Emperor penguin
| Emperor Penguin | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | A. forsteri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aptenodytes forsteri Gray, 1844
| |
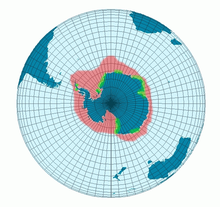
| |
| Emperor Penguin range (breeding colonies in green) | |
The Emperor Penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri) is the tallest and heaviest of all living penguin species and is endemic to Antarctica. The male and female are similar in plumage and size, reaching 122 cm (48 in) in height and weighing anywhere from 22 to 45 kg (48 to 99 lb). The dorsal side and head are black and sharply delineated from the white belly, pale-yellow breast and bright-yellow ear patches. Like all penguins it is flightless, with a streamlined body, and wings stiffened and flattened into flippers for a marine habitat.
Its diet consists primarily of fish, but can also include crustaceans, such as krill, and cephalopods, such as squid. In hunting, the species can remain submerged up to 18 minutes, diving to a depth of 535 m (1,755 ft). It has several adaptations to facilitate this, including an unusually structured hemoglobin to allow it to function at low oxygen levels, solid bones to reduce barotrauma, and the ability to reduce its metabolism and shut down non-essential organ functions.
The Emperor Penguin is perhaps best known for the sequence of journeys adults make each year in order to mate and to feed their offspring. The only penguin species that breeds during the Antarctic winter, it treks 50–120 km (31–75 mi) over the ice to breeding colonies which may include thousands of individuals. The female lays a single egg, which is incubated by the male while the female returns to the sea to forage; parents subsequently take turns foraging at sea and caring for their chick in the colony. The lifespan is typically 20 years in the wild, although observations suggest that some individuals may live to 50 years of age.
Taxonomy
The Emperor Penguin was described in 1844 by English zoologist George Robert Gray, who created its generic name from Ancient Greek word elements, ἀ-πτηνο-δύτης [a-ptēno-dytēs], "without-wings-diver". Its specific name is in honour of the German naturalist Johann Reinhold Forster, who accompanied Captain James Cook on his second Pacific Voyage and officially named five other penguin species.
Together with the similarly coloured but smaller King Penguin (A. patagonicus), the Emperor Penguin is one of two extant species in the genus Aptenodytes. Fossil evidence of a third species—Ridgen's Penguin (A. ridgeni)—has been found in fossil records from the late Pliocene, about three million years ago, in New Zealand.[2] Studies of penguin behaviour and genetics have proposed that the genus Aptenodytes is basal; in other words, that it split off from a branch which led to all other living penguin species.[3] Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA evidence suggests this split occurred around 40 million years ago.[4]
Description

The adult Emperor Penguin stands up to 122 cm (48 in) tall. The weight ranges from 22 to 45 kg (48-99 lb) and varies by sex,with males weighing more than females. The weight also varies by season, as both male and female penguins lose substantial mass while raising hatchlings and incubating eggs. The mean weight of males at the start of the breeding season is 38 kg (83 lb) and that of females is 29.5 kg (65 lb). After the breeding season this drops to 23 kg (50 lb) for both sexes.[5][6][7] Like all penguin species, the Emperor has a streamlined body to minimise drag while swimming, and wings that have become stiff, flat flippers.[8] The tongue is equipped with rear-facing barbs to prevent prey from escaping when caught.[9] Males and females are similar in size and colouration.[5] The adult has deep black dorsal feathers, covering the head, chin, throat, back, dorsal part of the flippers, and tail. The black plumage is sharply delineated from the light-coloured plumage elsewhere. The underparts of the wings and belly are white, becoming pale yellow in the upper breast, while the ear patches are bright yellow. The upper mandible of the 8 cm (3 in) long bill is black, and the lower mandible can be pink, orange or lilac.[10] In juveniles, the auricular patches, chin and throat are white, while its bill is black.[10] The Emperor Penguin chick is typically covered with silver-grey down and has a black head and white mask.[10] A chick with all-white plumage was found in 2001, but was not considered to be an albino as it did not have pink eyes.[11] Chicks weigh around 315 g (11 oz) after hatching, and fledge when they reach about 50% of adult weight.[12]
