Doti District
Doti District
डोटी जिल्ला | |
|---|---|
 Saileswori Temple | |
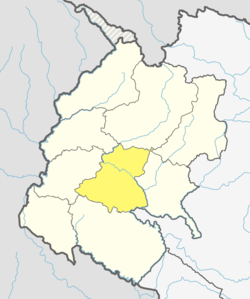 Location of Doti District | |
| Country | |
| Province | Sudurpashchim Province |
| Admin HQ. | Silgadhi |
| Government | |
| • Type | Coordination committee |
| • Body | DCC, Doti |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,025 km2 (782 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
• Total | 211,746 |
| • Density | 100/km2 (270/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+05:45 (NPT) |
| Main Language(s) | Doteli |
Doti District (Nepali: डोटी जिल्ला pronounced [ɖoʈi] ), part of Sudurpashchim Province, is one of the 77 districts of Nepal. This district, with Silgadhi as its headquarters, covers an area of 2,025 square kilometres (782 sq mi) with a population of 207,066 in 2001 and increasing marginally to 211,746 in 2011.[1]
History
[edit]Doti was a medieval kingdom of Kumaon. It was founded by Niranjan Malla Dev, the last son of the Katyuri dynasty and younger brother of Abhay Pal of Askot. Previously, the area between Ramganga in the west and the Karnali River in the east was under the control of the Raikas (rulers of the Doti kingdom, alternately Kumaun or Rainka Maharaj).[2]
Ancient Doti was a part of Kumaon Kingdom, Now remaining Kumaon region is part of Uttrakhand a state in modern-day india, Nepal's neighboring country. Kingdom of Kumaon lost Doti during the expansion of Nepal Kingdom in 1790. It was formed after the Katyuri Kingdom's disintegration during the 13th century.[3] Doti was one of eight different princely states formed after the disintegration, and all claim Katyuri heritage.[4] The seven other known states are:
- Baijnath-Katyuri
- Dwarahat
- Baramandal
- Askot
- Sira
- Sora
- Sui (Kali Kumaon)
The Katyuri Kingdom's dissolution is attributed to the invasion of Khas Kings Ashoka Challa and Krachalla, from the Karnali zone (Dullu) in 1191 and 1223 respectively.[5] Later, the whole land between Ramganga in the west (Uttarakhand) and the Karnali in the east (which divides the far western region from other parts of Nepal), came under the Raikas' rule — after the establishment of the Katyuri's dynastic Raikas Doti. Brahma Dev Mandi at Kanchanpur; a district within Mahakali, was established by Katyuri King Brahma Dev.
Raikas of Doti and their lineage
[edit]Historical evidence [6] of the following raikas has been discovered:
- Niranjan Malla Dev (founder of Doti Kingdom beginning of the 13th century)
- Nagi Challa (1238)
- Ripu Challa (1279)
- Nirai Pal (1353) may be from Askot as historical evidence from 1354 AD relating to him has been found in Almora.[7]
- Nag Malla (1384)
- Dhir Malla (1400)
- Ripu Malla (1410)
- Anand Malla (1430)
- Balinarayan Malla (1400)[8]
- Sansar Malla (1442)
- Kalyan Malla (1443)
- Suratan Malla (1478)
- Kriti Malla (1482)
- Prithivi Malla (1488)
- Medini Jay Malla (1512)
- Ashok Malla (1517)
- Raj Malla (1539)
- Arjun Malla/Shahi (1500 [8])
- Bhupati Malla/Shahi (1558)
- Sagaram Shahi (1567)
- Hari Malla/Shahi (1581; last Raika of Sira, and the adjoining part of Nepal[8][9])
- Rudra Shahi (1630)
- Vikram Shahi (1642)
- Mandhata Shahi (1671)
- Raghunath Shahi (1690)
- Hari Shahi (1720)
- Krishna Shahi (1760)
- Deep Shahi (1785)
- Prithivi Pati Shahi (1790; He had fought against the Gorkha Ruler and also with the British in 1814 AD)[10][11]
Conflict with Gorkha Kingdom
[edit]The historic place of war between the Doti Kingdom and Gorkha kingdom during the period of Expanding Kingdom of Nepal in 1790, is Nari-Dang which lies on the bank of the Seti River and Dumrakot was the base of the Doti Kingdom during the fighting against the Gorkhalis.[12]
Doti was captured by Gorkha forces, and the Gorkha rulers went on to destroy several historical sites in Doti — attempting to cover its legendary bravery and tenacity.[12] The Dotyali people were also subject to ethnic prejudice, and were frequently excluded from government jobs and offices of state.[12] Somehow in 1950, a few Dotyalis established their identities as national heroes based solely on their courage, daring, and contribution to their country.[12] Noted among them are Martyr Dashrath Chand Ministry of Home Affairs, Martyr Bhim Dutta Pant Ministry of Home Affairs, and K.I. Singh,[13][14] a revolutionary leader who later became prime minister.
