Official (gridiron football)

In gridiron football, an official is a person who has responsibility in enforcing the rules and maintaining the order of the game.
During professional and most college football games, seven officials operate on the field. Since 2015, Division I college football conferences have used eight game officials, the Alliance of American Football (AAF) in its only season in 2019 and the 2020 version of XFL have used eight game officials. College games outside the Division I level use six or seven officials. Arena football, high school football, and other levels of football have other officiating systems, which use less than the standard seven officials. High school football played under the National Federation of State High School Associations (NFHS) rules typically use five officials for varsity and 3, 4, or 5 for non-varsity games.
Football officials are commonly, but incorrectly, referred to collectively as referees, but each position has specific duties and a specific name: Common positions include referee (which is the lead member of the officiating team), umpire, head linesman (or down judge), line judge, field judge (or back umpire), side judge, back judge and center judge. The CFL used an eighth official (with no official position name) only during the 2018 playoffs, but that official's only responsibility was watching for head contact with the quarterback. Because the referee is responsible for the general supervision of the game, the position is sometimes referred to as head referee or crew chief.[1][2][3]
Equipment
[edit]
American football officials generally use the following equipment:
- Whistle
- Used to signal a reminder to players that the ball is dead; i.e., that the play has ended or never began.
- Penalty marker or flag
- A bright-yellow-colored flag that is thrown on the field toward or at the spot of a foul. Officials in Canadian amateur football use an orange-colored flag; the CFL switched to yellow flags in 2022. For fouls where the spot is unimportant, such as fouls which occur at the snap or during a dead ball, the flag is typically thrown vertically. The flag is wrapped around a weight, such as sand or beans (or occasionally ball bearings, although this has been discouraged since an incident in an NFL game demonstrated that those could injure players), so that it can be thrown with some distance and accuracy and to ensure it remains in place and not moved by wind. Officials typically carry a second flag in case there are multiple fouls on a play. Officials who run out of flags when they see multiple fouls on a play may drop their hat or a bean bag instead.
- Bean bag
- Used to mark various spots that are not fouls but which may be possible spots of penalty enforcement or illegal touching of a scrimmage kick. For example, a bean bag is used to mark the spot of a fumble or the spot where a player caught a punt. It is typically colored white, blue, black, or orange, depending on the official's league, college conference, level of play, or weather conditions. Unlike penalty flags, bean bags may be tossed to a spot parallel to the nearest yard line, not necessarily to the actual spot.[4]
- Down indicator
- A specially designed wristband that is used to remind officials of the current down. It has an elastic loop attached to it that is wrapped around the fingers. Usually, officials put the loop around their index finger when it is first down, the middle finger when it is second down, and so on. Instead of the custom-designed indicator, some officials use two thick rubber bands tied together as a down indicator: one rubber band is used as the wristband and the other is looped over the fingers. Some officials, especially umpires, may also use a second indicator to keep track of where the ball was placed between the hash marks before the play (i.e., the right hash marks, the left ones, or at the midpoint between the two). This is important when the ball is re-spotted after an incomplete pass or a foul.
- Game data card and pencil
- Officials write down important administrative information, such as the winner of the pregame coin toss, team timeouts, and fouls called. Game data cards can be disposable paper or reusable plastic. A pencil with a special bullet-shaped cap is often carried. The cap prevents the official from being stabbed by the pencil while it is in his pocket.
- Stopwatch
- Officials will carry a stopwatch (typically a digital wristwatch) when necessary for timing duties, including keeping game time, keeping the play clock, and timing timeouts and the interval between quarters.
Uniform
[edit]
For ease of recognition, officials are usually clad in a black-and-white vertically striped shirt and black trousers with a thin white stripe down the side (this was formerly white knickers with black/white striped stirrup stockings or one-piece stockings). Officials also wear a black belt, black shoes, and a baseball cap. A letter indicating the role of each official appears on the back of the shirt at some levels, while NFL officials have numbers with a small letter or letters above. Shortly after the September 11, 2001 attacks, an American flag was added to the shirts of NFL officials, but was removed in 2006.