The Emperor Penguin's dark plumage fades to brown from November until February, before the yearly moult in January and February.[10] Moulting is rapid in this species compared with other birds, taking only around 34 days. Emperor Penguin feathers emerge from the skin after they have grown to a third of their total length, and before old feathers are lost, to help reduce heat loss. New feathers then push out the old ones before finishing their growth.[13]
The average yearly survival rate of the Emperor Penguin has been measured at 95.1%, with an average life expectancy of 19.9 years. The same researchers estimated that 1% of Emperor Penguins hatched could feasibly reach an age of 50 years.[14] In contrast, only 19% of chicks survive their first year of life.[15] Therefore, 80% of the Emperor Penguin population comprises adults five years and older.[14]
Vocalization
As the species has no fixed nest sites that individuals can use to locate their own partner or chick, the Emperor Penguin must rely on vocal calls alone for identification.[16] It uses a complex set of calls that are critical to individual recognition between parents, offspring, and mates,[5] displaying the widest variation in individual calls of all penguins.[16] Vocalizing Emperor Penguins use two frequency bands simultaneously. Chicks use a frequency-modulated whistle to beg for food and to contact parents.[5]
Adaptations to cold
The Emperor Penguin breeds in the coldest environment of any bird species; air temperatures may reach −40 °C (−40 °F), and wind speeds may reach 144 km/h (89 mph). Water temperature is a frigid −1.8 °C (28.8 °F),which is much lower than the Emperor Penguin's average body temperature of 39 °C (102 °F). The species has adapted in several ways to counteract heat loss.[18] Feathers provide 80–90% of its insulation, and it has a layer of sub-dermal fat which may be up to 3 cm (1.2 in) thick before breeding.[19] This resultant blubber layer impedes the mobility of the Emperor on land compared to its less well fat-insulated cousin, the Magellanic Penguin.[20] Its stiff feathers are short, lanceolate (spear-shaped), and densely packed over the entire skin surface. With around 100 feathers covering one square inch (15 feathers per cm2), it has the highest feather density of any bird species.[21] An extra layer of insulation is formed by separate shafts of downy filaments between feathers and skin. Muscles allow the feathers to be held erect on land, reducing heat loss by trapping a layer of air next to the skin. Conversely, the plumage is flattened in water, thus waterproofing the skin and the downy underlayer.[22] Preening is vital in facilitating insulation and in keeping the plumage oily and water-repellent.[23]
The Emperor Penguin is able to thermoregulate (maintain its core body temperature) without altering its metabolism, over a wide range of temperatures. Known as the thermoneutral range, this extends from −10 to 20 °C (10 to 70 °F). Below this temperature range, its metabolic rate increases significantly, although an individual can maintain its core temperature between 37.6 and 38.0 °C (99.7 to 100.4 °F) down to −47 °C (−53 °F).[24] Movement by swimming, walking, and shivering are three mechanisms for increasing metabolism; a fourth process involves an increase in the breakdown of fats by enzymes, which is induced by the hormone glucagon.[25] At temperatures above 20 °C (68 °F), an Emperor Penguin may become agitated as its body temperature and metabolic rate rise to increase heat loss. Raising its wings and exposing the undersides increases the exposure of its body surface to the air by 16%, facilitating further heat loss.[26]
Adaptations to pressure and low oxygen
In addition to the cold, the Emperor Penguin encounters another stressful condition on deep dives —markedly increased pressure of up to 40 times that of the surface, which in most other terrestrial organisms would cause barotrauma. The bones of the penguin are solid rather than air-filled, which eliminates the risk of mechanical barotrauma. However, it is unknown how the species avoids the effects of nitrogen-induced decompression sickness.
