reformist zeal of the Progressive Era. The wartime economic boom had collapsed and the country was deep in a recession. Wilson's advocacy for America's entry into the League of Nations, in the face of a return to non-interventionist opinion, challenged his effectiveness as president, and there were wars and revolutions overseas. At home, the year 1919 was marked by major strikes in the meatpacking and steel industries, and large-scale race riots in Chicago and other cities. Anarchist attacks on Wall Street produced fears of radicals and terrorists. The Irish Catholic and German communities were outraged at Wilson's perceived support of their traditional enemy, Great Britain, and his political position was critically weakened after he suffered a stroke in 1919 that left him severely disabled.
Harding all but ignored Cox in the race, and essentially campaigned against Wilson by calling for a "return to normalcy". Harding won a landslide victory, sweeping every state outside of the South and becoming the first Republican since the end of Reconstruction to win a former state of the Confederacy, Tennessee. Harding's victory margin of 26.2 percent in the popular vote remains the largest popular-vote percentage margin for a Republican, and the largest ever since widespread popular elections began in the 1820s. However, subsequent candidates (in 1936, 1964 and 1972) have exceeded his share of the popular vote.[3] Cox won just 34.1 percent of the popular vote, and Socialist Eugene V. Debs won 3.4 percent, despite being in prison at the time. It was the first election in which women had the right to vote in all 48 states, which caused the total popular vote to increase dramatically, from 18.5 million in 1916 to 26.8 million in 1920.[4] Both major-party vice-presidential nominees would later succeed to the presidency: Calvin Coolidge (Republican) upon Harding's death in 1923 and Franklin D. Roosevelt (Democratic) after defeating Republican president Herbert Hoover in 1932.
Nominations
[edit]Republican Party nomination
[edit] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warren G. Harding | Calvin Coolidge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United States Senator from Ohio (1915–1921) |
48th Governor of Massachusetts (1919–1921) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ID: 39 votes[5] HCV: 692.2 votes 144,762 votes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Candidates
[edit]| Candidates in this section are sorted by their highest vote count on the nominating ballots | ||||||
| Leonard Wood | Frank Orren Lowden | Hiram Johnson | William Cameron Sproul | Nicholas Murray Butler | Calvin Coolidge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Chief of Staff of the Army from New Hampshire (1910–1914) |
Governor of Illinois (1917–1921) |
U.S. Senator from California (1917–1945) |
Governor of Pennsylvania (1919–1923) |
Columbia University President from New York (1902–1945) |
Governor of Massachusetts (1919–1921) | |
| ID: 145 votes[5] HCV: 314.5 votes 710,863 votes |
ID: 78 votes[5] HCV: 311.5 votes 389,127 votes |
ID: 110 votes[5] HCV: 148 votes 965,651 votes |
ID: 0 votes[5] HCV: 84 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[5] HCV: 69.5 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[5] HCV: 34 votes 0 votes | |
| Robert M. La Follette | Jeter Pritchard | Miles Poindexter | Howard Sutherland | Herbert Hoover | ||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| U.S. Senator from Wisconsin (1906–1925) |
Court of Appeals Judge from North Carolina (1904–1921) |
U.S. Senator from Washington (1911–1923) |
U.S. Senator from West Virginia (1917–1923) |
Director of the U.S. Food Administration from California (1917–1918) | ||
| ID: 0 votes[5] NFN HCV: 24 votes 0 votes |
ID: 17 votes[5] HCV: 21 votes 0 votes |
ID: 14 votes[5] HCV: 20 votes 3,806 votes |
ID: 0 votes[5] HCV: 17 votes 33,849 votes |
ID: 0 votes[5] HCV: 10.5 votes 303,815 votes | ||
Following the return of former president Theodore Roosevelt to the Republican Party after the previous election, speculation quickly grew as to whether he would make another run for the presidency. Roosevelt's health declined seriously in 1918, however, and he died on January 6, 1919. Attention then turned to the party's unsuccessful 1916 candidate, Charles Evans Hughes, who had narrowly fallen short of defeating Wilson that year, but Hughes remained aloof as to the prospect of another run, and ultimately ruled himself out following the death of his daughter early in 1920.
On June 8, the Republican National Convention met in Chicago. The race was wide open, and soon the convention deadlocked between Major General Leonard Wood and Governor Frank Orren Lowden of Illinois.
Other names placed in nomination included Senators Warren G. Harding from Ohio, Hiram Johnson from California, and Miles Poindexter from Washington, Governor Calvin Coolidge of Massachusetts, philanthropist Herbert Hoover, and Columbia University President Nicholas M. Butler. Senator Robert M. La Follette from Wisconsin was not formally placed in nomination, but received the votes of his state delegation nonetheless. Harding was nominated for president on the tenth ballot, after some delegates shifted their allegiances. The results of the ten ballots were as follows:
| Presidential Balloting, Republican National Convention 1920 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballot | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 Before shifts |
10 After shifts |
| Warren G. Harding | 65.5 | 59.0 | 58.5 | 61.5 | 78.0 | 89.0 | 105.0 | 133.0 | 374.5 | 644.7 | 692.2 |
| Leonard Wood | 287.5 | 289.5 | 303.0 | 314.5 | 299.0 | 311.5 | 312.0 | 299.0 | 249.0 | 181.5 | 156.0 |
| Frank Orren Lowden | 211.5 | 259.5 | 282.5 | 289.0 | 303.0 | 311.5 | 311.5 | 307.0 | 121.5 | 28.0 | 11.0 |
| Hiram Johnson | 133.5 | 146.0 | 148.0 | 140.5 | 133.5 | 110.0 | 99.5 | 87.0 | 82.0 | 80.8 | 80.8 |
| William Cameron Sproul | 84.0 | 78.5 | 79.5 | 79.5 | 82.5 | 77.0 | 76.0 | 76.0 | 78.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nicholas Murray Butler | 69.5 | 41.0 | 25.0 | 20.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Calvin Coolidge | 34.0 | 32.0 | 27.0 | 25.0 | 29.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 30.0 | 28.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Robert M. La Follette | 24.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 22.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 |
| Jeter Connelly Pritchard | 21.0 | 10.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Miles Poindexter | 20.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 2.0 | 0 |
| Howard Sutherland | 17.0 | 15.0 | 9.0 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Herbert Hoover | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 10.5 | 9.5 |
| Scattering | 11.0 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 3.5 |
-
First Presidential Ballot
-
Second Presidential Ballot
-
Third Presidential Ballot
-
Fourth Presidential Ballot
-
Fifth Presidential Ballot
-
Sixth Presidential Ballot
-
Seventh Presidential Ballot
-
Eighth Presidential Ballot
-
Ninth Presidential Ballot
-
Tenth Presidential Ballot
Before Shifts -
Tenth Presidential Ballot
After Shifts
Harding's nomination, said to have been secured in negotiations among party bosses in a "smoke-filled room," was engineered by Harry M. Daugherty, Harding's political manager, who became United States Attorney General after his election. Before the convention, Daugherty was quoted as saying, "I don't expect Senator Harding to be nominated on the first, second, or third ballots, but I think we can afford to take chances that about 11 minutes after two, Friday morning of the convention, when 15 or 12 weary men are sitting around a table, someone will say: 'Who will we nominate?' At that decisive time, the friends of Harding will suggest him and we can well afford to abide by the result." Daugherty's prediction described essentially what occurred, but historians Richard C. Bain and Judith H. Parris argue that Daugherty's prediction has been given too much weight in narratives of the convention.
