Georgia State Route 8
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
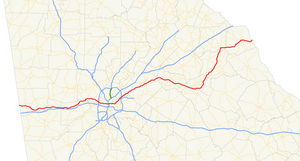 | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by GDOT | ||||
| Length | 186 mi[1] (299 km) | |||
| Existed | 1919[2]–present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| West end | ||||
| East end | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Country | United States | |||
| State | Georgia | |||
| Counties | Haralson, Carroll, Douglas, Cobb, Fulton, DeKalb, Gwinnett, Barrow, Clarke, Oconee, Madison, Franklin, Hart | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
| ||||
State Route 8 (SR 8) is a 183-mile-long (295 km) state highway that travels west-to-east through portions of Haralson, Carroll, Douglas, Cobb, Fulton, DeKalb, Gwinnett, Barrow, Clarke, Oconee, Madison, Franklin, and Hart counties, bisecting the northern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. The highway travels from its western terminus at US 78 and SR 4 at the Alabama state line west of Tallapoosa to its eastern terminus at US 29 at the South Carolina state line at the south end of Lake Hartwell. This was also the proposed State Route 808 (SR 808).[citation needed] The highway is concurrent with either US 29 or US 78 for its entire length.
Route description
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2013) |
SR 8 starts at the Alabama state line west of Tallapoosa in Haralson County, and closely parallels I-20 from there into Atlanta. SR 8 heads through Bremen and crosses through Carroll County and Villa Rica and on through Douglasville in Douglas County. The highway continues through Austell in Cobb County before it reaches the City of Atlanta and Fulton County, crossing the Downtown Connector on its way into Decatur in DeKalb County.
In Decatur, SR 8 turns northeast, crossing I-285 in Tucker, and paralleling I-85 through Lilburn and Lawrenceville in Gwinnett County to Auburn in Barrow County, where the highway turns southeast and heads into Winder. Continuing southeast, SR 8 makes a southern half-circle around Athens in Clarke County, just briefly touching Oconee County, before turning sharply northeast and heading through Danielsville in Madison County to Franklin Springs in Franklin County. There, the highway turns east, travels through Royston, and heads to its eastern terminus after heading through Hartwell.
The following portions of SR 8 are included as part of the National Highway System, a system of roadways important to the nation's economy, defense, and mobility:
- A small portion in Douglasville[3]
- From the US 278/SR 6 intersection in Lithia Springs, through Atlanta, to an intersection with the southern terminus of Jimmy Carter Boulevard and the northern terminus of Mountain Industrial Boulevard in Tucker[3]
- From the west end of the SR 11/SR 53 concurrency in Lawrenceville to the SR 72 intersection in the northeast part of Athens[4][5]
History
[edit]1920s
[edit]SR 8 was established at least as early as 1919 on its current path, except for the Lawrenceville–Athens segment going through Winder, and the segment from Hartwell to the South Carolina state line traveling to the east-northeast. At this time, SR 34 was established from Carrollton to Villa Rica.[2] By the end of September 1921, SR 16 was established from the Alabama state line to Carrollton.[2][6] By October 1926, US 78 was designated on the path of SR 8 from the Alabama state line to Decatur and a segment west-southwest of Athens. US 29 was designated on SR 8 from Atlanta to the South Carolina state line. SR 16 from Alabama and Carrollton and SR 34 from Carrollton to Villa Rica were redesignated as a southern branch of SR 8. An unnumbered road was established from US 29/SR 8 in Hartwell east-southeast to the South Carolina state line, at a point just south-southeast of the current eastern terminus of SR 8. Four segments had a "completed hard surface": from northwest of Atlanta to Decatur, the eastern two-thirds of the Gwinnett County portion of the Decatur–Lawrenceville segment, from northwest of Watkinsville to the northeast part of Athens, and the eastern part of the Royston–Hartwell segment.[6][7] By October 1929, US 19 was designated on the Atlanta–Lawrenceville segment. The Decatur–Lawrenceville segment had a completed hard surface.[7][8]