While diving, the Emperor Penguin's oxygen use is markedly reduced, as its heart rate is reduced to as low as five beats per minute and non-essential organs are shut down, thus facilitating longer dives.[9] Its hemoglobin and myoglobin are able to bind and transport oxygen at low blood concentrations; this allows the bird to function with very low oxygen levels that would otherwise result in loss of consciousness.[27]
Distribution and habitat
The Emperor Penguin has a circumpolar distribution in the Antarctic almost exclusively between the 66° and 77° south latitudes. It almost always breeds on stable pack ice near the coast and up to 18 km (11 mi) offshore.[5] Breeding colonies are usually located in areas where ice cliffs and icebergs shelter them from the wind.[5] The total population is estimated at around 400,000–450,000 individuals, which are distributed among as many as 40 independent colonies.[7] Around 80,000 pairs breed in the Ross Sea sector.[28] Major breeding colonies are located at Cape Washington (20,000–25,000 pairs), Coulman Island in Victoria Land (around 22,000 pairs), Halley Bay, Coats Land (14,300–31,400 pairs), and Atka Bay in Queen Maud Land (16,000 pairs).[7] Two land colonies have been reported: one on a shingle spit at Dion Island on the Antarctic Peninsula,[29] and one on a headland at Taylor Glacier in the Australian Antarctic Territory.[30] Vagrants have been recorded on Heard Island,[31] South Georgia, and in New Zealand.[7][32]
Conservation status
The Emperor Penguin is listed as a species of "least concern" by the IUCN. Along with nine other species of penguin, it is currently under consideration for inclusion under the US Endangered Species Act. The primary reasons for this are declining food availability due to the effects of climate change and industrial fisheries on the crustacean and fish populations. Other reasons for their potential placement on this list include disease, habitat destruction, and disturbance at breeding colonies by humans. Of particular concern is the impact of tourism.[33] One study has shown Emperor Penguin chicks in a créche to become more apprehensive following helicopter approach to 1,000 m (3,281 ft).[34]
Population declines of 50% in the Terre Adélie region have been observed due to increased adult mortality, especially of males, during an abnormally prolonged warm period in the late 1970s, which resulted in reduced sea-ice coverage. On the other hand, egg hatching success rates declined when the sea-ice extent increased. The species is therefore considered to be highly sensitive to climatic changes.[35]
A Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution study in January 2009 found Emperor Penguins could be pushed to the brink of extinction by the year 2100 due to global climate change. By applying mathematical models to predict how the loss of sea ice from climate warming would affect a big colony of Emperor Penguins at Terre Adélie, Antarctica, they forecast a decline of 87% in the colony's population by the end of the century, from the current 3,000 breeding pairs in the colony to 400 breeding pairs. The decline may be mirrored in the whole Emperor Penguin population, estimated at about 200,000 breeding pairs.[36]
In 2009, satellite images of areas of excrement-stained ice that are large enough to be visible from space helped scientists to discover ten previously unknown emperor penguin colonies in Antarctica. [37]
Behaviour

The Emperor Penguin is a social animal in its nesting and its foraging behaviour; birds hunting together may coordinate their diving and surfacing.[38] Individuals may be active day or night. A mature adult travels throughout most of the year between the nesting area and ocean foraging areas; the species disperses into the oceans from January to March.[7]
The American physiologist Gerry Kooyman revolutionized the study of penguin foraging behaviour in 1971 when he published his results from attaching automatic dive-recording devices to Emperor Penguins. He found that the species reaches depths of 265 m (869 ft), with dive periods of up to 18 minutes.[38] Later research revealed a small female had dived to a depth of 535 m (1,755 ft) near McMurdo Sound. It is possible that the Emperor Penguin can dive even deeper, as the accuracy of the recording devices is diminished at greater depths.[39] Further study of one bird's diving behaviour revealed regular dives to 150 m (490 ft) in water around 900 m (3,000 ft) deep, and shallow dives of less than 50 m (160 ft), interspersed with deep dives of more than 400 m (1,300 ft) in depths of 450 to 500 m (1500 to 1600 ft).[40] This was suggestive of feeding near or at the sea bottom.[41]
Both male and female Emperor Penguins forage for food up to 500 km (311 mi) from colonies while collecting food to feed chicks, covering 82–1,454 km (51–903 mi) per individual per trip. A male returning to the sea after incubation heads directly out to areas of permanent open water, known as polynyas, around 100 km (62 mi) from the colony.[40]
An efficient swimmer, the Emperor Penguin exerts pressure with both its upward and downward strokes while swimming.[21] The upward stroke works against buoyancy and helps maintain depth.[42] Its average swimming speed is 6–9 km/h (4–6 mph).[43] On land, the Emperor Penguin alternates between walking with a wobbling gait and tobogganing—sliding over the ice on its belly, propelled by its feet and wing-like flippers. Like all penguins, it is flightless.[8]