Once the presidential nomination was finally settled, the party bosses and Sen. Harding recommended Wisconsin Sen. Irvine Lenroot to the delegates for the second spot, but the delegates revolted and nominated Coolidge, who was very popular over his handling of the Boston Police Strike from the year before. The Tally:
| Vice Presidential Balloting, Republican Nat'l Convention 1920 | |
|---|---|
| Calvin Coolidge | 674.5 |
| Irvine Lenroot | 146.5 |
| Henry Justin Allen | 68.5 |
| Henry W. Anderson | 28 |
| Asle Gronna | 24 |
| Hiram Johnson | 22.5 |
| Jeter Connelly Pritchard | 11 |
| Abstaining | 9 |
Source for convention coverage: Richard C. Bain and Judith H. Parris, Convention Decisions and Voting Records (Washington DC: Brookings Institution, 1973), pp. 200–208.
Democratic Party nomination
[edit] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| James M. Cox | Franklin D. Roosevelt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 46th & 48th Governor of Ohio (1913–1915 & 1917–1921) |
Assistant Secretary of the Navy (1913–1920) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ID: 74 votes[6] HCV: 699.5 votes 86,194 votes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other candidates
[edit]| Candidates in this section are sorted by their highest vote count on the nominating ballots | ||||||
| William Gibbs McAdoo | Mitchell Palmer | Al Smith | John W. Davis | Edward Edwards | Robert Latham Owen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| U.S. Secretary of the Treasury from California (1913–1918) |
U.S. Attorney General from Pennsylvania (1919–1921) |
Governor of New York (1919–1920) |
Ambassador to Britain from West Virginia (1918–1921) |
Governor of New Jersey (1920–1923) |
U.S. Senator from Oklahoma (1907–1925) | |
| ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 467 votes 74,987 votes |
ID: 104 votes[6] HCV: 267 votes 140,010 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 109 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 71.5 votes 0 votes |
ID: 28 votes[6] HCV: 42 votes 28,470 votes |
ID: 20 votes[6] HCV: 41 votes 0 votes | |
| Thomas Marshall | Edwin T. Meredith | Carter Glass | Homer Cummings | Furnifold Simmons | James Gerard | |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| U.S. Vice President from Indiana (1913–1921) |
U.S. Secretary of Agriculture from Iowa (1920–1921) |
U.S. Senator from Virginia (1920–1946) |
Chair of the DNC from Connecticut (1919–1920) |
U.S. Senator from North Carolina (1901–1931) |
Ambassador to Germany from New York (1913–1917) | |
| ID: 0 votes[6] NFN HCV: 37 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 28 votes 0 votes |
ID: 24 votes[6] HCV: 27 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 27 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 25 votes 0 votes |
ID: 10 votes[6] HCV: 21 votes 4,706 votes | |
| John Sharp Williams | Gilbert Hitchcock | Francis Harrison | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
| U.S. Senator from Mississippi (1911–1923) |
U.S. Senator from Nebraska (1911–1923) |
Philippine Governor-General from New York (1913–1921) | ||||
| ID: 0 votes[6] NFN HCV: 20 votes 0 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 18 votes 37,452 votes |
ID: 0 votes[6] HCV: 6 votes 0 votes | ||||

It was widely accepted prior to the election that President Woodrow Wilson would not run for a third term, and certainly would not be nominated if he did so. While Vice President Thomas R. Marshall long had desired to succeed Wilson, his indecisive handling of the situation around Wilson's illness and incapacity destroyed any credibility he had as a candidate, and in the end he did not formally put himself forward for the nomination.
Although William Gibbs McAdoo (Wilson's son-in-law and former Treasury Secretary) was the strongest candidate, Wilson blocked his nomination in hopes a deadlocked convention would demand that he run for a third term, even though he was seriously ill, physically immobile, and in seclusion at the time. The Democrats, meeting in San Francisco between June 28 and July 6 (the first time a major party held its nominating convention in an urban center on the Pacific coast), nominated another newspaper editor from Ohio, Governor James M. Cox, as their presidential candidate, and 38-year-old Assistant Secretary of the Navy Franklin D. Roosevelt, a fifth cousin and nephew-in-law of the late president Theodore Roosevelt, for vice-president.
Early favorites for the nomination had included McAdoo and Attorney General Alexander Mitchell Palmer. Others placed in nomination included New York governor Al Smith, United Kingdom ambassador John W. Davis, New Jersey governor Edward I. Edwards, and Oklahoma senator Robert Latham Owen.