1930s
[edit]By the middle of 1930, US 78 was split into two divided U.S. Routes: US 78N was designated on the original path of SR 8 from Alabama to Villa Rica, and US 78S was designated on the southern branch of SR 8.[8][9] Later that year, the Austell–Atlanta segment, as well as the entire Clarke County segment, had a completed hard surface.[9][10] By the beginning of 1932, four segments were also completed: the entire Carrollton–Villa Rica segment (except for its eastern end), from west-southwest of Douglasville to Austell, the Lawrenceville–Athens segment, and from the Madison–Franklin county line to the South Carolina state line.[10][11] In February 1932, US 19 was shifted off of SR 8 to the north; US 23 was designated on the Atlanta–Lawrenceville segment instead. The eastern part of the Carrollton–Villa Rica segment of US 78S and the southern branch of SR 8 had a completed hard surface.[12][13] Between May and August, the Villa Rica–Douglasville segment was completed.[14][15] In August, two segments were completed: the Athens–Danielsville segment and a segment just south of the Madison–Franklin county line.[15][16] Between November 1932 and May 1933, two segments were completed: the Bremen–Villa Rica and Danielsville–Royston segments.[17][18] In May, the entire Alabama–Bremen segment (except for the western end) was also completed.[18][19] The next month, the western terminus was also completed.[19][20] The next year, another southern branch of SR 8 was established from Hartwell to the South Carolina state line on the previously unnumbered road in the area. The western terminus of the original southern branch had a completed hard surface.[21][22] About two years later, the segment of the southern branch from the Alabama state line to Carrollton was completed.[23][24] In 1938, US 78S was redesignated as US 78 Alt., and US 78N was redesignated as the mainline US 78.[25][26] By the middle of 1939, US 23 was shifted off of SR 8, to the north.[26][27]
1940s and 1950s
[edit]In 1942, the southern branch of SR 8 from Hartwell to the South Carolina state line was decommissioned.[28][29] Between November 1946 and February 1948, the southern branch of SR 8 from Alabama to Villa Rica was redesignated as SR 8 Alt. US 29 in the Decatur area was split into two paths: the original was a direct path from Atlanta to Lawrenceville; the northern branch bypassed the city with SR 8 Spur; both branches were designated US 29.[30][31] In 1952, US 78 Alt., as well as the northern branch of US 29, was decommissioned.[32][33] The next year, the northern branch of US 29 was reinstated.[33][34] Between September 1953 and June 1954, the original branch of US 29 in the Decatur area was redesignated as US 29 Bus.[34][35] By June 1955, US 278 was designated on SR 8 from Austell to southeast of Avondale Estates.[35][36]
1960s
