Orbital ring

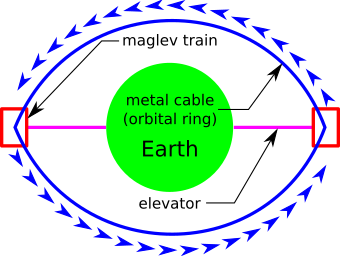
An orbital ring is a concept of an artificial ring placed around a body and set rotating at such a rate that the apparent centrifugal force is large enough to counteract the force of gravity. For the Earth, the required speed is on the order of 10 km/sec, compared to a typical low Earth orbit velocity of 8 km/sec. The structure is intended to be used as a space station or as a planetary vehicle for very high-speed transportation or space launch.
Because the cable is spinning faster than orbital velocity, there is a net outward force that is countered by internal tension within the cable. This resists any attempt to bend it and allows it to carry loads. In typical conceptions, a motorized platform is placed on the cable that runs in the opposite direction at the speed that makes it appear stationary above the ground. Above Earth's equator, a platform running at 9.5 km/sec in the direction opposite the cable will appear stationary and allow a cable to be lowered to form a space elevator. This elevator is only perhaps 500 kilometres (310 mi) long, which can be built with existing materials.
The requirement to construct a planet-sized cable in low-earth orbit and accelerate it to a faster-than-orbital velocity is an obvious practical problem. Other architectures have thus been proposed that use active support in different ways and are thus able to circumvent some of these limitations. The launch loop is a partial ring, perhaps 2000 km long, that runs between two ground stations instead of encircling the world. The particle ring uses a series of separate objects that can be launched individually to produce a collection similar to a solid ring and then controlled magnetically, with the disadvantage that they have no internal tension and lifting power is derived separately. The space fountain is a vertical version of the particle ring concept that forms a space elevator. The tethered ring is a dynamic structure that uses at least one complete and continuous non-orbiting ring with a diameter that is smaller than that of the planetary body. It can be built on the planet’s surface, accelerated to operating speed, and raised to a very high altitude mechanically by tensioning its numerous tethers.[1][2]
Concept
[edit]The orbital ring is somewhat similar to the "classic" space elevator concept. In the traditional space elevator, a large station is placed in geostationary orbit (GEO) so that it remains in a single location above the equator of Earth. A cable is then built and lowered towards Earth while a second cable, providing a counterweight, is built upward from the station and remains in place due to tidal forces. When the structure is complete, elevator-like cars can ride the cable into space. The main problem is that no known substance that can be manufactured in large quantities has the tensile strength needed to stretch from GEO to the surface. Orbital rings use a different mechanism.
In the orbital ring version, a kinetic ring is moving around the world at a higher speed than circular orbital velocity. This results in a net outward force that is countered by gravity acting on the stationary components. This can be accomplished at any altitude, although building the system above 500 kilometres (310 mi) in order to avoid most of the atmosphere is a practical requirement. A cable is then lowered from the ring to the ground and used in the same fashion as a traditional space elevator, with the difference being that the vertical cable is only 500 kilometres (310 mi) instead of 100,000 kilometres (62,000 mi) long. This length is within the capabilities of several known materials.
In order to support the elevator, the ring is not circular but slightly elliptical. Two or more stations are placed at the high ends of the path, but below the point where the orbit's apogee would be normally. The station bends the cable downward as it passes through in order to produce an upward force on the station. The resulting orbit for a two station system looks something more akin to an American football than a rounded ellipse. One can reduce the amount of tension in the orbiting ring to any required level by increasing the amount of lift generated by bending the cable. The main downside is that the elevator cable is now suspended from the high point of the system, rather than being close to the ground.
The moving ring does not need to be solid and does not need to be entirely encased by a solid sheath. Instead, a large number of individual magnetic objects can be placed in the desired orbit, and the stations deflect their path using magnets as they pass by. This version of the ring has the advantage of being much simpler to construct, as each element in the ring is completely separate and can be launched individually and requires no further working once in space.[a] It also does not have to be a complete ring; depending on the desired lifting power the total mass of objects might be much smaller than even the thinnest cable circling Earth. The main disadvantage is that the process of momentum exchange randomizes their velocity so some other system is required to shepherd the objects back into the correct orbits.
History
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2009) |
A detailed description of the concept was proposed and analyzed by Paul Birch in 1982, proposing a massive ring that would encircle the globe in low orbit, from which cables hang down to Earth's surface.[3][4][5]
In 1982, Soviet inventor Anatoly Yunitskiy also proposed an electromagnetic track encircling Earth, which he called "by wheel into space"[6] (later, "String Transportation System"). When the velocity of the string exceeds 10 km/sec, centrifugal forces detach the string from Earth's surface and lift the ring into space.