| (23–44) | Presidential Ballot | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23rd | 24th | 25th | 26th | 27th | 28th | 29th | 30th | 31st | 32nd | 33rd | 34th | 35th | 36th | 37th | 38th | 39th | 40th | 41st | 42nd | 43rd | 44th | ||||
| James M. Cox | 425 | 429 | 424 | 424.5 | 423.5 | 423 | 404.5 | 400.5 | 391.5 | 391 | 380.5 | 379.5 | 376.5 | 377 | 386 | 383.5 | 468.5 | 490 | 497.5 | 540.5 | 568 | 699.5 | |||
| William Gibbs McAdoo | 364.5 | 364.5 | 364.5 | 371 | 371.5 | 368.5 | 394.5 | 403.5 | 415.5 | 421 | 421 | 420.5 | 409 | 399 | 405 | 405.5 | 440 | 467 | 460 | 427 | 412 | 270 | |||
| A. Mitchell Palmer | 181.5 | 177 | 169 | 167 | 166.5 | 165.5 | 166 | 165 | 174 | 176 | 180 | 184 | 222 | 241 | 202.5 | 211 | 74 | 19 | 12 | 8 | 7 | 1 | |||
| John W. Davis | 50.5 | 54.5 | 58.5 | 55.5 | 60.5 | 62.5 | 63 | 58 | 57.5 | 55.5 | 56 | 54 | 33 | 28 | 50.5 | 50 | 71.5 | 76 | 55.5 | 49.5 | 57.5 | 52 | |||
| Robert L. Owen | 34 | 33 | 34 | 33 | 34 | 35.5 | 33 | 33 | 34 | 34 | 34 | 37 | 38.5 | 36 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 33 | 35 | 34 | 34 | 34 | |||
| Carter Glass | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 13 | 7.5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 24 | 5.5 | 1.5 | |||
| Homer Cummings | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Champ Clark | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |||
| Annette Abbott Adams | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Eugene C. Bonniwell | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| William Jennings Bryan | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Laura Clay | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Irvin S. Cobb | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Bainbridge Colby | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Josephus Daniels | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Walker Hines | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Andrieus A. Jones | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Ring Lardner | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| James H. Lewis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Thomas R. Marshall | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| John J. Pershing | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Joseph T. Robinson | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Cora Wilson Stewart | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Oscar Underwood | 0 | 1 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
Other candidates
[edit]Socialist Party
[edit]Socialist Party candidate Eugene V. Debs was incarcerated at the Atlanta federal penitentiary at the time for advocating non-compliance with the draft during World War I. He received the largest number of popular votes ever received by a Socialist Party candidate in the United States, although not the largest percentage of the popular vote. Debs received double this percentage in the election of 1912.[7] The 1920 election was Debs's fifth and last attempt to become president.[8]
In 1919, members of the Socialist Party who had come from Russian language federation of the party and other more radical groups within the party started to create their own papers and membership dues and cards. These members supported a platform that was similar to the Communist International and elected twelve of their members to the fifteen-member National Executive Committee. However, there was accusations of election irregularities and an Emergency Convention held on August 30, 1919, suspended seven of the party's twelve language federations and expelled the party affiliates in Michigan, Massachusetts, and Ohio. The more radical members of the party held a convention in New York City in June 1919, which was attended by 94 delegates from twenty states. A vote to create a new party was defeated by a vote of 55 to 38 causing 31 delegates to withdraw from the convention. These 31 delegates held their own convention in Chicago on September 1, where they founded the Communist Party USA.[9] The Communist Party USA attempted to give its presidential nomination to Debs, but he declined the nomination.[8]
The Socialist Party held its 1919 convention in Chicago with 140 delegates in attendance. Twenty-six delegates, who were members of the party's left-wing, left the convention. These delegates attempted to unite with the Communist Party USA, but formed the Communist Labor Party of America on September 2, after those attempts failed.[9]
The Socialist Party had 100,000 members before the splits, but it fell to 55,000 members while the Communist Party had 35,000 members and the Communist Labor Party had 10,000 members. The Communist Party claimed to have 60,000 members while the Communist Labor Party claimed to have 30,000 members. The United Communist Party was formed in May 1920 between the Communist Labor Party and some members of the Communist Party. The United Communist Party and the Communist Party united in December 1921 to form the Workers Party of America.[9]
Edward Henry, who was a friend of Debs, Lena Morrow Lewis, and Oscar Ameringer nominated Debs for the party's nomination on May 13, 1920, and the 134 delegates to the national convention voted unanimously to give him the nomination. Kate Richards O'Hare, who was also in prison, was considered for the vice-presidential nomination, but Seymour Stedman was selected by a vote of 106 to 26, which was later made unanimous, in order to have one of the candidates campaign. James H. Maurer was also considered for the vice-presidential nomination, but he declined due to his duties as head of the Pennsylvania Federation of Labor. Debs accepted the presidential nomination in an Atlanta prison on May 29, after being notified by Seymour, James Oneal, and Julius Gerber.[8][10][11][12]
During the campaign the Socialists had four airplanes drop socialist literature over Toledo, Ohio. The wife of Charles Edward Russell claimed that the ghost of Susan B. Anthony told her to vote for Debs. Over 60,000 people donated to the Socialist Party's campaign fund. Gerber predicted that Debs would receive three million votes and that five Socialists would be elected to Congress. Debs received 913,693 votes with his largest amount of support coming from New York. His vote total was over 50 percent more than what Allan L. Benson had received in the 1916 election. Debs later chose to not run for president in the 1924 election and instead supported Robert M. La Follette.[8][13]
| Presidential Ballot | |
| Eugene V. Debs | 132 |
|---|---|
Farmer-Labor Party
[edit]| 1920 Farmer-Labor Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Parley P. Christensen | Max S. Hayes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State Representative from Utah (1915–1917) |
Editor of the Cleveland Citizen from Ohio | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Candidates
[edit]| Candidates in this section are sorted by their highest vote count on the nominating ballots | ||||||
| Dudley Field Malone | Eugene V. Debs | Henry Ford | Lynn Frazier | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
| Collector of the Port of New York from New York (1913–1913) |
State Representative from Indiana (1885–1887) |
President of the Ford Motor Company from Michigan (1906–1919) |
Governor of North Dakota (1917–1921) | |||
| HCV: 174.6 votes | HCV: 68 votes | HCV: 12.3 votes | DN HCV: 9 votes | |||
| Herbert S. Bigelow | Louis F. Post | Jane Addams | Robert M. La Follette | |||
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
| Clergyman from Ohio |
Asst U. S. Secretary of Labor from New York (1913–1921) |
Co-founder of Hull House from Illinois |
U.S. Senator from Wisconsin (1906–1925) | |||
| HCV: 7 votes | HCV: 1.7 votes | HCV: 0 votes | DN | |||
Prohibition Party
[edit]
1920 Prohibition Party ticket | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Professor and Methodist Minister from Ohio |
American politician from New York | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Candidates
[edit]| Candidates in this section are sorted by their highest vote count on the nominating ballots | ||||||
| Robert H. Patton | Daniel A. Poling | Charles Hiram Randall | William Jennings Bryan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 | ||||
| Prohibition Party Convention Chair (1916) |
Intinerent Minister from Pennsylvania |
Congressman from California (1915–1921) |
U.S. Secretary of State from Nebraska (1913–1915) | |||
| HCV: 85 votes | HCV: 28 votes | HCV: 9 votes | DN | |||
Meeting in Lincoln, Nebraska, there was some question whether the Prohibition Party would field an independent ticket as opposed to endorsing either Harding or Cox, but this was predicated on either making a clear statement that they would not move to weaken the Eighteenth Amendment; neither chose to make any such commitment.[14] The ticket favored by most present was that of William Jennings Bryan for president and William "Billy" Sunday for vice president, and indeed when a motion was made to nominate Bryan by acclamation, of the more than two hundred present it was only opposed by six.[15] Upon hearing of his nomination however Bryan declined the gesture, not wishing to remain singularly focused on the prohibition question or to sever his ties with the Democratic Party entirely.[16] Some had considered Billy Sunday a possible substitute but Sunday was "satisfied" with Republican nominee Warren Harding, while others thought about potentially nominating Henry Ford as their standard-bearer. With the nomination thrown wide open, the party ultimately opted to nominate keynote speaker and Methodist minister Aaron Watkins of Ohio, over other candidates such as 1916 Convention Chair Robert Patton of Illinois, itinerant minister Daniel Poling of Pennsylvania, and Congressman Charles Randall of California. Historian David Leigh Colvin of New York was nominated for the vice presidency.