[edit]Between the beginning of 1956 and the beginning of 1961, US 29's path between Hartwell to the South Carolina state line was shifted southeast, off of SR 8 and onto SR 181; the formation of Lake Hartwell truncated SR 8.[37][38] Between June 1960 and June 1963, a bypass of the northern part of Athens, designated as SR 350, was established and paved as a divided highway from US 129/SR 15 in the north-central part of the city to US 29/SR 8 in the northeastern part.[39][40] By the beginning of 1966, SR 8 was routed on US 29 Bus. in the Decatur area. SR 350 was upgraded to a freeway. It was under construction on a path southwest to US 29/US 78/SR 8/SR 10 in the western part of the city. US 29 was shifted northward, onto SR 350, from the US 29 Temp./US 129/US 441 Temp./SR 15 interchange to the Madison Avenue interchange. US 441 Temp. was designated on SR 350 from the US 29 Temp./US 129/US 441 Temp./SR 15 interchange to the US 441/SR 15 Alt. interchange. US 29/US 78/SR 8/SR 10 entered downtown Athens on Broad Street. At Milledge Avenue, US 29 temporarily ended, and US 29 Temp./US 129/US 441 Temp./SR 15 traveled to the north-northwest. At Pulaski Street, SR 8 split off US 78/SR 10 to the north-northwest. At Dougherty Street, it intersected the southern terminus of SR 15 Conn. and traveled east-northeast to SR 15 Alt. (Thomas Street). SR 8/SR 15 Alt. traveled concurrently to the north-northwest and curved to the north-northeast on Madison Avenue. SR 15 Alt. split off at Hobson Avenue, and SR 8 continued to its interchange with US 29/SR 350.[40][41] In 1966, SR 350 was decommissioned. US 29/SR 8 was shifted northwest, onto the western part of the freeway. The former path through downtown, on US 78/SR 10, was redesignated as SR 8 Bus. US 29 Temp. was decommissioned. The freeway was extended eastward one exit. SR 8 was extended on this freeway to the new exit and resumed its northeastern path. SR 106 was extended on US 29 to the Athens freeway, at the US 29/SR 8/SR 8 Bus. interchange.[41][42] The next year, US 29 and SR 72 were both shifted onto the new path of SR 8 in the northeastern part of Athens to the freeway.[42][43]
1970s and 1980s
[edit]In 1976, SR 72 was proposed to be extended south-southeast and then south-southwest to US 78/SR 10 in the southeast part of Athens and then southwest and west-southwest to US 129/US 441/SR 15 in the southern part of the city.[44][45] The next year, SR 8 east-northeast of Hartwell was shifted southeast, onto US 29/SR 181. Its former path was redesignated as SR 8 Spur.[45][46] In 1980, the freeway in Athens was completed on the eastern, southeastern, and southern parts of the city, with US 129/US 441/SR 15 designated on these segments.[47][48] The next year, the eastern part of the freeway, north of US 78/SR 10, was downgraded to a divided highway.[48][49] In 1983, the southwestern part of the freeway, designated as SR 732, was proposed to connect both ends of it.[50][51] In 1985, US 29 Bus. in the Decatur area was decommissioned, with SR 8 shifted northwest, onto the US 29 mainline. US 441 Temp. in Athens was decommissioned. SR 72's western terminus was truncated to its current location in the far northeastern part of Athens.[51][52] In 1987, the Athens freeway was completed, with SR 10 on the southern part; its former path through downtown was redesignated as SR 10 Bus. SR 72 was re-extended to the freeway's northeastern interchange.[53][54] The next year, SR 10 was shifted off of the Athens freeway through downtown, replacing SR 10 Bus. The entire freeway was designated as SR 10 Loop. US 78 was shifted from downtown to the southern part of the freeway; its former path became US 78 Bus.[54][55] In 1989, a southern bypass of the Dacula–Athens area, designated as SR 817, was proposed from US 29/SR 8/SR 316 west-southwest of Dacula to the southwest corner of the Athens freeway.[55][56]
1990s and 2000s