The stripes were introduced in the 1920s. Prior to this, plain white shirts were worn. College football referee Lloyd Olds is credited with the idea after a quarterback mistakenly handed the ball to him.[5] The officials are colloquially called "zebras" due to their black-and-white striped shirts.[6] In addition, officials wore white (or red) "newsboy" style hats.
During the 1940s, the NFL officials wore color-striped shirts that represented their positions; black and white for referees, red and white for umpires, orange and white for head linemen, and green and white for field judges. During most of the American Football League's existence (1960–1967), officials wore red-orange striped jerseys. Around this time, the hat style of the officials changed to the current baseball cap. The referees wore red hats, the others white, each with the AFL logo; the league switched to the standard black and white stripes emulating the elder league for their last two seasons before their merger with the NFL was completed (1968 and 1969). The red and orange look was recreated in 2009 during AFL Legacy Weekends to mark the 50th anniversary of the AFL's founding.
The original United States Football League, which played from February to July in its three-season existence from 1983 to 1985, allowed officials to wear black shorts for warm-weather games. The United Football League, which launched play in October 2009, featured officials wearing solid red polo shirts without stripes with black numbers and black pants. As no teams in the league wore red or orange, there was no prospect of a clash of colors. In 2010, the UFL switched to a customized version of the traditional black and white stripes, and wore this uniform until its 2012 shutdown.
In its single aborted season in 2019, The Alliance of American Football's officials wore shirts that are black and white on top with stripes from the middle down, white stars on the sleeves and the number on the back and on the left front pocket. The pants were black with no stripe and used the same hat system (white for the referee, black for all other officials) as all other levels of football.
Stripes on officials' shirts in high school are one inch wide and in college are two inches wide. Although in some states, high school officials wear shirts with two-inch or two and one-quarter inch stripes. NFL officials wear shirts with an uneven striping pattern. If wearing knickers, high school officials wear socks with a "Northwestern stripe" pattern, which college officials used to wear; NFL officials wore socks with two white stripes bordering one black stripe.
In 2006, the NFL completely redesigned the shirts, going to a sleeker-looking uniform which, however, no longer identified a given official's position from the front. Also new for 2006 were black pants with a white stripe down the side to be worn in cold weather instead of the traditional white knickers. These looser-fitting pants allow for layering of warmer clothes underneath.[7] In the 2010 season, college officials and, in many states, high school officials, were given the option of wearing the black cold-weather pants. The black pants became mandatory for college officials in 2011 and for NFL officials in 2012. In 2014, several high school associations started mandating the wearing of the black slacks for varsity level games.
From 1982 to 1986, the D-I Atlantic Coast Conference allowed officials to wear white shorts for hot weather games.
For several decades, all NFL officials wore white hats. In 1979, the referees changed to black hats with white stripes, while the other officials continued to wear white ones. Finally, in 1988, the NFL switched to the high-school and college football convention: the referee wears a white hat (with the NFL logo since Super Bowl XXXIX), and the other officials wear black hats with white stripes. This has led to referees being referred to as "white hats". It was not until 2019 that the CFL finally mirrored this convention, which had also been in use at the lower levels of football in Canada; prior to this, the referee wore a black hat, with the other officiating crew members wearing white hats with a black bill and black piping.
Officials' hats are occasionally used as markers. If a player not carrying the ball steps out of bounds (a wide receiver running a deep passing route or a player running downfield on punt coverage, for example), the official will drop his or her hat to mark the spot of where the player went out of bounds. The hat also is often used to signal a second foul called by the official on a play (by those officials who may carry only one flag); to indicate unsportsmanlike conduct committed against the official himself (as when a player shoves an official); or when some other situation requires a physical mark and the official has already used the ordinary item on the play. Some conferences and high school associations discourage the use of the hat in these situations; the bean bag will be used instead.
