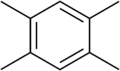
Durene
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.242 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14 | |
| Molar mass | 134.21816 |
| Melting point | 79.2 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Durene, or 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon used as a solvent. It is also an intermediate in the manufacture of pyromellitic acid, which is used for manufacturing curing agents, adhesives and coating materials. It is used in the manufacture of some raw materials for engineering plastics (polyimides) and cross-linking agent for alkyd resins.
1,2,4,5-Tetramethylbenzene has a simple proton NMR spectrum comprising two signals due to the 2 aromatic hydrogens (2H) and four methyl groups (12H). It is also readily soluble in chloroform. This compound is thus a useful internal standard.[1]
References
- ^ e.g. in Petr K. Sazonov, Vasyli A. Ivushkin, Galina A. Artamkina, and Irina P. Beletskaya (2003). "Metal carbonyl anions as model metal-centered nucleophiles in aromatic and vinylic substitution reactions". Arkivoc. 10: 323–334.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