[edit]In 1990, SR 181's western terminus was truncated to its current location, an intersection with US 29/SR 8 east-southeast of Hartwell, and off of US 29/SR 8.[56][57] The next year, SR 817's path from west-southwest of Dacula to SR 11 north of Bethlehem was completed as an eastern extension of SR 316. In the Athens area, the paths of SR 15 and SR 15 Alt. were swapped.[57][58] In 1993, SR 817's path from north of Bethlehem to US 78/SR 10 southeast of Bogart was also completed as an eastern extension of SR 316, with US 29 shifted onto the entire length. SR 8 was shifted onto US 29/SR 316 from southeast of Russell to southeast of Bogart.[59][60] In 1995, US 29/SR 8 was shifted to southern part of the Athens freeway. SR 72 was again truncated to its current western terminus.[61][62] The next year, SR 817's path in the southwestern part of Athens was completed as an eastern extension of SR 316, with US 29/US 78/SR 8 concurrent with it.[62][63] In 2001, US 129/US 441/SR 15 was shifted onto the freeway, in the south-central part of its path, for a concurrency with the freeway for less than 0.5 miles (0.80 km). They split off onto Macon Highway.[64][65] The next year, US 129/US 441/SR 15 was shifted off of Macon Highway and onto the Athens freeway.[65][66] In 2004, the unsigned state highway designation SR 422 was applied to the freeway.[67][68]
Major intersections
[edit]This section is missing mileposts for junctions. |
| County | Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haralson | | 0.0 | 0.0 | Western end of US 78 concurrency; western terminus; Alabama state line | |
| | 1.3 | 2.1 | Bently Bridge over Tallapoosa River | ||
| Tallapoosa | 4.0 | 6.4 | West end of SR 100 concurrency | ||
| 4.1 | 6.6 | East end of SR 100 concurrency | |||
| 5.0 | 8.0 | Northern terminus of SR 100 Spur | |||
| Bremen | 12.3 | 19.8 | |||
| 13.4 | 21.6 | ||||
| Carroll | Temple | 20.0 | 32.2 | Western terminus of SR 274 | |
| 20.4 | 32.8 | ||||
| 20.7 | 33.3 | Eastern terminus of SR 274 | |||
| Villa Rica | 25.7 | 41.4 | Western end of SR 61 concurrency; former US 78S west, US 78 Alt. west, and SR 8 Alt. west | ||
| 27.0 | 43.5 | Eastern end of SR 61 concurrency | |||
| Douglas | 28.2 | 45.4 | Northern terminus of SR 8 Conn. | ||
| Winston | |||||
| Douglasville | 35.8 | 57.6 | Western end of SR 5 concurrency | ||
| 38.0 | 61.2 | Western end of SR 92 concurrency | |||
| 38.1 | 61.3 | Eastern end of SR 92 concurrency | |||
| Lithia Springs | 44.9 | 72.3 | Western end of US 278 concurrency | ||
| Cobb | Austell | 46.9 | 75.5 | Dr. J.A. Griffith Bridge over Sweetwater Creek | |
| 47.2 | 76.0 | Eastern end of SR 5 concurrency; interchange | |||
| Mableton | 49.6 | 79.8 | Western terminus of SR 139 | ||
| 53.1 | 85.5 | Coogan Ray Bleodow Memorial Bridge over Nickajack Creek | |||
| Fulton | Atlanta | 54.9 | 88.4 | Northern terminus of SR 70 | |
| 55.1 | 88.7 | I-285 exit 12 | |||
| 56.5 | 90.9 | No left turn westbound | |||
| 60.4 | 97.2 | Western end of US 19/US 41/SR 3 concurrency | |||
| 60.7 | 97.7 | Eastern end of US 19/US 41/SR 3 concurrency; western end of US 29 concurrency | |||
| I-75 exit 249D | |||||
| 63.4 | 102.0 | Western end of SR 10 concurrency | |||
| Fulton–DeKalb county line | 64.0 | 103.0 | Western end of US 23 concurrency | ||
| DeKalb | Druid Hills | 65.7 | 105.7 | Eastern end of US 278 and SR 10 concurrencies | |
| Decatur | 67.2 | 108.1 | Eastern end of US 23 concurrency | ||
| Scottdale–North Decatur line | 69.4 | 111.7 | Eastern end of US 78 concurrency; eastbound exit and westbound entrance; western terminus of SR 410; interchange | ||
| Tucker | 71.4 | 114.9 | I-285 exit 38 | ||
| 74.6 | 120.1 | Hugh Howell Road | Former segment of SR 236 that was removed in 2024 | ||
| 74.9 | 120.5 | Eastern terminus of SR 236 | |||
| Gwinnett | Lilburn | 81.2 | 130.7 | Eastern terminus of SR 378 | |
| Lawrenceville | 89.8 | 144.5 | Eastern terminus of SR 120 | ||
| 90.1 | 145.0 | Western end of SR 20 concurrency | |||