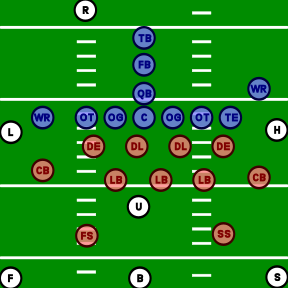
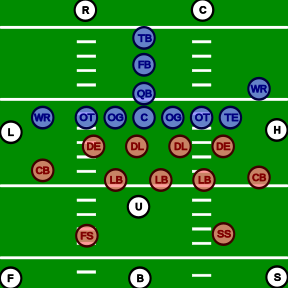
Positions and responsibilities
[edit]The following are the positions and responsibilities of each officiating positions. Prior to the snap and during the play, each official, by position, has a specific area of responsibility on the field to watch specific player positions and watch for specific fouls. Using these prescribed mechanics ensures that the officiating crew sees all 22 players and their actions wherever they occur on the field. Additionally, during the dead-ball interval between plays, each official has separate administrative duties, such as counting players, timing the play clock, monitoring (or timing) the game clock, and spotting the ball as ready for the next down.
Active
[edit]On-field
[edit]Referee
[edit]

The referee (R) is responsible for the general supervision of the game and has the final authority on all rulings. In the NFL, the referee also has final authority on the score and the down number in case of any disagreement.[8] Although all officials on the crew may be responsible for any decision involving the application or interpretation of the rules, the referee has the final decision.[9] Thus, this position is sometimes referred to as head referee and is considered to be the crew chief. The referee can be identified by a white cap, while the other officials wear black caps (the hat color scheme was reversed in the NFL from 1979 to 1987, and in Canadian football until 2019).
During each play from scrimmage, the referee is positioned behind the offensive team, favoring the right side (if the quarterback is a right-handed passer). The referee also counts offensive players.
On passing plays, the referee primarily focuses on the quarterback and approaching defenders. The referee determines any fouls for roughing the passer and, if the quarterback loses the ball, determines whether the ball was fumbled or if an incomplete pass had been thrown.
On running plays, the referee observes the quarterback during and after the time he hands off the ball to a running back, focusing on him until the action has cleared in case the play becomes a play action pass or some other trick passing play. After it has been established that the running back will keep the ball, the referee then checks the running back and the contact behind him.
During punts and field goals, the referee observes the kicker (and holder) and any contact made by defenders approaching them. On a punt out of bounds, referees use their vantage point behind the punter to direct the nearest sideline official to the spot where the ball went out of bounds.
In college football, the NFL, and other professional leagues, and in some high school games, the referee announces penalties and the jersey numbers of the players committing them (required for college and professional games; high school referees are no longer prohibited from announcing the number of a player committing a foul; on rare occasions, the player's position is announced instead of the jersey number), and clarifies complex and/or unusual rulings over a wireless microphone to both fans and the media. CFL referees, unlike their counterparts in the NFL and American college football, identify the team committing the foul when announcing penalty enforcement, instead of using "offense" or defense".[10]
During instant replay reviews in the NFL, the referee confers with the NFL's replay center in New York City, which makes the final ruling. In college football, the referee confers with a replay official, who is stationed in the press box above the field, on the play and then announces the final result over the wireless microphone.
In addition to the general equipment listed above, the referee also carries a coin to conduct the pregame (and if necessary, overtime) coin toss.
Umpire
[edit]
The umpire (U) traditionally stands behind the defensive line and linebackers, observing the blocks by the offensive line and defenders trying to ward off those blocks, looking for holding or illegal blocks. Prior to the snap, he counts all offensive players.
During passing plays, umpires move forward towards the line of scrimmage as the play develops to penalize any offensive linemen who move illegally downfield before the pass is thrown or penalize the quarterback for throwing the ball when beyond the original line of scrimmage. The umpire also assists in ruling incomplete passes when the ball is thrown short.
