Chikuhō Main Line
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2014) |
| Chikuhō Main Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Owner | JR Kyushu | ||
| Locale | Kitakyushu | ||
| Termini | |||
| Stations | 25 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Regional rail | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1891 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 66.1 km (41.1 mi) | ||
| Number of tracks | 2 (Wakamatsu–Orio, Orio–Iizuka) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||
| Electrification | 20 kV AC, 60 HZ (Orio–Keisen) | ||
| |||
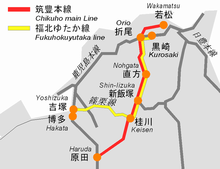
The Chikuhō Main Line (筑豊本線, Chikuhō-honsen) is a railway line in Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan, operated by Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu). It connects Wakamatsu Station in Kitakyushu with Haruda Station in Chikushino. Between Orio Station and Haruda Station, as well as from Keisen Station via the Sasaguri Line to Yoshizuka Station, the line functions as an alternate route to the Kagoshima Main Line.
Line data
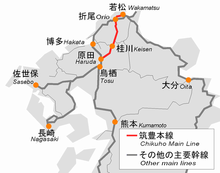
This is the shortest of all Japan Railways Group lines named Main (or trunk) Line (not counting the JR Shikoku main lines, which were stripped of their designation after JR Shikoku started operating). For comparison, the second shortest is Rumoi Main Line (66.8 km), although it once ran a longer distance.
The line is divided into three sections. Each section has an alias.
- Wakamatsu Line
- Wakamatsu–Orio, 10.8 km
- Fukuhoku Yutaka Line
- Orio–Keisen, 34.5 km
- Haruda Line
- Keisen–Haruda, 20.8 km
Stations
Wakamatsu–Orio (Wakamatsu Line)
| No. | Station | Distance (km) |
Transfers | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JE 06 | Wakamatsu | 0.0 | Wakamatsu-ku, Kitakyūshū | Fukuoka Prefecture | |
| JE 05 | Fujinoki | 2.9 | |||
| JE 04 | Okudōkai | 4.6 | |||
| JE 03 | Futajima | 6.3 | |||
| JE 02 | Honjō | 9.3 | Yahata Nishi-ku, Kitakyūshū | ||
| JE 01 | Orio | 10.8 | Kagoshima Main Line | ||
Orio–Keisen (Fukuhoku Yutaka Line)
Some rapid trains pass the stations marked "X".
| No. | Station | Distance (km) |
Transfers | Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC 26 | Orio | 0.0 | Kagoshima Main Line | Yahata Nishi-ku, Kitakyūshū | Fukuoka Prefecture | |
| JC 25 | Higashi Mizumaki | 2.7 | Mizumaki, Onga District | |||
| JC 24 | Nakama | 4.1 | Nakama | |||
| JC 23 | Chikuzen Habu | 5.6 | ||||
| JC 22 | Kurate | 7.9 | Kurate, Kurate District | |||
| JC 21 | Chikuzen Ueki | 10.4 | Nōgata | |||
| JC 20 | Shinnyū | 12.0 | ||||
| JC 19 | Nōgata | 14.0 | Heisei Chikuho Railway Ita Line | |||
| JC 18 | Katsuno | 16.7 | X | Kotake, Kurate District | ||
| JC 17 | Kotake | 20.5 | ||||
| JC 16 | Namazuta | 23.9 | X | Iizuka | ||
| JC 15 | Urata | 25.4 | X | |||
| JC 14 | Shin Iizuka | 26.8 | Gotōji Line | |||
| JC 13 | Iizuka | 28.6 | ||||
| JC 12 | Tentō | 31.5 | ||||
| JC 11 | Keisen | 34.5 | Sasaguri Line | Keisen, Kaho District | ||
Keisen–Haruda (Haruda Line)
| No. | Station | Distance (km) |
Transfers | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JG 01 | Keisen | 0.0 | Sasaguri Line | Keisen, Kaho District |
Fukuoka Prefecture |
| JG 02 | Kami Honami | 2.8 | Iizuka | ||
| JG 03 | Chikuzen Uchino | 5.9 | |||
| JG 04 | Chikuzen Yamae | 16.1 | Chikushino | ||
| JG 05 | Haruda | 20.8 | Kagoshima Main Line | ||
Rolling stock

A pre-series two-car BEC819 series AC battery electric multiple unit (BEMU) was tested on the line from April 2016,[1] and entered revenue service on 19 October 2016.[2] This will be followed by six more trainsets, entering service in spring 2017.[1]
History
The 39 km Wakamatsu to Iizuka section was built by the Chikuho Kogyo Railway, opening between 1891 and 1893, with the 12 km extension to Chikuzen Uchino opening in 1895.[citation needed] The company was nationalised in 1907, with the 15 km Chikuzen Uchino to Harada section opening in 1929.[citation needed]
The 25 km section from Wakamatsu to Nogata was double-tracked between 1893 and 1896, with the 4 km Nogata to Kotake section double-tracked between 1904 and 1906. The 8 km Kotake to Iizuka section was double-tracked between 1942 and 1944.[citation needed]
The 35 km Orio to Keisen section was electrified in 2001.[citation needed]
Former connecting/transfer lines
- Orio Station: the Nishitetsu Kitakyushu Line, a 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) gauge line electrified at 600 V DC was opened from Orio - Moji (29 km) between 1911 and 1914. It connected to a 10 km loop line opened between 1912 and 1929, and closed in 1985. The Moji - Sunatsu section closed in 1985, the Sunatsu - Kurosaki section closed in 1992, and the remainder (except for the 1 km Kurosaki - Kumanishi section, which is part of the Chikuho Electric Railway line) closed in 2000.
- Nakama Station: the 3.5 km Katsuki Line opened in 1908, with passenger services being introduced in 1912. Freight services ceased in 1974, and the line closed in 1985. A 3.8 km line from Katsuki hauled coal from 1915 until the mine closed in 1954.
- Nogata Station: A 14 km 3 ft (914 mm) gauge line to Fukumaru operated from 1914 until 1938.
- Katsuno Station: the 5 km Miyata Line opened in 1902. Freight services ceased in 1982, and the line closed in 1989. A 2 km branch to Sugamuta served the Kajima coal mine from 1904 until 1977.
- Kotake Station: the 8 km Kōbukuro Line to Futase opened in 1894 as a horse-drawn line servicing the Tetsuji mine. Steam locomotion was introduced in 1912, and passenger services in 1913. The line closed in 1969.

- Iizuka Station: the 26 km Kamiyamada Line opened to Shimoyamada in 1898, extended to Kamiyamada in 1929, and to Buzenkawasaki (as a passenger-only section) in 1966. Freight services ceased in 1980, and the line closed in 1988. A 2 km 3 ft (914 mm) gauge line from Okuma - Okumamachi operated from 1924 until 1933.
References
This article incorporates material from the corresponding article in the Japanese Wikipedia.
- ^ a b JR九州、819系「DENCHA」デビューへ エコでスマートな“蓄電池電車” [JR Kyushu to introduce 819 series "DENCHA" - an economical and smart battery train] (in Japanese). Japan: Tetsudo Shimbun. 29 January 2016. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
- ^ 地球にやさしい“蓄電池電車”「DENCHA」運行開始 JR筑豊線 [Environmentally friendly "Dencha" battery train enters service on JR Chikuho Line]. Sankei West (in Japanese). Japan: The Sankei Shimbun & Sankei Digital. 19 October 2016. Archived from the original on 19 October 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2016.