Dotyali language.
[edit]Dotiyali is the local language spoken in the Doti region; the far western region of Nepal, which is similar to the Kumauni language, a language spoken by people of Kumaon, a state in modern-day india, Nepal's neighboring country. According to Rahul Sankrityayan, Dotiyali is the dialect of the Kumauni language which was brought to Doti by a section of the Katyuri dynasty of Kumaun which had ruled over Doti until 1790.[12] The Doti kingdom was formed after the Katyuri kingdom had broken up into eight different princely states of different sections of the Katyuris. However, in Nepal it is considered as a Nepali dialect; though Local intellectuals and people of Doti, those who are speaking Dotiyali language that they are increasingly demanding their language to be recognized as one of the national language of Nepal.[15]
Geography and climate
[edit]| Climate Zone[16] | Elevation Range | % of Area |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Tropical | below 300 meters (1,000 ft) | 0.1% |
| Upper Tropical | 300 to 1,000 meters 1,000 to 3,300 ft. |
22.2% |
| Subtropical | 1,000 to 2,000 meters 3,300 to 6,600 ft. |
58.8% |
| Temperate | 2,000 to 3,000 meters 6,400 to 9,800 ft. |
17.6% |
| Subalpine | 3,000 to 4,000 meters 9,800 to 13,100 ft. |
1.2% |
Demographics
[edit]At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Doti District had a population of 211,746. Of these, 91.2% spoke Doteli, 6.8% Nepali, 1.0% Magar, 0.4% Kham, 0.1% Achhami, 0.1% Maithili, 0.1% Tharu and 0.2% other languages as their first language.[17]
Ethnicity/caste: 57.7% were Chhetri, 12.3% Kami, 7.9% Hill Brahmin, 4.6% Damai/Dholi, 3.5% other Dalit, 3.5% Thakuri, 3.4% Magar, 2.4% Sarki, 1.4% Badi, 1.1% Lohar, 0.5% Newar, 0.5% Sanyasi/Dasnami, 0.2% Kumal, 0.1% Gurung, 0.1% Majhi, 0.1% Musalman, 0.1% Tamang, 0.1% other Terai, 0.1% Tharu and 0.2% others.[18]
Religion: 99.0% were Hindu, 0.8% Buddhist, 0.1% Christian and 0.1% Muslim.[19]
Literacy: 55.2% could read and write, 3.4% could only read and 41.3% could neither read nor write.[20]
| Census year | Pop. | ±% p.a. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 153,135 | — | ||
| 1991 | 167,168 | +0.88% | ||
| 2001 | 207,066 | +2.16% | ||
| 2011 | 211,746 | +0.22% | ||
| 2021 | 205,683 | −0.29% | ||
| ||||
| Source: Citypopulation[21] | ||||
Administration
[edit]The district consists of nine municipalities, out of which two are urban municipalities and seven are rural municipalities. These are as follows:[22]
- Dipayal Silgadhi Municipality
- Shikhar Municipality
- Purbichauki Rural Municipality
- Badikedar Rural Municipality
- Jorayal Rural Municipality
- Sayal Rural Municipality
- Aadarsha Rural Municipality
- Dr. K. I. Singh Rural Municipality
- Bogatan Rural Municipality
Former Village Development Committees
[edit]Prior to the restructuring of the district, Doti District consisted of the following Village development committees:
- Banalek
- Banja Kakani
- Barchhen
- Basudevi
- Bhawardanda
- Bhadhegaun
- Bhumirajmandau
- Changra