As the umpire's traditional starting position is situated where much of the play's initial action occurs, it is considered by many to be the most dangerous officiating position.[6] For this reason, the NFL carried out experiments in the 2001 preseason with the umpire placed in the offensive backfield adjacent to the referee.[11] In March 2010, the NFL announced that this repositioning would be permanent, after five major injuries were suffered by umpires in 2009 (two concussions and three knee or shoulder injuries requiring surgery).[12] From 2010 to 2015, the umpire returned to the defensive side of the line of scrimmage during the last five minutes of the second half. In 2016, this provision was deleted, and the umpire stood in the offensive backfield on all plays. In 2023 the NFL returned the umpire to the defensive backfield with the side judge for field goal and extra point attempts.[13]
In addition to on-field duties, the umpire is responsible for the legality of all of the players' equipment.
Down judge/head line-judge/head linesman
[edit]The down judge (DJ) in the NFL, CFL, and the 2022 version of the USFL; head line-judge (H or HL) in college and some states for high school football; or head linesman (H or HL) stands at one end of the line of scrimmage (usually the side opposite the press box, always with the chain crew), looking for possible offsides, encroachment and other fouls before the snap. As the play develops, the head linesman is responsible for judging the action near that sideline, including whether a player is out of bounds. Responsibilities on a passing play include watching the receivers near that sideline to a point five to seven yards beyond the line of scrimmage.
The down judge/head line-judge marks the forward progress of the ball and is in charge of the chain crew with regard to its duties. In addition to the general equipment listed above, the head linesman/down judge also carries a chain clip that is used by the chain crew to properly place the chains and ensure an accurate spot when measuring for a first down.
The position was traditionally known as head linesman. The NFL transitioned to the gender-neutral term down judge in 2017, when it moved Sarah Thomas to the position.[14] The following year, the CFL followed suit with the name change. The NCAA transitioned to the gender-neutral term head line-judge.[15] Some states have revised their high school officials manuals to also use the term head line-judge.[16]
Line judge
[edit]The line judge (L or LJ) assists the head linesman/down judge at the other end of the line of scrimmage, looking for possible offsides, encroachment and other fouls before the snap. As the play develops, line judges are responsible for the action near their sideline, including whether a player is out of bounds. A line judge is also responsible for counting offensive players.
During the start of passing plays, they watch the receivers near their sideline to a point five to seven yards beyond the line of scrimmage. Afterwards, the line judge moves back towards the line of scrimmage, ruling if a pass is forward, a lateral, or if it is illegally thrown beyond the line of scrimmage.
On punts and field goal attempts, the line judge also determines whether the kick is made from behind the line of scrimmage.
In some high school and minor leagues, the line judge is the official timekeeper of the game. In other leagues, the responsibility is assigned to the field judge or the back judge.
For the NFL, this was the sixth official, added in 1965.[17][18]
Field judge
[edit]The field judge (F or FJ) or back umpire (BU) works downfield behind the defensive secondary on the same sideline as the line judge. The field judge makes decisions near the sideline on his or her side of the field, judging the action of nearby running backs, receivers and defenders. They rule on pass interference, illegal blocks downfield, and incomplete passes, and are also responsible for counting defensive players. The field judge has sometimes been the official timekeeper, and in a number of leagues will run the game clock on a six-person crew.[19][20]
Together with the back judge, the field judge rules whether field goal attempts are successful.
For the NFL, this was the fourth official, added in 1929.[18]
The position is called the back umpire in Canadian amateur football; all other leagues use the term field judge. However, in the CFL, this was the fifth official, added in 1951.[21]
Side judge
[edit]The side judge (S or SJ) works downfield behind the defensive secondary on the same sideline as the head linesman or down judge. Like the field judge, the side judge makes decisions near the sideline on the nearest side of field, judging the action of nearby running backs, receivers and defenders. Side judges rule on pass interference, illegal blocks downfield, and incomplete passes, and also count defensive players. During field goal attempts field judges serve as a second umpire.