| Presidential Balloting | Vice-Presidential Balloting | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballot | 1 | 2 | Ballot | 1 |
| Aaron S. Watkins | 85.0 | 108.0 | D. Leigh Colvin | 108.0 |
| Robert H. Patton | 85.0 | 74.0 | Herman P. Faris | 47.0 |
| Daniel A. Poling | 28.0 | 24.0 | Frank S. Regan | 15.0 |
| Charles H. Randall | 9.0 | 2.0 | James H. Woertendyke | 12.0 |
American Party
[edit]James E. Ferguson, a former governor of Texas, announced his candidacy on April 21, 1920, in Temple, Texas, under the badge of "American Party".[17] Ferguson was opposed to Democrats whom he saw as too controlled by elite academic interests as seen when Woodrow Wilson endorsed rival Thomas H. Ball in the gubernatorial primary, and hoped to help the Republicans carry Texas for the first time (Texas never went Republican during Reconstruction).[18] Initially Ferguson and running mate William J. Hough hoped to carry their campaign to other states,[19] but Ferguson was unable to get on the ballot anywhere outside of Texas. Ferguson did manage to gain almost 10 percent of the vote in Texas, and won eleven counties in the southeast of the state.[20]
General election
[edit]Return to normalcy
[edit]Warren Harding's main campaign slogan was a "return to normalcy", playing upon the weariness of the American public after the social upheaval of the Progressive Era, World War I, and the Spanish flu. Additionally, the international responsibilities engendered by the Allied victory in World War I and the Treaty of Versailles proved deeply unpopular, causing a reaction against Wilson, who had pushed especially hard for the latter.
Ethnic issues
[edit]
Irish Americans were powerful in the Democratic party, and groups such as Clan na Gael opposed going to war alongside their enemy Britain, especially after the violent suppression of the Easter Rising of 1916. Wilson won them over in 1917 by promising to ask Britain to give Ireland its independence. Wilson had won the presidential election of 1916 with strong support from German-Americans and Irish-Americans, largely because of his slogan "He kept us out of war" and the longstanding American policy of isolationism. At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, however, he reneged on his commitments to the Irish-American community, who vehemently denounced him. His dilemma was that Britain was his war ally. Events such as the anti-British Black Tom and Kingsland Explosions in 1916 on American soil (in part the result of wartime Irish and German co-ordination) and the Irish anti-conscription crisis of 1918 were all embarrassing to recall in 1920.[21][22]
Britain had already passed an Irish Home Rule Act in 1914, suspended for the war's duration. However the 1916 Easter Rising in Dublin had led to increased support for the more radical Sinn Féin who in 1919 formed the First Dáil, effectively declaring Ireland independent, sparking the Irish War of Independence. Britain was to pass the Government of Ireland Act in late 1920, by which Ireland would have 2 home-ruled states within the British empire. This satisfied Wilson. The provisions of these were inadequate to the supporters of the Irish Republic, however, which claimed full sovereignty. This position was also supported by many Irish Americans. The American Committee for Relief in Ireland was set up in 1920 to assist victims of the Irish War of Independence of 1919–21. Some Irish-American senators joined the "irreconcilables" who blocked the ratification of the Treaty of Versailles and United States membership in the League of Nations.
Wilson blamed the Irish Americans and German Americans for the lack of popular support for his unsuccessful campaign to have the United States join the League of Nations, saying, "There is an organized propaganda against the League of Nations and against the treaty proceeding from exactly the same sources that the organized propaganda proceeded from which threatened this country here and there with disloyalty, and I want to say—I cannot say too often—any man who carries a hyphen about with him [i.e., a hyphenated American] carries a dagger that he is ready to plunge into the vitals of this Republic whenever he gets ready."[23]
Of the $5,500,000 raised by supporters of the Irish Republic in the United States in 1919–20, the Dublin parliament (Dáil Éireann) voted in June 1920 to spend $500,000 on the American presidential election.[24] How this money was spent remains unclear. Ironically, the lawyer who had advised the fundraisers was Franklin D. Roosevelt[citation needed], the losing vice-presidential candidate. In any case, the Irish American city machines sat on their hands during the election, allowing the Republicans to roll up unprecedented landslides in every major city.[citation needed] Many German-American Democrats voted Republican or stayed home, giving the GOP landslides in the rural Midwest.
Campaign
[edit]
Wilson had hoped for a "solemn referendum" on the League of Nations, but did not get one. Harding waffled on the League, thereby keeping Idaho senator William Borah and other Republican "irreconcilables" in line. Cox also hedged. He went to the White House to seek Wilson's blessing and apparently endorsed the League, but—upon discovering its unpopularity among Democrats—revised his position to one that would accept the League only with reservations, particularly on Article Ten, which would require the United States to participate in any war declared by the League (thus taking the same standpoint as Republican Senate leader Henry Cabot Lodge). As reporter Brand Whitlock observed, the League was an issue important in government circles, but rather less so to the electorate. He also noted that the campaign was not waged on issues: "The people, indeed, do not know what ideas Harding or Cox represents; neither do Harding or Cox. Great is democracy."[25] False rumors circulated that Senator Harding had "Negro blood," but this did not greatly hurt Harding's election campaign.
Governor Cox made a whirlwind campaign that took him to rallies, train station speeches, and formal addresses, reaching audiences totaling perhaps two million, whereas Senator Harding relied upon a "Front Porch Campaign" similar to that of William McKinley in 1896. It brought thousands of voters to Marion, Ohio, where Harding spoke from his home. GOP campaign manager Will Hays spent some $8.1 million, nearly four times the money Cox's campaign spent. Hays used national advertising in a major way (with advice from adman Albert Lasker). The theme was Harding's own slogan "America First". Thus the Republican advertisement in Collier's Magazine for October 30, 1920, demanded, "Let's be done with wiggle and wobble." The image presented in the ads was nationalistic, using catch phrases like "absolute control of the United States by the United States," "Independence means independence, now as in 1776," "This country will remain American. Its next President will remain in our own country," and "We decided long ago that we objected to foreign government of our people."[26]
On election night, November 2, 1920, commercial radio broadcast coverage of election returns for the first time. Announcers at KDKA-AM in Pittsburgh read telegraph ticker results over the air as they came in. This single station could be heard over most of the Eastern United States by the small percentage of the population that had radio receivers.