| 90.3 | 145.3 | Eastern end of SR 20 concurrency; western end of SR 124 concurrency | |||
| 90.7 | 146.0 | Eastern end of SR 124 concurrency | |||
| | 94.3 | 151.8 | Eastern end of US 29 concurrency; western end of US 29 Bus. concurrency | ||
| Barrow | Auburn | 99.3 | 159.8 | Eastern terminus of SR 324 | |
| Winder | 107 | 172 | Western end of SR 11 and SR 53 concurrencies | ||
| Russell | 108 | 174 | Eastern end of SR 11 concurrency | ||
| | Eastern end of US 29 Bus. and SR 53 concurrencies; western end of US 29 and SR 316 concurrencies | ||||
| Statham | Southern terminus of SR 211 | ||||
| Oconee | | Western end of US 78 concurrency; western terminus of US 78 Bus. | |||
| | Eastern end of SR 316 concurrency; western end of SR 10 Loop concurrency; eastern terminus of SR 316; southern terminus of Epps Bridge Parkway | ||||
| Clarke | Athens | Western end of US 129/US 441/SR 15 concurrency | |||
| Southern terminus of SR 15 Alt. | |||||
| Eastern end of US 78 concurrency; eastern terminus of US 78 Bus. | |||||
| 135 | 217 | Eastern end of US 129/US 441/SR 15 and SR 10 Loop concurrencies | |||
| 136 | 219 | Western terminus of SR 72 | |||
| Madison | | 139 | 224 | Southern terminus of SR 106 | |
| Danielsville | 149 | 240 | Former southern terminus of SR 8 Conn.; former SR 98 Conn. | ||
| | 150 | 240 | Southern terminus of SR 281 | ||
| | 152 | 245 | Northern terminus of SR 191 | ||
| | 156 | 251 | Western end of SR 174 concurrency | ||
| Franklin | | 157 | 253 | Eastern end of SR 174 concurrency | |
| Franklin Springs | 160 | 260 | Eastern terminus of SR 145 | ||
| 160 | 260 | Southern terminus of SR 327 | |||
| Royston | 163 | 262 | |||
| Hart | 164 | 264 | |||
| Hartwell | 175 | 282 | Western end of SR 51/SR 77 concurrency | ||
| 175 | 282 | Eastern end of SR 51 concurrency | |||
| 176 | 283 | Northern terminus of SR 172 | |||
| 176 | 283 | Eastern end of SR 77 concurrency | |||
| Old Hwy. 29 north | Former US 29 north/SR 8 east; former SR 8 Spur north | ||||
| | 182 | 293 | Northern terminus of SR 181 | ||
| Savannah River | 183 | 295 | Eastern end of US 29 concurrency; eastern terminus of SR 8; South Carolina state line | ||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
Special routes
[edit]Carroll County alternate route
[edit]| Location | Carroll County |
|---|---|
| Existed | 1948[30][31]–1954[34][35] |
State Route 8 Alternate (SR 8 Alt.) was an alternate route of SR 8 that existed completely within Carroll County. The roadway that would eventually become SR 8 Alt. was established at least as early as 1919 as SR 34 from Carrollton to Villa Rica.[2] By the end of September 1921, SR 16 was established from the Alabama state line to Carrollton.[2][6] By October 1926, SR 16 from Alabama to Carrollton and SR 34 from Carrollton to Villa Rica were redesignated as a southern branch of SR 8.[6][7] By the middle of 1930, US 78 was split into two Divided U.S. Routes: US 78S was designated on the southern branch of SR 8.[8][9] By the beginning of 1932, the entire Carrollton–Villa Rica segment (except for its eastern end) had a "completed hard surface".[10][11] In February 1932, the eastern part of the Carrollton–Villa Rica segment of US 78S and the southern branch of SR 8 also had a completed hard surface.[12][13] In 1934, the western terminus was completed.[21][22] About two years later, from the Alabama state line to Carrollton was completed.[23][24] In 1938, US 78S was redesignated as US 78 Alt.[25][26] Between November 1946 and February 1948, the southern branch of SR 8 from Alabama to Villa Rica was redesignated as SR 8 Alt.[30][31] In 1952, US 78 Alt. was decommissioned.[32][33] Between September 1953 and June 1954, SR 8 Alt. was decommissioned[34][35]
The entire route was in Carroll County.
