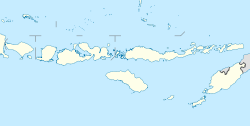
East Lombok Regency
East Lombok Regency
Kabupaten Lombok Timur | |
|---|---|
| Motto(s): Patuh Karya (Obedient and Productive) | |
 Location within West Nusa Tenggara | |
| Coordinates: 8°39′S 116°32′E / 8.650°S 116.533°E | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Capital | Selong |
| Government | |
| • Regent | M. Sukiman Azmy |
| • Vice Regent | Rumaksi [1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,605.55 km2 (619.91 sq mi) |
| Population (mid 2023 estimate) | |
• Total | 1,404,343 |
| • Density | 870/km2 (2,300/sq mi) |
| [2] | |
| Demographics | |
| • Ethnic groups | Sasak, Balinese, Tionghoa-peranakan, Sumbawa people, Flores people, Arab Indonesian |
| • Religion | Muslim, Hindu, Christian, Buddhist |
| • Languages | Indonesian (official), Sasak |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (ICST) |
| Area code | (+62) 376 |
| Website | lomboktimurkab |
East Lombok Regency is a regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten) of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok, of which it comprises the eastern third (including minor offshore islands); the administrative capital is the town of Selong. The Regency covers an area of 1,605.55 km2 and had a population of 1,105,582 at the 2010 Census[3] and 1,325,240 at the 2020 Census;[4] the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,404,343 (comprising 699,233 males and 705,110 females).[2]
Location
[edit]To the north lies the Java Sea. To the west are North Lombok Regency and Central Lombok Regency. To the south is the Lombok Basin and the Indian Ocean and to the east lies Elas Strait, a narrow body of water separating Lombok and the nearby small Gili Belang from Sumbawa which lies approximately 15 km to the east. The north of the Regency is on the eastern flank of Mount Rinjani, which at 3,726 m is the third highest mountain and the second largest volcano in the country. The mountain is an active volcano. The oldest recorded historical eruption was in 1847, and the last eruption was in May 2010.[5][6]
Administration
[edit]The area of East Lombok Regency is 2,679.88 km2, consisting of a land area of 1,605.55 km ² (59.91%) and a water (seabed) area of 1,074.33 km2 (40.09%).
Administrative structure
[edit]Kabupaten Lombok Timur (East Lombok Regency) is one of Lombok's four Regencies or administrative regions.
- TGH M Zainul Majdi, MA., Governor of NTB (West Nusa Tenggara), (Mataram is the Provincial Capital of West Nusa Tenggara)
- Drs. HM Sukiman AZMY, MM, Regent (Bupati) of Kabupaten Lombok Timur (East Lombok Regency).[7]
Administrative boundaries
[edit]| Boundary | District | Regency |
|---|---|---|
| North | Java Sea | |
| South | Lombok Basin | Indian Ocean |
| West | Praya Mount Rinjani |
Central Lombok Regency North Lombok Regency |
| East | Alas Strait | Sumbawa |
Administrative Districts
[edit]At the 2010 Census, the East Lombok Regency consisted of twenty districts (kecamatan), but an additional district (Lenek) was added in 2018 by splitting off 10 villages in the western part of Aikmel District. The districts are tabulated below with their areas and their populations at the 2010 Census[3] and the 2020 Census,[4] together with the official estimates as at mid 2023.[2] The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of administrative villages in each district (totaling 239 rural desa and 15 urban kelurahan), and its postal codes.