In college football, the side judge is responsible for either the game clock or the play clock, which are operated by an assistant that the side judge directs.
For the NFL and CFL, this was the seventh official, added in 1978 and 1991 respectively.[22][21]
Back judge
[edit]
The back judge (B or BJ) stands deep behind the defensive secondary in the middle of the field, judging the action of nearby running backs, receivers (primarily the tight ends) and nearby defenders. Like the side judge and the field judge, the back judge rules on pass interference, illegal blocks downfield, and incomplete passes. Back judges cover the area in the middle of the field between themselves and umpires. The back judge has the final say regarding the legality of kicks not made from scrimmage (kickoffs). The back judge is also responsible for ruling a "delay of game" infraction if the play clock expires.
Together with the field judge, the back judge rules whether field goal attempts are successful.
In college football and some high school leagues, the back judge is responsible for either the game clock or the play clock, which are operated by an assistant that the back judge directs.
For the NFL, this was the fifth official, added in 1947.[18][23] However, in the CFL, this was the sixth official, added in 1979.[21]
Center judge
[edit]The center judge (C) is positioned beside the referee in the offensive backfield adjacent to the referee, positioned equivalent to the umpire. Such responsibilities include ball spotting, penalty marking, and assisting the referee and umpire.[24] In NCAA Division I FBS, the Center Judge becomes the "Acting Referee" should the referee become injured and unable to continue officiating. The NFL has experimented with the center judge in the 2015 preseason for 5 or 6 games,[25][26][note 1] but instead positioned 20 yards downfield of the line of scrimmage to observe the center and guards.[26] In the professional level, the center judge has yet to be used in either the NFL or CFL; however, two leagues, the AAF and the 2020 XFL utilized the center judge.
In 2013, the D-I Big 12 Conference began using an eighth official, an alternate judge (A). The alternate judge stands in the offensive backfield opposite the head referee, in the same position as an NFL umpire, while keeping the Big 12 umpire in his traditional position behind the defensive line. The alternate judge will also help spot the ball.[27] In the 2014 season, any conference that wanted to use the eight-official system could do so on an experimental basis. The Atlantic Coast Conference, Big Ten Conference, American Athletic Conference, and Big 12 Conference implemented an eight-official system for games; the eighth official's position name changed to center judge (C) but this judge's location on the field was the same as the alternate judge was in 2013. The eight-person crews were used in bowl games, including games in the College Football Playoff, since officials from conferences using eight-person crews were chosen for the three playoff games. In the 2015 season, the center judge became standard across all of FBS. It is also used by the Kansas Jayhawk Community College Conference.
Ball-spotting official
[edit]In the 2020 version of the XFL, there is one official dedicated to spotting the ball, with the purpose to reduce downtime during the game. This official wears a red cap.[28]
Transitioning during turnovers, punts, and other returns
[edit]During turnovers, punts, and other returns by the defense, and play transitions from one direction to the other, the officials must also adjust. The field judge, side judge, and back judge become the trail/back positions, and the referee, head linesman/down judge, and line judge then become the lead/front positions. The umpire, having a traditional position in the middle of the field, usually stays stationary until the returner and the other players are past.
Off-field
[edit]Replay official
[edit]The replay official is located upstairs in the stadium of the game played. They can initiate replay reviews on in certain circumstances.
In CFL football, the replay official is not located at the stadium itself, but rather at the CFL Command Centre at the CFL Head Office in Toronto. The official is responsible for the final determination of challenges made by the two teams' head coaches; and in the final 3 minutes (and all of overtime) of the game initiating a review of any play they believe warrants such attention. The official also reviews all scoring plays during the game. When a review is underway, the referee speaks to the replay official via headset at the sideline. The replay official has the final call over all challenges and reviews.[29]
U Sports and other leagues in Canada do not utilize the replay-review process.