Andrew Meulenberg and his students, from 2008 to 2011, presented and published a number of papers based on types and applications of low-Earth-orbital rings as humanity's "stepping-stones-to-space". An overview mentions four applications of orbital rings: communication via a fiber-optic ring, surface-to-orbit transport with a "sling-on-a-ring" system, space-based solar power and climate change mitigation with a space sunshade. The "sling-on-a-ring" would involve rotating slings (made of colossal carbon tube) attached to the orbital ring that dip down into the atmosphere. The tip of a given sling would reach an altitude of 13–15 km at its lowest, and its rotation would cause it to have near-zero tangential velocity relative to the Earth's surface below. Consequently, the sling could pick up a payload from a conventional aircraft flying at that altitude, then lift up this payload to the orbital ring.[7]
Birch's model
[edit]Paul Birch published a series of three articles in the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society in 1982 that laid out the mathematical basis of ring systems.[3][4][5]
In the simplest design of an orbital ring system, a rotating cable or possibly an inflatable space structure is placed in a low Earth orbit above the equator. Not in orbit, but riding on this ring, supported electromagnetically on superconducting magnets, are ring stations that stay in one place above some designated point on Earth. Hanging down from these ring stations are short elevator cables made from materials with high-tensile-strength-to-mass-ratio.
Although this simple model would work best above the equator, Paul Birch calculated that since the ring station can be used to accelerate the orbital ring eastwards as well as hold the tether, it is therefore possible to deliberately cause the orbital ring to precess around Earth instead of staying fixed in space while Earth rotates beneath it. By precessing the ring once every 24 hours, the Orbital Ring will hover above any meridian selected on the surface of Earth. The cables which dangle from the ring are now geostationary without having to reach geostationary altitude or be placed into the equatorial plane. This means that using the Orbital Ring concept, one or many pairs of Stations can be positioned above any points on Earth desired, or can be moved everywhere on the globe. Thus, any point on Earth can be served by a space elevator. Also, a whole network of orbital rings can be built, which, by crossing over the poles, could cover the whole planet and be capable of taking over most freight and passenger transport. By an array of elevators and several geostationary ring stations, asteroid or Moon material can be received and gently put down where land fills are needed. The electric energy generated in the process would pay for the system expansion and ultimately could pave the way for a solar-system-wide terraforming and astroengineering activity on a sound economical basis.
Estimated cost
[edit]If built by launching the necessary materials from Earth, the cost for the system estimated by Birch in 1980s money was around $31 billion (for a "bootstrap" system intended to expand to 1000 times its initial size over the following year, which would otherwise cost 31 trillion dollars) if launched using Shuttle-derived hardware, whereas it could fall to $15 billion with space-based manufacturing, assuming a large orbital manufacturing facility is available to provide the initial 180,000 tons of steel, aluminum, and slag at a low cost, and even lower with orbital rings around the Moon. The system's cost-per-kilogram to accelerate payloads to low Earth orbit velocity would be around $0.05 in 1975 USD, assuming an energy requirement of 9 kWh/kg (roughly accurate) and an aspirational cost of electricity, provided by space-based solar power, of 0.005 US dollars per kWh.[8]
Types of orbital rings
[edit]The simplest type would be a circular orbital ring in LEO.
Two other types were also defined by Paul Birch:
- Eccentric orbital ring systems – these are rings that are in the form of a closed shape with varying altitude
- Partial orbital ring systems[3] – this is essentially a launch loop
In addition, he proposed the concept of "supramundane worlds" such as supra-Jovian and supra-stellar "planets". These are artificial planets that would be supported by a grid of orbital rings that would be positioned above a planet, supergiant or even a star.[9]
Orbital rings in fiction
[edit]In the close of Arthur C. Clarke's Fountains of Paradise (1979), a reference is made to an orbital ring that is attached in the distant future to the space elevator that is the basis of the novel.
Arthur C. Clarke's 3001: The Final Odyssey (1997) features an orbital ring held aloft by four enormous inhabitable towers (assumed successors to space elevators) at the Equator.
The manga Battle Angel Alita (1990-1995) prominently features a slightly deteriorated orbital ring.
The Star Trek novel, Ring Around the Sky features a decrepit ringworld in orbit above the planet, Kharzh'ulla, connected by a series of space elevators with the surface.
Orbital rings are used extensively in the collaborative fiction worldbuilding website Orion's Arm.[10]
The third part of Neal Stephenson's 2015 book Seveneves has an orbital ring around a Moon-less Earth.