| Location | mi | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Western terminus of SR 8 Alt. at the Alabama state line; former US 78S west/US 78 Alt. west | ||||
| Bowdon | |||||
| Carrollton | West end of US 27 Alt./SR 16 concurrency | ||||
| East end of US 27 Alt./SR 16 concurrency | |||||
| | Western terminus of SR 166 | ||||
| Villa Rica | Eastern terminus of SR 8 Alt.; southern terminus of SR 61 | ||||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
Villa Rica connector route
[edit]| Location | Villa Rica |
|---|---|
| Length | 0.2 mi[69] (320 m) |
| Existed | 2008[70][71]–present |
State Route 8 Connector (SR 8 Conn.) is a 0.2-mile-long (0.32 km) connector route for SR 8 that exists entirely within the city limits of Villa Rica. It is known as Liberty Road for its entire length. It begins at an interchange with Interstate 20 (I-20) in the eastern part of the city. Here, Liberty Road continues to the south-southeast. It travels to the north-northeast and curves to a nearly due-north direction. Almost immediately, it intersects the southern terminus of Mirror Lake Boulevard. Here, the connector turns right. It travels to the east-northeast and curves to the north-northwest. It then meets its northern terminus, an intersection with US 78/SR 8 (Bankhead Highway).[69] Between the beginning of 1995 and the beginning of 2009, SR 8 Conn. was established from I-20 to US 78/SR 8, at the location of the current Colonel R. H. Burson Bridge.[70][71] By 2013, the northern terminus of the connector route was shifted eastward on a curve.[71][72]
The entire route is in Villa Rica, Douglas County.
| mi[69] | km | Destinations | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.0 | Southern terminus; I-20 exit 26 | |||
| 0.2 | 0.32 | Northern terminus | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
Decatur spur route
[edit]| Location | Decatur |
|---|---|
| Existed | 1946[73][30]–1954[34][35] |
State Route 8 Spur (SR 8 Spur) was a short-lived spur route of SR 8 that existed almost entirely within the city limits of Decatur. Between the beginning of 1945 and November 1946, it was established on a northern branch of US 29 (Scott Boulevard) between two intersections with US 29/SR 8 west-southwest of the city and north-northeast of it.[73][30] In 1952, the northern branch of US 29 was decommissioned.[32][33] The next year, this branch route was reinstated.[33][34] Between September 1953 and June 1954, SR 8 Spur was decommissioned.[34][35]
The entire route was in DeKalb County.
| Location | mi | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Western terminus of SR 8 Spur; southern terminus of northern branch of US 29; south end of US 29 concurrency | ||||
| | Eastern terminus of SR 8 Spur; northern terminus of northern branch of US 29; north end of US 29 concurrency | ||||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
Athens business loop
[edit]| Location | Athens |
|---|---|
| Existed | 1966[41][42]–1978[46][74] |
State Route 8 Business (SR 8 Bus.) was a business route of SR 8 that existed entirely within the city limits of Athens. It traveled along the route of what is now US 78 Bus./SR 10.
Between 1963 and 1966, a freeway around the northern side of Athens (present-day SR 10 Loop) was partially designated as SR 350. At this time, US 29, US 78, SR 8, and SR 10 traveled on what is now US 78 Bus. At Milledge Avenue, US 29 temporarily ended. at this intersection, US 29 Temp. turned off onto US 129/US 441 Temp./SR 15. US 78, SR 8, and SR 10 continued to the northeast. At Lumpkin Street, SR 15 Alt. joined the concurrency. At Thomas Street, SR 8 and SR 15 Alt. turned left and curved to the northeast onto Madison Avenue. At Hobson Avenue, SR 15 Alt. turned off, and SR 8 continued to the northeast to the interchange with US 29 and SR 350. There, SR 8 rejoined US 29.[40][41] In 1966, SR 350 was completed. It was redesignated as part of US 29 and SR 8 and was extended to the east for one exit. At this time, SR 8's former path through downtown Athens was redesignated as SR 8 Bus.[41][42] In 1978, SR 8 Bus. was decommissioned.[46][74]
The entire route was in Athens, Clarke County.