| Kode Wilayah |
Name of District (kecamatan) |
Area in km2 |
Pop'n Census 2010 |
Pop'n Census 2020 |
Pop'n Estimate mid 2023 |
Admin centre |
No. of villages |
Post codes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52.03.01 | Keruak (a) | 40.49 | 47,901 | 57,705 | 61,067 | Keruak | 15 | 83673 |
| 52.03.20 | Jerowaru (b) | 142.78 | 53,181 | 61,411 | 66,171 | Jerowaru | 15 | 83672 |
| 52.03.02 | Sakra | 25.09 | 52,731 | 64,080 | 68,051 | Sakra | 12 | 83671 |
| 52.03.19 | Sakra Barat (West Sakra) |
32.20 | 46,840 | 58,184 | 61,465 | Rensing | 18 | 83670 |
| 52.03.18 | Sakra Timur (East Sakra) |
37.03 | 40,909 | 52,012 | 55,346 | Lepak | 10 | 83674 |
| 52.03.03 | Terara | 41.41 | 65,485 | 75,889 | 80,780 | Terara | 16 | 83664 |
| 52.03.11 | Montong Gading | 25.66 | 40,603 | 48,801 | 50,910 | Montong Betok | 8 | 83663 |
| 52.03.04 | Sikur | 78.27 | 67,550 | 79,023 | 83,048 | Sikur | 14 | 83662 |
| 52.03.05 | Masbagik | 33.17 | 93,993 | 107,893 | 113,439 | Masbagik | 10 | 83661 |
| 52.03.12 | Pringgasela | 134.26 | 50,059 | 63,110 | 67,250 | Pringgasela | 10 | 83660 |
| 52.03.06 | Sukamulia | 14.49 | 30,373 | 36,373 | 38,420 | Sukamulia | 9 | 83652 |
| 52.03.13 | Suralaga | 27.02 | 51,940 | 64,681 | 67,793 | Suralaga | 15 | 83651 |
| 52.03.07 | Selong | 31.68 | 82,627 | 92,464 | 96,015 | Selong | 12 | 83611-83613, 83617-63619 |
| 52.03.17 | Labuhan Haji | 49.57 | 53,023 | 64,492 | 67,448 | Labuhan Haji | 12 | 83615-83617 |
| 52.03.08 | Pringgabaya | 136.20 | 90,548 | 110,813 | 117,161 | Pringgabaya | 15 | 83654 |
| 52.03.16 | Suela | 115.01 | 37,441 | 45,421 | 48,513 | Suela | 8 | 83655 |
| 52.03.09 | Aikmel | 81.09 | 92,853 | 70,121 | 74,219 | Aikmel | 14 | 83653 |
| 52.03.14 | Wanasaba | 55.89 | 59,317 | 68,302 | 74,466 | Wanasaba | 14 | 83650 |
| 52.03.15 | Sembalun | 217.08 | 18,786 | 23,568 | 25,190 | Sembalun | 6 | 83657 |
| 52.03.21 | Lenek | 41.83 | (c) | 43,520 | 47,444 | Lenek | 10 | 83657 |
| 52.03.10 | Sambelia (d) | 245.22 | 29,422 | 37,377 | 40,147 | Sambelia | 11 | 83656 |
| Totals | 1,605.55 | 1,105,582 | 1,325,240 | 1,404,343 | Selong | 254 |
Notes: (a) including 4 small islands off the east coast of Lombok Island. (b) includes 24 islands off the southeast corner of Lombok Island.
(c) the 2010 Census population of the new Lenek District is included in the figures for Aikmel District, from which it was subsequently split off in 2018.
(d) includes 7 islands off the northeast corner of Lombok Island, of which the largest are Gili Sulat and Gili Lawang.
The districts are subdivided into 239 rural Desa and 15 urban Kelurahan; of the latter 11 are in Selong District and 4 are in Labuhan Haji District.[8]
Population
[edit]The majority of the population are Sasak people, who speak the Sasak language.
In the 2010 Census, East Lombok Regency recorded 1,105,582 inhabitants, 24.7% being officially below the Indonesian poverty level;[9] the 2020 Census showed the population having risen to 1,325,240, and the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,404,343 (comprising 699,233 males and 705,110 females).[2] The population of this regency are primarily Muslim.
Ethnicity
[edit]The Sasak people are the indigenous people of Lombok and form the vast majority of East Lombok's residents, with few people of Balinese origin compared with West Lombok. East Lombok is also home to people of Balinese, Chinese, Tionghoa-peranakan people of mixed Indonesian and Chinese descent and small number of Arab Indonesian people, mainly of Yemeni descent who originally settled in the early port city of Ampenan.
Religion
[edit]Islam is the religion of the majority of the population of East Lombok. Other religions practised in East Lombok are Christianity, Catholicism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and Confucianism.
Language
[edit]Most people in east Lombok normally speak the Sasak language. Sasak is the native language of the indigenous people of Lombok. Indonesian is the language most widely used in everyday interactions at places such as hotels, larger shops in the township of Praya and in government offices. When at home or a place of recreation east Lombok residents tend to use local eastern Lombok dialects of the Sasak language.