Visual media and gaming
[edit]In the movie Starship Troopers, an orbital ring is shown encircling the Moon.
The second iteration of the anime series Tekkaman features a complete ring, though abandoned and in disrepair due to war, and without surface tethers.
The anime series Kiddy Grade also uses orbital rings as a launch and docking bay for spaceships. These rings are connected to large towers extending from the planets surface.
The anime Mobile Suit Gundam 00 also prominently features an orbital ring, which consists primarily of linked solar panels. The ring is connected to earth via three space elevators. This ring effectively provides near unlimited power to Earth. Later in the series the ring also shows space stations mounted on its surface.
The opening battle of Star Wars: The Clone Wars's, Season 6, Episode 1, takes place on the ring-shaped, Ringo Vinda space station, surrounding the planet of Ringo Vinda.
Also in the Star Wars universe, Kuat shipyards, is another orbital ring around the world of Kuat. In Star Wars: Legends, Dac, the homeworld of the Calamari and the Quarrens has a massive orbital shipyard that encircles their oceanic planet.
In the Warhammer 40,000 universe, Mars has a large orbital ring called the Ring of Iron. It is primarily used as a shipyard for interstellar craft. It is the largest man made structure in the galaxy. The planet Medusa also has such a ring, called Telstarax, hailing from the Dark Age of Technology, but it is largely plundered and wrecked.
The game X3 Terran Conflict features a free-floating orbital ring around Earth, which is shattered by an explosion and subsequently de-orbited in X3: Albion Prelude
In the game Xenoblade Chronicles 2 there is a giant tree that has grown around the base of an Orbital Ring.
In Escape Velocity: Nova Earth no longer has a moon orbiting around it because it had been stripped mined for centuries and now exist as an orbital ring around the planet. Over half of it is owned by Sigma Shipyard corporation.
In the game Stellaris, orbital rings can be constructed around colonized planets. They can act as regular space stations or they can boost their planets' production through buildings and modules.
Notes
[edit]- ^ As opposed to a similar launch of a complete ring which would require the pieces to be connected together once in orbit.
See also
[edit]- Megascale engineering
- Non-rocket spacelaunch
- Niven Ring (in the novel Ringworld): orbital ring around a star
- Space tether
- Skyhook
- Gravity elevator
References
[edit]- ^ US 11014692B2, issued 2021-05-25
- ^ Swan, Philip (2023). "The Techno-Economic Viability of Actively Supported Structures for Terrestrial Transit and Space Launch". 2023 IEEE Aerospace Conference. pp. 1–20. doi:10.1109/AERO55745.2023.10115896. ISBN 978-1-6654-9032-0. Retrieved 2023-12-12.
- ^ a b c Paul Birch, "Orbital Ring Systems and Jacob's Ladders - I", Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, Vol. 35, 1982, pp. 475–497. (see pdf) (Accessed 6 April 2016).
- ^ a b Paul Birch, "Orbital Ring Systems and Jacob's Ladders - II", Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, Vol. 36, 1982, 115. (pdf).
- ^ a b Paul Birch, "Orbital Ring Systems and Jacob's Ladders - III", Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, Vol. 36, 1982, 231. (pdf).
- ^ Anatoly Yunitskiy, "в космос на колесе" ("To Space by Wheel"), Техника-молодежи ("Technical Youth"), No. 6, June 1982, ISSN 0320-331X, pp. 34–37 and back cover. (pdf (alternate source: pdf Archived 2015-05-05 at the Wayback Machine) (Accessed 25 July 2019).
- ^ Meulenberg, Andrew; Karthik Balaji, P.S. (2011). "The LEO Archipelago: A system of earth-rings for communications, mass-transport to space, solar power, and control of global warming". Acta Astronautica. 68 (11–12): 1931–1946. arXiv:1009.4043. Bibcode:2011AcAau..68.1931M. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2010.12.002. S2CID 119271804.
- ^ "Orbital Ring Systems and Jacob's Ladders - II, Section 3.3".
- ^ Paul Birch, "Supramundane Planets", Journal of the British interplanetary Society, Vol. 44, 1991, 169.
- ^ Space Fountains and Orbital Rings, Orion's Arm.
External links
[edit]- Video: MegaStructures 01: Orbital Rings & Space Elevators
- Better more recent video: Orbital Rings
- Paul Birch Web Archive at Orion's Arm
- String Transport Systems: on Earth and in space (Anatoly Yunitskiy's book)
![]() Media related to Orbital ring at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Orbital ring at Wikimedia Commons