Sky judge
[edit]The Alliance of American Football used the sky judge, who had the authority to assess penalties (or overturn penalties) for unsafe play, and (within the final five minutes of the fourth quarter) either call or overturn pass interference penalties against either the offense or defense. The XFL (2020) has adopted this.[30]
Alternate
[edit]One or more alternate(s) may be designated to replace any on-field official who is injured or otherwise unable to finish a game.
In some leagues, alternates are only appointed for postseason play when there are typically an ample number of qualified officials available to work the reduced number of games.
Inactive
[edit]CFL eighth official
[edit]Late in the 2018 playoffs, the CFL added an eighth official to the on-field crew; it did not have an official position title. This official lined up in the offensive backfield, and whose sole responsibility was judging helmet contact on the quarterback. This position was only used in the Eastern and Western finals and the Grey Cup.[31] The eighth official did not return in 2019.
Deep judge
[edit]In four games in the 2010 preseason, the NFL experimented with an eighth official, a deep judge (DJ), in the defensive backfield opposite the back judge. The primary responsibility for this new position is the action of receivers, and it allowed the NFL to adjust coverage after the umpire was moved to the offensive backfield. The experiment was continued for 12 games in the 2011 preseason, and was then discontinued afterwards.[32]
Second umpire
[edit]For the 2015 and 2019 NFL preseasons, for 8 and 2 games respectively, the NFL experimented with the umpire (U2),[26] positioned in the offensive backfield. Their responsibilities were to focus on center pre-snap and offensive guards and tackles.[25]
Middle judge
[edit]For the 2016, 2017, and 2019 NFL preseasons, for 16, 5, and 2 games respectively, the NFL experimented with the middle judge (MJ).[26] Main responsibilities were to look for holding near the line of scrimmage. The middle judge is placed in the center of the field, adjacent to the back judge (BJ).
List of officiating systems
[edit]| Officiating System | Officials | Leagues |
|---|---|---|
| Three | Referee (R), umpire (U), head line-judge[note 2] (HL) | Youth |
| Four | Referee, umpire, head line judge, line judge (LJ) | Youth varsity, high school sub-varsity, some high school varsity |
| Five | Referee, umpire, head line judge, line judge, back judge (BJ) | Arena football, high school varsity, semi-pro |
| Six | Referee, umpire, head line judge, line judge, field judge (FJ), side judge (SJ) | High school |
| Seven | Referee, umpire, head line-judge/down judge (DJ),[note 3] line judge, back judge, field judge, side judge | High School, NFL, CFL, 2022 USFL, NCAA Division I FCS, NCAA Division II, NCAA Division III, NJCAA |
| Eight | Referee, umpire, head line-judge, line judge, back judge, field judge, side judge, center judge (CJ) | NCAA Division I FBS, AAF, XFL |
History
[edit]When the NFL began in 1920, only three officials (referee, umpire, and head linesman) were used. The field judge was added in 1929 and the back judge in 1947. In response to scrambling quarterbacks (Fran Tarkenton in particular), the line judge was added in 1965 to watch the opposite side of the line of scrimmage.[17][18] The side judge was added for 1978, when the NFL implemented new rules to open up the passing game.[22] In 2017, the NFL renamed the head linesman to down judge.
Up until 1950, the forerunner leagues to the present-day Canadian Football League (founded in 1958) used only four officials: The referee, umpire, head linesman and line judge. Over the next 40 years, the system would change into what is more-or-less equal to what most American football leagues use today, a seven-official system. The first new addition to the crew was the field judge (also referred to as the back umpire) in 1951, then the next addition being the back judge in 1979, and the seventh official, the side judge being added in 1991.