Harding's landslide came from all directions except the South. Irish- and German-American voters who had backed Wilson and peace in 1916 now voted against Wilson and Versailles. "A vote for Harding", said the German-language press, "is a vote against the persecutions suffered by German-Americans during the war". Not one major German-language newspaper supported Governor Cox.[27] Many Irish Americans, bitterly angry at Wilson's refusal to help Ireland at Versailles, simply abstained from voting in the presidential election. This allowed the Republicans to mobilize the ethnic vote, and Harding swept the big cities.

This was the first election in which women from every state were allowed to vote, following the passage of the 19th Amendment to the Constitution in August 1920 (just in time for the general election).
Tennessee's vote for Warren G. Harding marked the first time since the end of Reconstruction that even one of the eleven states of the former Confederacy had voted for a Republican presidential candidate. Tennessee had last been carried by a Republican when Ulysses S. Grant claimed it in 1868.
Even though Cox lost badly, his running mate Franklin D. Roosevelt became a well-known political figure because of his active and energetic campaign. In 1928, he was elected Governor of New York, and in 1932 he was elected president. He remained in power until his death in 1945 as the longest-serving American president in history.
Results
[edit]
The total vote for 1920 was roughly 26,750,000, an increase of eight million from 1916.[29] Harding won in all twelve cities with populations above 500,000. Harding won a net vote total of 1,540,000 from the twelve largest cities which was the highest amount for any Republican and fifth highest for any candidate from 1920 to 1948.[30] The Democratic vote was almost exactly the vote from 1916, but the Republican vote nearly doubled, as did the "other" vote. As pointed out earlier, the great increase in the total number of votes is mainly attributable to the passage of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which gave women the right to vote.

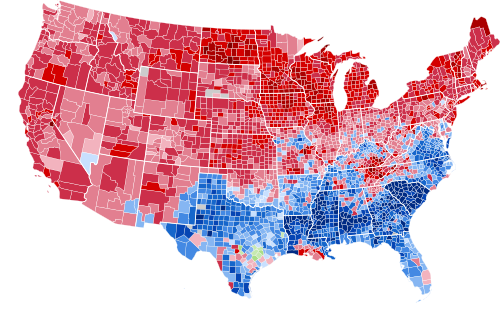
Nearly two-thirds of the counties (1,949) were carried by the Republicans. The Democrats carried only 1,101 counties, a smaller number than Alton Parker had carried in 1904 and consequently the smallest number during the Fourth Party System until that point (Al Smith would carry even fewer in 1928). Not a single county was carried by the Democrats in the Pacific section, where they had carried 76 in 1916. In the Mountain section Cox carried only thirteen counties, seven of them located in New Mexico bordering Texas, whereas Wilson carried all but twenty-one Mountain Section counties in 1916. At least one county was lost in every section in the Union and in every state except South Carolina and Mississippi. Eleven counties in Texas recorded a plurality for Ferguson. With the tipping point state of Rhode Island being decided by a 31.2 percent margin, the 1920 election has the largest margin of victory in the tipping point state in American history.[20]
Wilson had won the support of Americans of German, Italian, Irish, or Jewish descent in the 1916 election, but Cox lost in all of those demographics and received less support from Jewish voters than Debs. Harding received support from over 90 percent of black voters.[30]
The distribution of the county vote accurately represents the overwhelming character of the majority vote. Harding received 60.35 percent of the total vote, the largest percentage in the Fourth Party System, exceeding Franklin D. Roosevelt's in 1932. Although the Democratic share was 34.13 percent, in no section did its voting share sink below 24 percent, and in three sections, the Democrats topped the poll. The Democratic Party was still a significant opposition on national terms, even though Cox won only eleven states and had fewer votes in the electoral college than Parker had won in 1904. More than two-thirds of the Cox vote was in states carried by Harding. The distribution of the vote by counties, and the study of percentages in sections, states, and counties, seem to show that it was Wilson and foreign policies that received the brunt of attack, not the Democratic Party and the domestic proposals of the period 1896–1914.[31] This is one of two elections since the Civil War (along with 1924) where national turnout was below 50 percent.
This was also the third presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1940, 1944, and 2016.
5.83% of Harding's votes came from the eleven states of the former Confederacy, with him taking 35.09% of the vote in that region.[32]
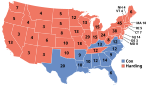
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote | Electoral vote |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
| Warren G. Harding | Republican | Ohio | 16,166,126 | 60.35% | 404 | Calvin Coolidge | Massachusetts | 404 |
| James M. Cox | Democratic | Ohio | 9,140,256 | 34.12% | 127 | Franklin D. Roosevelt | New York | 127 |
| Eugene V. Debs | Socialist | Indiana | 914,191 | 3.41% | 0 | Seymour Stedman | Illinois | 0 |
| Parley P. Christensen | Farmer-Labor | Illinois | 265,395 | 0.99% | 0 | Max S. Hayes | Ohio | 0 |
| Aaron S. Watkins | Prohibition | Indiana | 188,709 | 0.70% | 0 | D. Leigh Colvin | New York | 0 |
| James E. Ferguson | American | Texas | 47,968 | 0.18% | 0 | William J. Hough | New York | 0 |
| William Wesley Cox | Socialist Labor | Missouri | 31,084 | 0.12% | 0 | August Gillhaus | New York | 0 |
| Robert Colvin Macauley | Single Tax | Pennsylvania | 5,750 | 0.02% | 0 | Richard C. Barnum | Ohio | 0 |
| Other | 28,746 | 0.11% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 26,788,225 | 100% | 531 | 531 | ||||
| Needed to win | 266 | 266 | ||||||
Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. "1920 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved June 10, 2023.
Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 31, 2005.