As a defence against the cold, a colony of Emperor Penguins forms a compact huddle (also known as the turtle formation) ranging in size from ten to several hundred birds, with each bird leaning forward on a neighbour. Those on the outside tend to shuffle slowly around the edge of the formation, producing a slow churning action, and giving each bird a turn on the inside and the outside.[44]
Diet
The Emperor Penguin's diet consists mainly of fish, crustaceans and cephalopods,[45] although its composition varies from population to population. Fish are usually the most important food source, and the Antarctic silverfish (Pleuragramma antarcticum) makes up the bulk of the bird's diet. Other prey commonly recorded include other fish of the family Nototheniidae, the Glacial Squid (Psychroteuthis glacialis), and the hooked squid species Kondakovia longimana, as well as Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba).[41] The Emperor Penguin searches for prey in the open water of the Southern Ocean, in either ice-free areas of open water or tidal cracks in pack ice.[5] One of its feeding strategies is to dive to around 50 m (164 ft), where it can easily spot sub-ice fish like the Bald notothen (Pagothenia borchgrevinki) swimming against the bottom surface of the sea-ice; it swims up to the bottom of the ice and catches the fish. It then dives again and repeats the sequence about half a dozen times before surfacing to breathe.[46]
Predators

The Emperor Penguin's predators include birds and aquatic mammals; the Southern Giant Petrel (Macronectes giganteus) is the predominant avian predator, responsible for up to 34% of chick deaths in some colonies. The South Polar Skua (Stercorarius maccormicki) mainly scavenges for dead chicks, as the live chicks are too large to be attacked by the time of its annual arrival in the colony.[47]
The primary aquatic predators are both mammals: the Leopard Seal (Hydrurga leptonyx), which takes some adult birds, as well as fledglings soon after they enter the water,[23] and the Orca (Orcinus orca), which takes adult birds.[48]
Courtship and breeding
The Emperor Penguin is able to breed at around three years of age, and usually commences breeding around one to three years later.[12] The yearly reproductive cycle begins at the start of the Antarctic winter, in March and April, when all mature Emperor Penguins travel to colonial nesting areas, often walking 50 to 120 km (31 to 75 mi) inland from the edge of the pack ice.[49] The start of travel appears to be triggered by decreasing day lengths; Emperor Penguins in captivity have been induced successfully into breeding by using lighting systems mimicking seasonal Antarctic day lengths.[50]
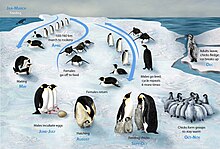
The penguins start courtship in March or April, when the temperature can be as low as −40 °C (−40 °F). A lone male gives an ecstatic display, where it stands still and places its head on its chest before inhaling and giving a courtship call for 1–2 seconds; it then moves around the colony and repeats the call. A male and female then stand face to face, with one extending its head and neck up and the other mirroring it; they both hold this posture for several minutes. Once in pairs, couples waddle around the colony together, with the female usually following the male. Before copulation, one bird bows deeply to its mate, its bill pointed close to the ground, and its mate then does the same.[51]
Emperor Penguins are serially monogamous. They have only one mate each year, and stay faithful to that mate. However, fidelity between years is only about 15%.[51] The narrow window of opportunity available for mating appears to be an influence, as there is a priority to mate and breed which often precludes waiting for the appearance of the previous year's partner.[52]

The female penguin lays one 460–470 g (1 lb) egg in May or early June;[51] it is vaguely pear-shaped, pale greenish-white, and measures around 12 × 8 cm (4¾ x 3 in).[49] It represents just 2.3% of its mother's body weight, making it one of the smallest eggs relative to the maternal weight in any bird species.[53] 15.7% of the weight of an Emperor Penguin egg is shell; like those of other penguin species, the shell is relatively thick, which minimises risk of breakage.[54]
After laying, the mother's nutritional reserves are exhausted and she very carefully transfers the egg to the male, before immediately returning to the sea for two months to feed.[49] The transfer of the egg can be awkward and difficult, and many couples drop the egg in the process. When this happens, the chick inside is quickly lost, as the egg cannot withstand the freezing temperatures on the icy ground. The male spends the winter incubating the egg in his brood pouch, balancing it on the tops of his feet, for 64 consecutive days until hatching.[51] The Emperor Penguin is the only species where this behaviour is observed; in all other penguin species both parents take shifts incubating.[55] By the time the egg hatches, the male will have fasted for around 115 days since arriving at the colony.[51] To survive the cold and winds of up to 200 km/h (120 mph), the males huddle together, taking turns in the middle of the huddle. They have also been observed with their backs to the wind to conserve body heat. In the four months of travel, courtship, and incubation, the male may lose as much as 20 kg (44 lb), from around 38 kg to just 18 kg (84 lb to 40 lb).[56][57]