- Chhapali
- Chhatiwan
- Dahakalikasthan
- Daud
- Dhanglagau
- Dhirkamandau
- Durgamandau
- Gadasera
- Gaguda
- Gaihragaun
- Ganjari
- Ghanteshwar
- Girichauka
- Jijodamandau
- Kadamandau
- Kalena
- Kalikasthan
- Kanachaur
- Kapalleki
- Kedar Akhada
- Khatiwada
- Khirsain
- Ladagada
- Lamikhal
- Lana Kedareshwar
- Latamandau
- Lakshminagar
- Mahadevsthan
- Mannakapadi
- Mudabhara
- Mudhegaun
- Nirauli
- Pachanali
- Pokhari
- Ranagaun
- Sanagaun
- Saraswatinagar
- Satphari
- Simchaur
- Tijali
- Tikha
- Tikhatar
- Toleni
- Baglekh
- Barpata
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "National Population and Housing Census 2011(National Report)" (PDF). Central Bureau of Statistics. Government of Nepal. November 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-04-18.
- ^ Badri Datta Pande ; History of Kumaun (1937)
- ^ Bhoj Raj Bhattrai. A Historey of Doti Kingdom.
- ^ Prof.Dr. Jay Raj pant wrote "Far-Western region of Nepal is called Doti Culturally " : In History of Doti Kingdom (2013)
- ^ Yaswant Singh Kathoch. A New History of Ittarakhand.
- ^ Badri Dutt Pandey. History of Kumaun.
- ^ Advin T. Atkinson (Translated by Ramesh Thapaliyal) (2003). "An old stone has found on the hills of Almora in which name Niraipal and 1348 written". Himalayan Gazetteer Hindi Edition. ISBN 8190100130. p. 267.
- ^ a b c Dr. Ram Singh; A New History of Uttarakhand(2006).Mall Raikas of Sira.
- ^ Advin T. Atkinson ; Himalayan Gazetteer; ( Translated by Ramesh Thapaliyal ) Hindi Edition (2003) ISBN 8190100130;..Page 285..Rudra Chand had captured whole territory east of kaliriver in 1581 along with Sira.
- ^ Advin T. Atkinson(2003). "Doteli King and East india company agreed to help each other". Himalayan Gazetteer Hindi Edition. p. 380.
- ^ Raja Ram Subedi (1997). History of Karnali Region. Subedi has mentioned Pritivipati Shah went to pilibhit and offered his service to British india.
- ^ a b c d e "History of Nepal". T.R.Vaidya Publications. Archived from the original on 2005-02-09. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ Time magazine. 5 August 1957.
- ^ The New York Times. 6 October 1982. State Guest of PR of China in 1952 for three years during the rule of Mao Tse-tung & Chou en Lai
- ^ "The Unreached Peoples Prayer Profiles". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2014-08-01.
- ^ The Map of Potential Vegetation of Nepal - a forestry/agroecological/biodiversity classification system (PDF), . Forest & Landscape Development and Environment Series 2-2005 and CFC-TIS Document Series No.110., 2005, ISBN 978-87-7903-210-1, retrieved November 22, 2013
- ^ NepalMap Language [1]
- ^ NepalMap Caste [2]
- ^ NepalMap Religion [3]
- ^ NepalMap Literacy [4]
- ^ "NEPAL: Administrative Division". www.citypopulation.de.
- ^ "स्थानिय तह" (in Nepali). Ministry of Federal Affairs and General Administration. Retrieved 1 September 2018.
- Sources
- "Districts of Nepal". Statoids.
- A New History of Uttarakhand by Y.S. Kathoach
- Dotiyali language
29°16′N 80°56′E / 29.267°N 80.933°E