Geography of results
[edit]
-
Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Cartographic gallery
[edit]-
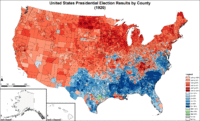
Map of presidential election results by county
-
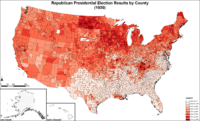
Map of Republican presidential election results by county
-
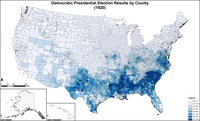
Map of Democratic presidential election results by county
-
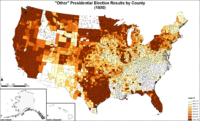
Map of "other" presidential election results by county
-
Cartogram of presidential election results by county
-
Cartogram of Republican presidential election results by county
-
Cartogram of Democratic presidential election results by county
-
Cartogram of "other" presidential election results by county
Results by state
[edit]Source:[33]
| States/districts won by Cox/Roosevelt |
| States/districts won by Harding/Coolidge |
| Warren G. Harding Republican |
James Cox Democratic |
Eugene Debs Socialist |
Parley Christensen Farmer-Labor |
Aaron Watkins Prohibition |
James Ferguson American |
William Cox Socialist Labor |
Margin | State Total | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | # | |
| Alabama | 12 | 74,556 | 31.37 | - | 159,965 | 67.31 | 12 | 2,369 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | 748 | 0.31 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -85,409 | -35.94 | 237,638 | AL |
| Arizona | 3 | 37,016 | 55.61 | 3 | 29,546 | 44.39 | - | 222 | 0.33 | - | 15 | 0.02 | - | 4 | 0.01 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7,470 | 11.22 | 66,562 | AZ |
| Arkansas | 9 | 71,117 | 38.73 | - | 107,409 | 58.49 | 9 | 5,111 | 2.78 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -36,292 | -19.76 | 183,637 | AR |
| California | 13 | 624,992 | 66.20 | 13 | 229,191 | 24.28 | - | 64,076 | 6.79 | - | - | - | - | 25,204 | 2.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 395,801 | 41.93 | 944,050 | CA |
| Colorado | 6 | 173,248 | 59.32 | 6 | 104,936 | 35.93 | - | 8,046 | 2.75 | - | 3,016 | 1.03 | - | 2,807 | 0.96 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 68,312 | 23.39 | 292,053 | CO |
| Connecticut | 7 | 229,238 | 62.72 | 7 | 120,721 | 33.03 | - | 10,350 | 2.83 | - | 1,947 | 0.53 | - | 1,771 | 0.48 | - | - | - | - | 1,491 | 0.41 | - | 108,517 | 29.69 | 365,518 | CT |
| Delaware | 3 | 52,858 | 55.71 | 3 | 39,911 | 42.07 | - | 988 | 1.04 | - | 93 | 0.10 | - | 986 | 1.04 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 12,947 | 13.65 | 94,875 | DE |
| Florida | 6 | 44,853 | 30.79 | - | 90,515 | 62.13 | 6 | 5,189 | 3.56 | - | - | - | - | 5,124 | 3.52 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -45,662 | -31.34 | 145,681 | FL |
| Georgia | 14 | 41,089 | 27.72 | - | 107,162 | 72.28 | 14 | 465 | 0.31 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -66,073 | -44.57 | 148,251 | GA |
| Idaho | 4 | 88,975 | 65.60 | 4 | 46,579 | 34.34 | - | 38 | 0.03 | - | - | - | - | 32 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 42,396 | 31.26 | 135,624 | ID |
| Illinois | 29 | 1,420,480 | 67.81 | 29 | 534,395 | 25.51 | - | 74,747 | 3.57 | - | 49,630 | 2.37 | - | 11,216 | 0.54 | - | - | - | - | 3,471 | 0.17 | - | 886,085 | 42.30 | 2,094,714 | IL |
| Indiana | 15 | 696,370 | 55.14 | 15 | 511,364 | 40.49 | - | 24,703 | 1.96 | - | 16,499 | 1.31 | - | 13,462 | 1.07 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 185,006 | 14.65 | 1,262,964 | IN |
| Iowa | 13 | 634,674 | 70.91 | 13 | 227,921 | 25.46 | - | 16,981 | 1.90 | - | 10,321 | 1.15 | - | 4,197 | 0.47 | - | - | - | - | 982 | 0.11 | - | 406,753 | 45.44 | 895,082 | IA |
| Kansas | 10 | 369,268 | 64.75 | 10 | 185,464 | 32.52 | - | 15,511 | 2.72 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 183,804 | 32.23 | 570,318 | KS |
| Kentucky | 13 | 452,480 | 49.25 | - | 456,497 | 49.69 | 13 | 6,409 | 0.70 | - | - | - | - | 3,322 | 0.36 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -4,017 | -0.44 | 918,708 | KY |
| Louisiana | 10 | 38,538 | 30.49 | - | 87,519 | 69.24 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -48,981 | -38.75 | 126,396 | LA |
| Maine | 6 | 136,355 | 68.92 | 6 | 58,961 | 29.80 | - | 2,214 | 1.12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 77,394 | 39.12 | 197,840 | ME |
| Maryland | 8 | 236,117 | 55.11 | 8 | 180,626 | 42.16 | - | 8,876 | 2.07 | - | 1,645 | 0.38 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1,178 | 0.27 | - | 55,491 | 12.95 | 428,443 | MD |
| Massachusetts | 18 | 681,153 | 68.55 | 18 | 276,691 | 27.84 | - | 32,267 | 3.25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3,583 | 0.36 | - | 404,462 | 40.70 | 993,718 | MA |
| Michigan | 15 | 762,865 | 72.76 | 15 | 233,450 | 22.27 | - | 28,947 | 2.76 | - | 10,480 | 1.00 | - | 9,646 | 0.92 | - | - | - | - | 2,539 | 0.24 | - | 529,415 | 50.50 | 1,048,411 | MI |
| Minnesota | 12 | 519,421 | 70.59 | 12 | 142,994 | 19.43 | - | 56,106 | 7.62 | - | - | - | - | 11,489 | 1.56 | - | - | - | - | 5,828 | 0.79 | - | 376,427 | 51.16 | 735,838 | MN |
| Mississippi | 10 | 11,576 | 14.03 | - | 69,277 | 83.98 | 10 | 1,639 | 1.99 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -57,701 | -69.95 | 82,492 | MS |
| Missouri | 18 | 727,162 | 54.56 | 18 | 574,799 | 43.13 | - | 20,242 | 1.52 | - | 3,291 | 0.25 | - | 5,142 | 0.39 | - | - | - | - | 2,164 | 0.16 | - | 152,363 | 11.43 | 1,332,800 | MO |
| Montana | 4 | 109,430 | 61.13 | 4 | 57,372 | 32.05 | - | - | - | - | 12,204 | 6.82 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 52,058 | 29.08 | 179,006 | MT |
| Nebraska | 8 | 247,498 | 64.66 | 8 | 119,608 | 31.25 | - | 9,600 | 2.51 | - | - | - | - | 5,947 | 1.55 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 127,890 | 33.41 | 382,743 | NE |
| Nevada | 3 | 15,479 | 56.92 | 3 | 9,851 | 36.22 | - | 1,864 | 6.85 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5,628 | 20.70 | 27,194 | NV |
| New Hampshire | 4 | 95,196 | 59.84 | 4 | 62,662 | 39.39 | - | 1,234 | 0.78 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 32,534 | 20.45 | 159,092 | NH |
| New Jersey | 14 | 611,541 | 67.65 | 14 | 256,887 | 28.42 | - | 27,141 | 3.00 | - | 2,200 | 0.24 | - | 4,734 | 0.52 | - | - | - | - | 923 | 0.10 | - | 354,654 | 39.23 | 903,943 | NJ |