| mi | km | Destinations | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western terminus; west end of US 78/SR 10 concurrency; interchange | |||||
| East end of US 78/SR 10 concurrency | |||||
| Southern terminus of SR 15 Conn. | |||||
| South end of SR 15 Alt. concurrency | |||||
| North end of SR 15 Alt. concurrency | |||||
| Eastern terminus of SR 8 Bus.; southern terminus of SR 106; interchange | |||||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
Danielsville connector route
[edit]| Location | Danielsville |
|---|---|
| Existed | 1946[73][30]–1949[31][75] |
State Route 8 Connector (SR 8 Conn.) was a short-lived connector route of SR 8 that partially existed in Danielsville. The highway that would eventually become SR 8 Conn. was established at least as early as 1919 as part of SR 36 between Ila and an intersection with SR 8 in Danielsville.[2] In 1940, this segment had a "completed hard surface".[76][77] By the end of 1946, SR 98 through Danielsville had been moved to a western bypass of the city. Its former path through the city was redesignated as SR 8 Conn. northwest of the city.[73][30] Between February 1948 and April 1949, SR 98 Conn. was extended through the city of Danielsville, absorbing the entire length of SR 8 Conn.[31][75]
The entire route was in Madison County.
| Location | mi | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danielsville | Southern terminus | ||||
| | Northern terminus | ||||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
Royston spur route
[edit]| Location | Royston |
|---|---|
| Existed | 1949[78][79]–1985[51][52] |
State Route 8 Spur (SR 8 Spur) was a spur route of SR 8 that existed entirely within the city limits of Royston. Between 1939 and 1950, it was established from US 29/SR 8 to SR 17.[78][79] In 1985, it was decommissioned.[51][52]
The entire route was in Royston, Franklin County.
| mi | km | Destinations | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western terminus | |||||
| Eastern terminus | |||||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
Hartwell spur route
[edit]| Location | Hartwell |
|---|---|
| Existed | 1977[45][46]–1983[50][51] |
State Route 8 Spur (SR 8 Spur) was a short-lived spur route of SR 8 that partially existed in Hartwell. In 1977, SR 8's path east of Hartwell was shifted southeast onto the path of US 29/SR 181, between Hartwell and the South Carolina state line. Its former path became SR 8 Spur.[45][46] In 1983, the spur route was decommissioned.[50][51]
The entire route was in Hart County.
| Location | mi | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hartwell | Southern terminus | ||||
| | Shore of Lake Hartwell | Northern terminus | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Overview map of SR 8" (Map). Google Maps. Retrieved January 3, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f State Highway Department of Georgia (1920). System of State Aid Roads as Approved Representing 4800 Miles of State Aid Roads Outside the Limits of the Incorporated Towns (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b National Highway System: Atlanta, GA (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. May 9, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ National Highway System: Georgia (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. May 8, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ National Highway System: Athens-Clarke County, GA (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. May 9, 2019. Retrieved August 19, 2019.
- ^ a b c d State Highway Department of Georgia (1921). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (October 1926). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (October 1929). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (June 1930). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (November 1930). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (February 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (March 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (May 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (August 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (September 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (November 1932). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (May 1933). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (June 1933). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (July 1933). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (April–May 1934). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (October 1, 1934). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1936). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (July 1, 1936). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia State Highway Board (January 1, 1938). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (September 1, 1938). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (July 1, 1939). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1942). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1943). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g State Highway Department of Georgia (1946). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to November 7, 1946.)