Hatching may take as long as two or three days to complete, as the shell of the egg is thick. Newly hatched chicks are semi-altricial, covered with only a thin layer of down and entirely dependent on their parents for food and warmth.[58] If the chick hatches before the mother's return, the father feeds it a curd-like substance composed of 59% protein and 28% lipid, which is produced by a gland in his esophagus.[59] The young chick is brooded in what is called the guard phase, spending time balanced on its parent's feet and sheltered in the brood pouch.[58]

The female penguin returns at any time from hatching to ten days afterwards, from mid-July to early August.[49] She finds her mate among the hundreds of fathers by his vocal call and takes over caring for the chick, feeding it by regurgitating the food that she has stored in her stomach. The male then leaves to take his turn at sea, spending around 24 days there before returning.[49] His trip is slightly shorter than it was originally, because the melting of ice in the summer gradually decreases the distance between the breeding site and the open sea. The parents then take turns, one brooding while the other forages at sea.[51]
About 45–50 days after hatching, the chicks form a crèche, huddling together for warmth and protection. During this time, both parents forage at sea and return periodically to feed their chicks.[58] A crèche may comprise up to several thousand birds densely packed together and is essential for surviving the low Antarctic temperatures.[60]
From early November, chicks begin moulting into juvenile plumage, which takes up to two months and is often not completed by the time they leave the colony; adults cease feeding them during this time. All birds make the considerably shorter trek to the sea in December or January and spend the rest of the summer feeding there.[23][61]
Relationship with humans
The species has been bred outside Antarctica at SeaWorld San Diego; more than 20 individuals have hatched there since 1980.[62][63] Considered a flagship species, 55 individuals were counted in captivity in North American zoos and aquaria in 1999.[64] The species is kept in captivity in only two places in the world.[65]
Cultural references
The species' unique life cycle in such a harsh environment has been described in print and visual media. Apsley Cherry-Garrard, the Antarctic explorer, said: "Take it all in all, I do not believe anybody on Earth has a worse time than an Emperor Penguin".[66] Widely distributed in cinemas in 2005, the French documentary La Marche de l'empereur, which was also released with the English title March of the Penguins, told the story of the penguins' reproductive cycle.[65][67] The subject has been covered for the small screen twice by the BBC and presenter David Attenborough, first in episode five of the 1993 series on the Antarctic Life in the Freezer,[68] and again in the 2006 series Planet Earth.[69]
The computer-animated movie Happy Feet (2006) features Emperor Penguins as its primary characters, with one in particular that loves to dance; although a comedy, it too depicts their life cycle and promotes an underlying serious environmental message of threats from global warming and depletion of food sources by overfishing.[70] The computer-animated movie Surf's Up (2007) features a surfing Emperor Penguin named Zeke "Big-Z" Topanga.[71] More than 30 countries have depicted the bird on their stamps – Australia, Great Britain, Chile and France have each issued several.[72] It has also been depicted on a 1962 10 franc stamp as part of an Antarctic expedition series.[73] Canadian band The Tragically Hip included a song 'Emperor Penguin' on their 1998 album Phantom Power.
Notes
- ^ Template:IUCN2006 Database entry includes justification for why this species is of least concern
- ^ Williams, (The Penguins) p. 13
- ^ Jouventin P (1982). "Visual and vocal signals in penguins, their evolution and adaptive characters". Adv. Ethol. 24: 1–149.
- ^ Baker AJ, Pereira SL, Haddrath OP, Edge KA (2006). "Multiple gene evidence for expansion of extant penguins out of Antarctica due to global cooling". Proc Biol Sci. 273 (1582): 11–17. doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3260. PMID 16519228. Retrieved 2008-03-21.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f g University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. "Aptenodytes forsteri". Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- ^ "Emperor Penguin, Aptenodytes forsteri at MarineBio.org". Marinebio.org. MarchineBio Advertising. Retrieved 2008-11-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c d e Marchant, S (1990). Handbook of Australian, New Zealand and Antarctic Birds, Vol. 1A. Melbourne: Oxford University Press.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Williams (The Penguins) p. 3
- ^ a b Owen J (2004-01-30). ""Penguin Ranch" Reveals Hunting, Swimming Secrets". National Geographic website. National Geographic. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ^ a b c d Williams (The Penguins) p. 152
- ^ CDNN (2001-09-08). "Scientists find rare all-white emperor penguin". CDNN. Cyber Diver News Network. Retrieved 2008-03-29.