| New Mexico | 3 | 57,634 | 54.68 | 3 | 46,668 | 44.27 | - | - | - | - | 1,104 | 1.05 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10,966 | 10.40 | 105,406 | NM |
| New York | 45 | 1,871,167 | 64.56 | 45 | 781,238 | 26.95 | - | 203,201 | 7.01 | - | 18,413 | 0.64 | - | 19,653 | 0.68 | - | - | - | - | 4,841 | 0.17 | - | 1,089,929 | 37.60 | 2,898,513 | NY |
| North Carolina | 12 | 232,848 | 43.22 | - | 305,447 | 56.70 | 12 | 446 | 0.08 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -72,599 | -13.48 | 538,741 | NC |
| North Dakota | 5 | 160,072 | 77.79 | 5 | 37,422 | 18.19 | - | 8,282 | 4.02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 122,650 | 59.60 | 205,776 | ND |
| Ohio | 24 | 1,182,022 | 58.47 | 24 | 780,037 | 38.58 | - | 57,147 | 2.83 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 401,985 | 19.88 | 2,021,653 | OH |
| Oklahoma | 10 | 243,831 | 50.11 | 10 | 217,053 | 44.61 | - | 25,726 | 5.29 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 26,778 | 5.50 | 486,610 | OK |
| Oregon | 5 | 143,592 | 60.20 | 5 | 80,019 | 33.55 | - | 9,801 | 4.11 | - | - | - | - | 3,595 | 1.51 | - | - | - | - | 1,515 | 0.64 | - | 63,573 | 26.65 | 238,522 | OR |
| Pennsylvania | 38 | 1,218,216 | 65.76 | 38 | 503,843 | 27.20 | - | 70,571 | 3.81 | - | 15,704 | 0.85 | - | 42,696 | 2.30 | - | - | - | - | 753 | 0.04 | - | 714,373 | 38.56 | 1,852,616 | PA |
| Rhode Island | 5 | 107,463 | 63.97 | 5 | 55,062 | 32.78 | - | 4,351 | 2.59 | - | - | - | - | 510 | 0.30 | - | - | - | - | 495 | 0.29 | - | 52,401 | 31.19 | 167,981 | RI |
| South Carolina | 9 | 2,610 | 3.91 | - | 64,170 | 96.05 | 9 | 28 | 0.04 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -61,560 | -92.14 | 66,808 | SC |
| South Dakota | 5 | 110,692 | 60.74 | 5 | 35,938 | 19.72 | - | - | - | - | 34,707 | 19.04 | - | 900 | 0.49 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 74,754 | 41.02 | 182,237 | SD |
| Tennessee | 12 | 219,829 | 51.29 | 12 | 206,558 | 48.19 | - | 2,239 | 0.52 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13,271 | 3.10 | 428,626 | TN |
| Texas | 20 | 114,538 | 23.54 | - | 288,767 | 59.34 | 20 | 8,121 | 1.67 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 47,968 | 9.86 | - | - | - | - | -174,229 | -35.80 | 486,641 | TX |
| Utah | 4 | 81,555 | 55.93 | 4 | 56,639 | 38.84 | - | 3,159 | 2.17 | - | 4,475 | 3.07 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 24,916 | 17.09 | 145,828 | UT |
| Vermont | 4 | 68,212 | 75.82 | 4 | 20,919 | 23.25 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 774 | 0.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 47,293 | 52.57 | 89,961 | VT |
| Virginia | 12 | 87,456 | 37.85 | - | 141,670 | 61.32 | 12 | 807 | 0.35 | - | 243 | 0.11 | - | 857 | 0.37 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -54,214 | -23.47 | 231,033 | VA |
| Washington | 7 | 223,137 | 55.96 | 7 | 84,298 | 21.14 | - | 8,913 | 2.24 | - | 77,246 | 19.37 | - | 3,800 | 0.95 | - | - | - | - | 1,321 | 0.33 | - | 138,839 | 34.82 | 398,715 | WA |
| West Virginia | 8 | 282,007 | 55.30 | 8 | 220,789 | 43.30 | - | 5,618 | 1.10 | - | - | - | - | 1,528 | 0.30 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 61,218 | 12.00 | 509,942 | WV |
| Wisconsin | 13 | 498,576 | 71.10 | 13 | 113,422 | 16.17 | - | 80,635 | 11.50 | - | - | - | - | 8,647 | 1.23 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 385,154 | 54.92 | 701,280 | WI |
| Wyoming | 3 | 35,091 | 64.15 | 3 | 17,429 | 31.86 | - | - | - | - | 2,180 | 3.99 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 17,662 | 32.29 | 54,700 | WY |
| TOTALS: | 531 | 16,144,093 | 60.32 | 404 | 9,139,661 | 34.15 | 127 | 913,693 | 3.41 | - | 265,398 | 0.99 | - | 188,787 | 0.71 | - | 47,968 | 0.18 | - | 31,084 | 0.12 | - | 7,004,432 | 26.17 | 26,765,180 | US |
States that flipped from Democratic to Republican
[edit]- Arizona
- California
- Colorado
- Idaho
- Kansas
- Maryland
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Mexico
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Tennessee
- Utah
- Washington
- Wyoming
Close states
[edit]Margin of victory less than 1% (13 electoral votes):
- Kentucky, 0.44% (4,017 votes)
Margin of victory less than 5% (12 electoral votes):
- Tennessee, 3.10% (13,271 votes)
Margin of victory between 5% and 10% (10 electoral votes):
- Oklahoma, 5.50% (26,778 votes)
Tipping point state:
- Rhode Island, 31.19% (52,401 votes)
Statistics
[edit]Counties with Highest Percentage of the Vote (Republican)
- McIntosh County, North Dakota 95.76%
- Leslie County, Kentucky 94.22%
- Sevier County, Tennessee 93.60%
- Sheridan County, North Dakota 92.98%
- Billings County, North Dakota 92.81%
Counties with Highest Percentage of the Vote (Democratic)
- Chester County, South Carolina 100.00%
- Edgefield County, South Carolina 100.00%
- Clarendon County, South Carolina 100.00%
- Bamberg County, South Carolina 100.00%
- Hampton County, South Carolina 100.00%
Counties with Highest Percentage of the Vote (American)
- Austin County, Texas 61.72%
- Fort Bend County, Texas 59.35%
- Lavaca County, Texas 57.76%
- Fayette County, Texas 55.12%
- Washington County, Texas 54.04%
See also
[edit]- History of the United States (1918–1945)
- History of the United States Democratic Party
- History of the United States Republican Party
- Inauguration of Warren G. Harding
- 1920 United States House of Representatives elections
- 1920 United States Senate elections
References
[edit]- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ Gunderman, Richard (October 30, 2020). "100 years ago, the first commercial radio broadcast announced the results of the 1920 election – politics would never be the same". The Conversation. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ^ Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Elections (compare national data by year)
- ^ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Status Of Republican Delegates". The Chicago Tribune. May 23, 1920. Retrieved November 17, 2022.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "Democratic Convention Situation". The Chicago Tribune. May 23, 1920. Retrieved November 17, 2022.