- ^ a b c d e State Highway Department of Georgia (1948). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to February 28, 1948.)
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (1952). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to January 1, 1952.)
- ^ a b c d e State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1953). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to January 1, 1953.)
- ^ a b c d e f g State Highway Department of Georgia (1953). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to September 1, 1953.)
- ^ a b c d e f State Highway Department of Georgia (1954). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to June 1, 1954.)
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (1955). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017. (Corrected to June 1, 1955.)
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1956). General Highway Map: Hart County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation – via GDOT Maps.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1961). General Highway Map: Hart County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation – via GDOT Maps.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (1960). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map) (1960–1961 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 23, 2017. (Corrected to June 1, 1960.)
- ^ a b c State Highway Department of Georgia (1963). State Highway System and Other Principal Connecting Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 23, 2017. (Corrected to June 1, 1963.)
- ^ a b c d e State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1966). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c d State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1967). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1968). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (January 1976). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map) (1976–1977 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c d Georgia Department of Transportation (January 1977). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map) (1977–1978 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Georgia Department of Transportation (January 1977). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map) (1977–1978 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1980). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1980–1981 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1981). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1981–1982 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1982). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c Georgia Department of Transportation (1983). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1983–1984 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f Georgia Department of Transportation (1984). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1984–1985 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c Georgia Department of Transportation (1986). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1986–1987 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1987). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1987–1988 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1988). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1988–1989 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1989). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1989–1990 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1990). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1990–1991 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1991). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1991–1992 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1992). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1992–1993 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1993). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1993–1994 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1994). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1994–1995 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1995). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1995–1996 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1996). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1996–1997 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (1997). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (1997–1998 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (2001). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (2001–2002 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (2002). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (2002–2003 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (2003). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (2003–2004 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (2004). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (2004–2005 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (2005). Official Highway and Transportation Map (PDF) (Map) (2005–2006 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Overview map of SR 8 Conn" (Map). Google Maps. Retrieved January 4, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1995). General Highway Map: Douglas County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation – via GDOT Maps.
- ^ a b c Georgia Department of Transportation (2009). General Highway Map: Douglas County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation – via GDOT Maps.
- ^ Georgia Department of Transportation (2013). General Highway Map: Douglas County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation – via GDOT Maps.
- ^ a b c d State Highway Department of Georgia (January 1, 1945). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (January 1978). Official Highway Map (PDF) (Map) (1978-79 ed.). Scale not given. Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2017.
- ^ a b State Highway Department of Georgia (1949). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 23, 2017. (Corrected to April 1, 1949.)
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (April 1, 1940). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ State Highway Department of Georgia (October 1, 1940). System of State Roads (PDF) (Map). Scale not given. Atlanta: State Highway Department of Georgia. OCLC 5673161. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1940). General Highway Map: Franklin County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Perry inset – via GDOT Maps.
- ^ a b Georgia Department of Transportation (1950). General Highway Map: Franklin County, Georgia (Map). Atlanta: Georgia Department of Transportation. Perry inset – via GDOT Maps.
External links
[edit] Media related to Georgia State Route 8 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Georgia State Route 8 at Wikimedia Commons
- State highways in Georgia (U.S. state)
- Roads in Atlanta
- Transportation in Athens, Georgia
- Transportation in Haralson County, Georgia
- Transportation in Carroll County, Georgia
- Transportation in Douglas County, Georgia
- Transportation in Cobb County, Georgia
- Transportation in Fulton County, Georgia
- Transportation in DeKalb County, Georgia
- Transportation in Gwinnett County, Georgia
- Transportation in Barrow County, Georgia
- Transportation in Clarke County, Georgia
- Transportation in Oconee County, Georgia
- Transportation in Madison County, Georgia
- Transportation in Franklin County, Georgia
- Transportation in Hart County, Georgia
- Villa Rica, Georgia
- Decatur, Georgia
- Tucker, Georgia

