Floating production storage and offloading
(Petro-Canada)
(Petro-Canada)
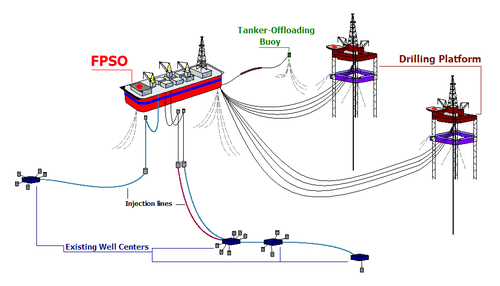
A Floating Production, Storage and Offloading vessel (FPSO; also called a "unit" and a "system") is a type of floating tank system used by the offshore oil and gas industry and designed to take all of the oil or gas produced from a nearby platform (s), process it, and store it until the oil or gas can be offloaded onto waiting tankers, or sent through a pipeline. A FSO is a similar system, but without the possibility to do any processing of the oil or gas.
Oil produced from offshore production platforms can be transported to the mainland either by pipeline or by tanker. When a tanker solution is chosen, it is necessary to accumulate oil in some form of tank such that an oil tanker is not continuously occupied whilst sufficient oil is produced to fill the tanker. Often the solution is a decommissioned oil tanker which has been stripped down and equipped with facilities to be connected to a mooring buoy. Oil is accumulated in the FPSO until there is sufficient amount to fill a transport tanker at which point the transport tanker connects to the stern of the floating storage unit and offloads the oil.
A FPSO have the capability to carry out some form of oil separation process obviating the need for such facilities to be located on an oil platform.
FPSO's are particularly effective in remote or deepwater locations where seabed pipelines are not cost effective.
The world's largest FPSO is the Kizomba A, it has a storage capacity of 2.2 million barrels. Built at a cost of over US$800 million by Hyundai Heavy Industries in Ulsan, Korea, it is operated by Esso Exploration Angola (ExxonMobil). Located in 1200 metres (3,940 ft) of water at Deepwater block 15, 200 statute miles (320 km) offshore in the Atlantic Ocean from Angola, West Africa, it weighs 81,000 tonnes and is 285 metres long, 63 metres wide, and 32 metres high ((935 ft by 207 ft by 105 ft).
Current FPSO's
- SeaRose FPSO, on the White Rose oil field, offshore Newfoundland
- Terra Nova FPSO, on the Terra Nova oil field, offshore Newfoundland
- Ramform Banff FPSO, in the North Sea
- Anasuria FPSO, on the Teal, Teal South and Guillemot A oil fields, North Sea
- Texaco (Now Chevron) Captain oil field FPSO December 1996 North Sea
- Shell Curlew oil field FPSO September 1997 North Sea
- BP Foinaven oil field FPSO November 1996 North Sea
- Kerr-McGee Gryphon oil field FPSO September 1993 North Sea
- Kerr-McGee Janice oil field FPS February 1999 North Sea
- Kerr-McGee Leadon oil field FPSO September 2001 North Sea
- Conoco (Now ConocoPhillips) MacCulloch oil field FPSO April 1997 North Sea
- Enterprise (now Shell) Pierce oil field FPS February 1999 North Sea
- Talisman Energy Ross oil field FPSO March 1999 North Sea]
- BP Schiehallion FPSO oil field July 1998 North Sea
- Shell Teal, Teal South and Guillemot A oil field FPSO August 1996 North Sea
- Amerada Hess Triton - Bittern, Guillemot West & North West oil fields FPSO March 2000 North Sea
- Norne FPSO, offshore Norway
- Sea Eagle FPSO, offshore Nigeria
- Bonga FPSO, 2005, off the coast of the Niger Delta, Africa
- Kizomba A, offshore Angola, West Africa
- Kizomba B, offshore Angola, West Africa
- Girassol, offshore Angola, West Africa
- Marlim Sul, offshore Brazil
- Capixaba, offshore brazil
- BHP Billiton Griffin FPSO , offshore northwest Australia
FPSO builders
- Acergy [1]
- Aker Kværner
- Bluewater [2][3]
- Chicago Bridge & Iron [4]
- Hyundai Heavy Industries
- KBR (Halliburton)
- Keppel Shipyard
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Mitsui Engineering & Shipbuilding (Mitsui) [5]
- Nortechs Offshore [6]
- Saipem [7]
- SBM Offshore[8]
- Samsung Heavy Industries (Samsung) [9]
- Technip [10]
External links
- FPSO FAQ's at the United Kingdom Offshore Operators Association
- FPSO's at the U.S. Department of the Interior's Minerals Management Service - Gulf of Mexico OCS Region
- FPSO pages at Offshore-Technology
- FPSO pages at Ship-Technology
- 2004 worldwide survey of FPSO's from Mustang Engineering and BHP Billiton Adobe Acrobat *.PDF
- http://www.exxonmobileurope.com/Corporate/Newsroom/Publications/TheLamp_3_2005/story2.asp
- http://www.exxonmobil.com/Corporate/Newsroom/Newsreleases/xom_nr_110804.asp
- http://www.sbmoffshore.com/