- ^ "1912". President Elect. Archived from the original on December 30, 2008. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
- ^ a b c Haynes, Fred (1924). Social Politics in the United States. The Riverside Press Cambridge.
- ^ A Political Guide for the Workers. Socialist Party of America. 1920. p. 8.
- ^ Laidler, Henry W. (June 1, 1920). The Socialist Convention. The Socialist Review.
- ^ Coleman, McAlister (1930). Eugene V. Debs: A Man Unafraid. Greenberg Publisher.
- ^ Ray, P. Orman (1924). An Introduction to Political Parties and Practical Politics. Charles Scribner's Sons.
- ^ "Want to nominate Prohibition Ticket" (PDF). The New York Times. Lincoln, Nebraska. July 19, 1920. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 28, 2022.
- ^ "Drys in Stampede Nominate Bryan; Vote him, willing or not, their Party Standard Bearer in Coming Campaign. - Woman Chairman Leads – Delegates, Impatient at Talk of Refusal, Parade and Should for Convention Nominee". The New York Times. July 22, 1920.
- ^ "Bryan rejects 'dry' nominate; Wires from Montana when he returns from fishing trip and hears of it. Will remain in his party although not sure how he will vote – Drys name Ohioan for President". The New York Times. July 23, 1920.
- ^ Havel, James T.; The Elections, 1789–1992, p. 106 ISBN 0028646231
- ^ Richardson, Darcy G.; Others: "Fighting Bob" La Follette and the Progressive Movement: Third-Party Politics in the 1920s, p. 76-79 ISBN 0595481264
- ^ Richardson; Others, p. 81
- ^ a b c Scammon, Richard M. (compiler); America at the Polls: A Handbook of Presidential Election Statistics 1920–1964 pp. 426-430, 456 ISBN 0405077114
- ^ "The enemy within; the inside story of German sabotage in America : Landau, Henry, b. 1892 : Free Download & Streaming : Internet Archive". Archive.org. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
- ^ "Essay by M. Plowman (2009) on the complexities of the "Indo-Irish-German" conspiracy in the USA during the war" (PDF). Lse.ac.uk. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved August 18, 2016.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "American Rhetoric: Woodrow Wilson -- "Final Address in Support of the League of Nations"". www.americanrhetoric.com. Retrieved November 16, 2022.
- ^ "Dáil Éireann – 29/Jun/1920 MINISTERIAL MOTIONS. - PRESIDENTIAL ELECTION CAMPAIGN IN U.S.A". Oireachtasdebates.oireachtas.ie. February 24, 2015. Retrieved August 18, 2016.
- ^ Sinclair, p. 168
- ^ Sinclair, p. 162
- ^ Sinclair, p. 163
- ^ The Presidential Vote, 1896–1932 – Google Books. Stanford University Press. 1934. ISBN 978-0-8047-1696-3. Retrieved August 12, 2014.
- ^ The Presidential Vote, 1896–1932, Edgar E. Robinson, p. 19
- ^ a b Murphy, Paul (1974). Political Parties In American History, Volume 3, 1890-present. G. P. Putnam's Sons.
- ^ The Presidential Vote, 1896–1932, Edgar E. Robinson, pg. 21
- ^ Sherman 1973, p. 263.
- ^ "1920 Presidential General Election Data – National". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 18, 2013.
Works cited
[edit]- Sherman, Richard (1973). The Republican Party and Black America From McKinley to Hoover 1896-1933. University of Virginia Press. ISBN 0813904676.
Further reading
[edit]- Bagby, Wesley M. (1962). The Road to Normalcy: The Presidential Campaign and Election of 1920. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press.
- Boller, Paul F. Jr. (2004). Presidential Campaigns: From George Washington to George W. Bush. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 212–217. ISBN 0-19-516716-3.
- Brake, Robert J. "The porch and the stump: Campaign strategies in the 1920 presidential election." Quarterly Journal of Speech 55.3 (1969): 256–267.
- Burchell, R. A. "Did the Irish and German Voters Desert the Democrats in 1920? A Tentative Statistical Answer" Journal of American Studies 5#2 (1972) pp. 153–164 online
- Daniel, Douglass K. "Ohio Newspapers and the 'Whispering Campaign' of the 1920 Presidential Election." Journalism History 27.4 (2002): 156–164.
- Cooper, John Milton (2001). Breaking the Heart of the World: Woodrow Wilson and the Fight for the League of Nations. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-80786-7.
- Duff, John B. (1970). "German-Americans and the Peace, 1918–1920". American Jewish Historical Quarterly. 59 (4): 424–459. ISSN 0002-9068.
- Duff, John B. (1968). "The Versailles Treaty and the Irish-Americans". Journal of American History. 55 (3). Organization of American Historians: 582–598. doi:10.2307/1891015. ISSN 0021-8723. JSTOR 1891015.
- McCoy, Donald R. (1971). "The Election of 1920". In Schlesinger, Arthur M. Jr.; Israel, Fred L. (eds.). History of American Presidential Elections. New York: Chelsea House. ISBN 0-07-079786-2.
- Morello, John A. (2001). Selling the President, 1920: Albert D. Lasker, Advertising, and the Election of Warren G. Harding. Westport, CT: Praeger. ISBN 0-275-97030-2.
- Pietrusza, David (2007). 1920: The Year of the Six Presidents. New York: Carroll & Graf. ISBN 978-0-7867-1622-7.
- Frederick, Richard G. "The Front Porch Campaign and the Election of Harding." in A Companion to Warren G. Harding, Calvin Coolidge, and Herbert Hoover (2014): 94–111.
- Sinclair, Andrew (1965). The Available Man: The Life behind the Masks of Warren Gamaliel Harding. New York: Macmillan.
- Walters, Ryan S. The Jazz Age President: Defending Warren G. Harding (2022) excerpt also online review
Primary sources
[edit]- "The Presidential Election of 1920". American Leaders Speak: Recordings from World War I and the 1920 Election. Library of Congress. Retrieved November 16, 2002.
- Chester, Edward W A guide to political platforms (1977) online
- Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. National party platforms, 1840–1964 (1965) online 1840–1956
- Eugene V. Debs, A Word to the Workers! New York: New York Call, n.d. [1920]. —Socialist campaign leaflet.
External links
[edit]- Presidential Election of 1920: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- 1920 popular vote by counties
- 1920 Election Links Archived December 11, 2018, at the Wayback Machine