Land use
[edit]Rivers and catchment areas:' Lombok Island has four main watersheds. Menanga watershed, which is administratively in the territory of East Lombok, has been declared by the Governor of Nusa Teggara Barat to be a critical watershed by Decree No. 122 in 2005. Lombok is faced with a serious water supply and management problem, caused by increasing forest and water table damage, land degradation and poor forestry management. West Nusa Tenggara province as a whole is threatened with a water crisis caused by increasing forest and water table damage and degradation.[10]
Services and development
[edit]The region is essentially agrarian in activity with rice, copra, casava, tobacco, timber and other crops. Rainfall is lower in the south of the Regency and higher in the north as the land rises toward Mount Rinjani. Rinjani supplies a rainfall catchment area to the region and several into eastern Lombok rivers flow from its slopes. The sea supports a small local fishing industry, seaweed harvesting, a pearl industry and prawn farming.
The growing tourism industry in Lombok has had little effect on the eastern coast. The proximity of the new Lombok International Airport will possible lead to an increase in tourism related business and development in east Lombok in coming years.
Transport
[edit]Public ferries' provide services for both passengers and vehicles. Labuhan Lombok is in East Lombok Regency and provides connections eastward to Sumbawa. Tanjung Lembar in the south west of the island is Lombok's main port and handles small freighters, fishing boats and the combination vehicle and passenger ferries heading westward to Bali.
- Alat Strait: Labuhan Lombok - Pototano, Sumbawa with 8 ferries providing 18 crossings per day.
- Lombok Strait: Lembar Lombok - Padang Bai, Bali, with 12 ferries providing crossings once every hour.[11]
These ferries connecting to nearby Sumbawa and Bali provide the principal facilities for road transport movements in and out of Lombok. Disruptions on these routes can significantly affect trade and the provision of supplies to the island as the shipping operators on these routes will often suspend services due to breakdown or heavy seas.
East Lombok is served by the Lombok International Airport (Bandara Internasional Lombok) (IATA: LOP, ICAO: WADL). The new airport provides domestic terminal facilities serving destinations in Java, Bali and Sumbawa. The main terminal building also provides international terminal facilities, currently limited to international connections to Malaysia provided by AirAsia. International flights to Kuala Lumpur provided by Garuda and Merpati airlines depart from the Domestic terminal.
The new international airport will provide facilities for wide bodied aircraft with more modern terminal facilities and improved cargo facilities.
Lombok International Airport in Central Lombok is south west of Praya in south central Lombok. The airport commenced operations on 1 October 2011 replacing the previous international and domestic facilities at Selaparang Airport near Ampenan in West Lombok Regency which formally closed for operations on the evening of 30 September 2011. All services previously operated at the Selaparang airport were moved across to the new airport at that time.
References
[edit]- ^ lomboktimurkab.go.id http://lomboktimurkab.go.id/beranda/bupati-lombok-timur-dari-masa-ke-masa/. Retrieved January 24, 2019.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)[title missing] - ^ a b c d Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 28 February 2024, Kabupaten Lombok Timur Dalam Angka 2024 (Katalog-BPS 1102001.5203)
- ^ a b Biro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011.
- ^ a b Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021.
- ^ "Pusat Vulkanologi & Mitigasi Bencana Geologi - VSI - Contact". Archived from the original on 2010-07-29. Retrieved 2010-10-06.
- ^ "Global Vulcanism Program-Rinjani Eruptive History". Global Vulcanism Program. May 2 – Dec 20, 2009. Archived from the original on 2007-08-20. Retrieved 2010-05-10.
- ^ "Musyawarah Pimpinan Daerah Kabupaten Lombok Timur-". Website of the Regency of East Lombok. September 2010. Retrieved 12 September 2010.
- ^ "Letak Geografis Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Barat (Letak Geografis Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Barat)". Badan Pusat Statistik Provinsi Nusa Tenggara Barat. 13 December 2009. Archived from the original on 30 July 2010. Retrieved 30 Aug 2010.
- ^ Liputan6.com (28 August 2010). "Lombok Timur Pemasok Utama TKI NTB".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "NTB Akan Alami Krisis Air Bersih". Official Website of the Province of NTB. July 20, 2010. Archived from the original on 22 November 2010. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- ^ "Regional Economy-West Nusa Teggara provincial profile". Archived from the original on 1 December 2010. Retrieved 1 September 2010.