Hamburg-Mitte
Hamburg-Mitte | |
|---|---|
 Hamburg center Binnenhafen | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Hamburg |
| City | Hamburg |
| Subdivisions | 22 quarters |
| Area | |
• Total | 107.1 km2 (41.4 sq mi) |
| Population (31.12.2006) | |
• Total | 233,144 |
| • Density | 2,200/km2 (5,600/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Dialling codes | 040 |
| Vehicle registration | HH |
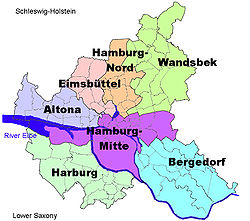
Hamburg-Mitte (Rough translation: Hamburg center) located in the Free and Hanseatic city of Hamburg, Germany is one of the seven boroughs of Hamburg, covering mostly the urban center of the city of Hamburg. The quarters Hamburg-Altstadt (Rough translation: Hamburg old city) and Neustadt (Rough translation: new city) are the historical origin of Hamburg. In 2006 the population was 233,144.
History

In 1937 several settlements (e.g. Finkenwerder), villages and rural areas were passed into Hamburg enforced by the Greater Hamburg Act.
On March 1, 2008 due to a law of Hamburg,[1] the quarter Wilhelmsburg was transferred from the borough Harburg. The neighborhood HafenCity was formed from parts of the quarters Klostertor, Altstadt and Rothenburgsort. The other part of Klostertor was transferred to Hammerbrook. From small parts of the borough Hamburg-Mitte (And Altona and Eimsbüttel) the neighborhood Sternschanze was created as a quarter in the borough Altona.
Geography
The borough severs Hamburg from the east to the west. In 2006, according to the statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg-Mitte has a total area of 107.1 square kilometres (41 sq mi).
It consists of the quarters Billbrook, Billstedt, Borgfelde, Finkenwerder, HafenCity, Hamburg-Altstadt, Hamm-Nord, Hamm-Mitte, Hamm-Süd, Hammerbrook, Horn, Kleiner Grasbrook, Neustadt, Neuwerk, Rothenburgsort, St. Georg, St. Pauli, Steinwerder, Veddel, Waltershof and Wilhelmsburg.
Demographics
In 2006 233,144 people lived in the borough. The population density was 2,177/km2 (5,638/sq mi). 14.9% were children under the age of 18, and 15.6% were 65 years of age or older. 43% belong to ethnic minorities.[2] 17,550 people were registered as unemployed and 72,608 were employees subject to social insurance contributions.[3]
In 1999 there were 126,753 households, out of which 17.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them and 52.4% of all households were made up of single occupants. The average household size was 1.83.[4]
Population by year[3]
| 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 |
| 232,467 | 235,759 | 242,434 | 249,156 | 250,585 | 252,695 | 251,965 | 248,802 | 246,374 | 242,029 | 237,648 | 230,542 | 228,349 |
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 |
| 228,060 | 227,199 | 227,915 | 228,117 | 227,557 | 230,680 | 233,114 |
In 2006 there were 71,559 criminal offences in borough (307 crimes per 1000 people).[5]
Diet of the borough
Simultaneously with elections to the state parliament (Bürgerschaft), the Bezirksversammlung is elected as representatives of the citizens. It consists of 53 representatives.
Elections
Elections were held in Hamburg on 24 February 2008. The four parties having more than 5 percent in recent polls (minimum to qualify) are the social-democratic SPD, the conservative CDU, the ecologist Green Party (GAL) and the left-wing Die Linke. The liberal Free Democratic Party (FDP) has 2 directly elected representatives.[6]

| Party | Percent | Seats |
|---|---|---|
| SPD | 37.2 | 17 |
| CDU | 31.6 | 21 |
| GAL | 13.2 | 7 |
| Die Linke | 10.2 | 6 |
| FDP | 4.2 | 2 |
Education
The borough has 31 elementary schools and 31 secondary schools.[7]
Culture

Recreation
Planten un Blomen (plants and flowers) is a park located in the quarter St. Pauli and Neustadt. Located in the quarter Billstedt is the lake Öjendorfer See.
Economy
The facilities of the port of Hamburg are located mostly in Hamburg-Mitte in the quarters of Kleiner Grasbrook, Steinwerder, Veddel, Waltershof and Wilhelmsburg.
Infrastructure
The main local office (Bezirksamt Hamburg-Mitte) is located on Klosterwall Street. It has 4 local offices or "Customer Centres." These are Customer Centre Hamburg-Mitte, Customer Centre Billstedt, Customer Centre St. Pauli, and Customer Centre Wilhelmsburg. The offices are responsible, among other things, for the application for a residence permit for purposes of study after entering the country.
Health systems
There were 125 day-care centers for children and 536 physicians in private practice and 72 pharmacies.[7] The Asklepios Klinik St. Georg located in the quarter St. Georg, is the main hospital in Hamburg-Mitte.
Transportation
The borough is serviced by the rapid transit system of the city train and the underground railway with several stations. The central station Hamburg Hauptbahnhof is also for long-distance passenger trains for the German railway company.
According to the Department of Motor Vehicles (Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt), in the Hamburg-Mitte borough 66,831 private cars were registered (290 cars/1000 people).[7] There were 2,432 traffic accidents in total, including 1,905 traffic accidents resulting in injuries.[8]
Notes
- ^ Act of the areal organisation
- ^ http://www.statistik-nord.de/uploads/tx_standocuments/SI_SPEZIAL_V_2010_01.pdf
- ^ a b Residents registration office, source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (31.12.2006)
- ^ Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (1999)
- ^ State Investigation Bureaux (Landeskriminalamt), source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
- ^ Final election result, source: statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2008)
- ^ a b c Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (31.12.2006)
- ^ Traffic accident statistic, statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
References
- Statistical office Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein, official website Template:De icon
- Act of the areal organisation, July 6, 2006 Gesetz über die räumliche Gliederung der Freien und Hansestadt Hamburg (RäumGiG) Template:De icon