- ^ a b Williams 1995, p. 159.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 45.
- ^ a b Template:Fr icon Mougin J-L, van Beveren M (1979). "Structure et dynamique de la population de manchots empereur Aptenodytes forsteri de la colonie de l'archipel de Pointe Géologie, Terre Adélie". Compte Rendus Academie Science dé Paris. 289D: 157–60.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 47.
- ^ a b Williams 1995, p. 68.
- ^ Antarctic Photo Library of the US Antarctic Program retrieved May 30 2008
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 107.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 108.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan (2008) Magellanic Penguin, GlobalTwitcher.com, ed. N. Stromberg
- ^ a b Hile J (2004-03-29). "Emperor Penguins: Uniquely Armed for Antarctica". National Geographic website. National Geographic. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ Williams 1995, pp. 107–108.
- ^ a b c Kooyman GL, Gentry RL, Bergman WP, Hammel HT (1976). "Heat loss in penguins during immersion and compression". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. 54A: 75–80.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Cite error: The named reference "Kooy90" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Williams 1995, p. 109.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 110.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 111.
- ^ Norris S (2007-12-07). "Penguins Safely Lower Oxygen to "Blackout" Levels". National Geographic website. National Geographic. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ^ Harper PC, Knox GA, Wilson GJ, Young EC (1984). "The status and conservation of birds in the Ross Sea sector of Antarctica". In Croxall JP, Evans PGH, Schreiber RW (ed.). Status and Conservation of the World's Seabirds. Cambridge: ICBP. pp. 593–608.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stonehouse, B (1953). "The Emperor Penguin Aptenodytes forsteri Gray I. Breeding behaviour and development". Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey Scientific Report. 6: 1–33.
- ^ Robertson, G (1992). "Population size and breeding success of Emperor Penguins Aptenodytes forsteri at Auster and Taylor Glacier colonies, Mawson Coast, Antarctica". Emu. 92: 65–71.
- ^ Downes MC, Ealey EHM, Gwynn AM, Young PS (1959). "The Birds of Heard Island". Australian National Antarctic Research Report. Series B1: 1–35.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Croxall JP, Prince PA (1983). "Antarctic Penguins and Albatrosses". Oceanus. 26: 18–27.
- ^ Burger J. & Gochfeld M. (2007) "Responses of Emperor Penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) to encounters with ecotourists while commuting to and from their breeding colony". Polar Biology 30(10): 1303–1313 doi:10.1007/s00300-007-0291-1
- ^ Giese M, Riddle M (1997). (abstract) "Disturbance of emperor penguin Aptenodytes forsteri chicks by helicopters". Polar Biology. 22 (6): 366–71. doi:10.1007/s003000050430. Retrieved 2008-03-22.
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help) - ^ Barbraud, C. (2001). "Emperor penguins and climate change". Nature. 411 (6834): 183–186. doi:10.1038/35075554. PMID 11346792.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Dunham, Will. "Melting Sea Ice May Doom Emperor Penguins, Study Finds." The Washington Post, January 26, 2008. Retrieved on 2008-01-26.
- ^ Penguin poo viewed from space reveals new Antarctic colony locations, The Guardian, June 2, 2009
- ^ a b Kooyman GL, Drabek CM, Elsner R, Campbell WB (1971). "Diving behaviour of the Emperor Penguin Aptenodytes forsteri". Auk. 88: 775–95.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Williams 1995, p. 89.
- ^ a b Ancel A, Kooyman GL, Ponganis PJ, Gendner JP, Lignon J, Mestre X (1992). "Foraging behaviour of Emperor Penguins as a resource detector in Winter and Summer". Nature. 360: 336–39. doi:10.1038/360336a0.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Williams 1995, p. 156.
- ^ Lovvorn, J. R. (2001). "Upstroke thrust, drag effects, and stroke-glide cycles in wing-propelled swimming by birds". American Zoologist. 41: 154–165. doi:10.1093/icb/41.2.154.
- ^ Kooyman GL, Ponganis PJ, Castellini MA, Ponganis EP, Ponganis KV, Thorson PH, Eckert SA, LeMaho Y (1992). (abstract) "Heart rates and swim speeds of emperor penguins diving under sea ice". Journal of Experimental Biology. 165 (1): 1161–80. Retrieved 2008-03-30.
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pinshow B., Fedak M.A. , Battles D.R, & Schmidt-Nielsen K. (1976) "Energy expenditure for thermoregulation and locomotion in emperor penguins" American Journal of Physiology 231(3): 903–12
- ^ Cherel Y, Kooyman GL. (1998) "Food of emperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri) in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica" Marine Biology 130(3): 335–44 doi:10.1007/s002270050253
- ^ Ponganis PJ, Van Dam RP, Marshall G, Knower T, Levenson DH (2003). (abstract) "Sub-ice foraging behavior of emperor penguins". Journal of Experimental Biology. 203 (21): 3275–78. Retrieved 2008-03-21.
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Williams, p. 40.
- ^ Prévost, J (1961). Ecologie du manchot empereur. Paris: Hermann.
- ^ a b c d e Williams 1995, p. 158.
- ^ Groscolas, R (1986). "The endocrine control of reproduction and molt in male and female Emperor (Aptenodytes forsteri) and Adélie (Pygoscelis adeliae) Penguins. I. Annual changes in plasma levels of gonadal steroids and luteinizing hormone". Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 62: 43–53. doi:10.1016/0016-6480(86)90092-4.
- ^ a b c d e f Williams 1995, p. 157.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 55.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 23.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 24
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 27.
- ^ Robin, J. P. (1988). "Protein and lipid utilization during long-term fasting in emperor penguins". Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 254: R61–R68.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Le Maho, Y. (1976). "Thermoregulation in fasting emperor penguins under natural conditions". Am. J. Physiol. 231: 913–922.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Williams 1995, p. 28.
- ^ Template:Fr icon Prévost J, Vilter V (1963). "Histologie de la sécrétion oesophagienne du Manchot empereur". Proceedings of the XIII International Ornithological Conference: 1085–94.
- ^ Williams 1995, p. 30.
- ^ Pütz, K.; Plötz, J. (1991). "Moulting starvation in emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri) chicks". Polar Biology. 11 (4): 253–258. doi:10.1007/BF00238459..
- ^ Todd, FS (1986). "Techniques for propagating King and Emperor penguins Aptenodytes patagonica and A. forsteri at Sea World, San Diego". International Zoo Yearbook. 26 (1): 110–24. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.1986.tb02208.x.
- ^ "Animal Bytes - Penguins". SeaWorld official website. SeaWorld. 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ Diebold EN, Branch S, Henry L (1999). "Management of penguin populations in North American zoos and aquariums" (PDF). Marine Ornithology. 27: 171–76. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Bowes P (2005-08-19). "Penguin secrets captivate US viewers". BBC website. British Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 2008-03-23.
- ^ Cherry-Garrard, A (1922). "introduction". The Worst Journey in the World. Carroll & Graf. pp. xvii.
- ^ Template:Fr icon "La Marche de l'empereur, un film de Luc Jacquet". Official Site. Retrieved 2008-03-19.
- ^ Presenter – David Attenborough (1993). "The Big Freeze". Life in the Freezer. Season 1. Episode 5. BBC.
- ^ Presenter – David Attenborough (2006). "Ice Worlds". Planet Earth. Season 1. Episode 6. BBC.
- ^ Lovgren S (2006-11-16). ""Happy Feet": Movie Magic vs. Penguin Truths". National Geographic website. National Geographic. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ^ Lovgren S (2007). "Behind the Scenes of the New Movie "Surf's Up"". National Geographic website. National Geographic. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ^ Scharning K (2008). "Penguins Spheniscidae". Theme Birds on Stamps. self. Retrieved 2008-03-29.
- ^ Scharning K (2008). "Bird stamps from Belgium". Theme Birds on Stamps. self. Retrieved 2008-03-29.
References
- Williams, Tony D. (1995). The Penguins. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press. ISBN 019854667X.
External links
- University of Michigan info site with citations for specific studies
- Photographs of Emperor penguins
- Morphology of the Emperor Penguin including 3D computed tomographic (CT) animations of skeletons
- Emperors of the Extreme article from Scripps Institution of Oceanography
- Roscoe, R. "Emperor Penguin". Photo Volcaniaca. Retrieved 13 April 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dateformat=ignored (help) - Emperor penguin videos, photos & sounds on the Internet Bird Collection