The practice of having the referee announce penalties or clarify complex and/or unusual rulings over a wireless microphone started in the NFL in 1975. College football and other professional leagues soon adopted this practice.
For years, college football referees were prohibited from announcing the number of a fouling player, except in the Western Athletic Conference and Mountain West Conference (and in all conferences when ejecting the offending player). In 2004, the rules were changed throughout college football to permit the fouling player's number to be announced. Under NFHS rules used in all states except Texas for high school games, announcing the player's number went from "not allowed" to "not required" in 2014.
Among the various Halls of Fame for major North American sports, the Pro Football Hall of Fame is unique in that it did not induct any officials until Art McNally in 2022; the Baseball Hall of Fame, Basketball Hall of Fame, and Hockey Hall of Fame have each inducted numerous game officials as members. (1966 inductee Hugh L. Ray was inducted for his 14-season tenure as the league's head of officiating, an off-field position.) However, in Canada, the Canadian Football Hall of Fame has inducted a few game officials as members of their Hall of Fame.
NFL employment status
[edit]Because their regular season spans only 18 weeks, the NFL is one of only two major sports leagues in the United States that only pay their officials on a contract basis as opposed to being full-time salaried employees, the other being Major League Soccer. Advantages to this system include being able to eliminate unqualified officials simply by not offering them a contract the following season. Critics argue that full-time officials would be free from the distractions of a second job, but proponents of part-time officials point out that the NFL would lose a number of qualified officials because many of them are owners, presidents, or CEOs of various companies. Proponents also argue that there is only one game per week and the regular season is only four months long, and that having full-time officials does not necessarily guarantee that they will make fewer officiating mistakes. The level of training and review in which NFL officials participate makes additional time redundant. In any event, veteran officials can earn substantial salaries for their work. The National Football League Referees Association (NFLRA) serves as the union that represents officials in the NFL.
Female officials
[edit]Historically, American football officials have been men.
In 2007, Sarah Thomas became the first woman to officiate a major college football game, working a game between Memphis and Jacksonville State.[33] Thomas later became the first woman to officiate a bowl game when she worked as a line judge during the 2009 Little Caesars Pizza Bowl between Marshall and Ohio.[34] Since then, other women have officiated Division I college football games.[35] In 2015, Thomas became the NFL's first permanent female official.[36] She entered as a line judge, and moved to the down judge (head linesman) role in her third season.[14][37] In 2017, she was an alternate in an NFL wild card game.[38] In 2019, she became the first female official to officiate an NFL playoff game in an AFC divisional round between Los Angeles Chargers at New England Patriots.[39] She worked NFC divisional games in 2020 and 2021,[38] and was the down judge for Super Bowl LV.
In 2021, line judge Maia Chaka became the NFL's second full-time female on-field official. Robin DeLorenzo became the third the next season when she was hired as a down judge.
Terri Valenti became the first woman to officiate professional football when she began working United Football League games in 2009.[40] The UFL later hired Thomas in 2010.[41] In 2017, the NFL hired her as a replay official. She officated the 2020 AFC Championship game.[38] She is also doing replay officiating for the XFL.[42][43]
In 2012, Shannon Eastin became the first female official of an NFL game.[44] She was a replacement line judge while the league had locked out the regular officials due to a labor dispute. Darin Gantt of Profootballtalk.com and Sam Farmer of the Los Angeles Times lamented that it was in this manner that this gender barrier was broken.[45][46]
In 2017, Amanda Sauer-Cook became the first ever female referee in a Division I game,.[47] Her first game as referee was Morgan State at Rutgers.[47] She is also the first openly bisexual official to work in a major professional football league and in college football.[42][47] For the defunct 2019 Alliance of American Football, and the 2020 XFL, she works as center judge.[48][43]
In 2019, the AAF had three female officials. In 2020, the XFL has six female officials. Having six total officiating crews, there will be one female official for each crew. There is also one female replay official.[42]
See also
[edit]- List of American Football League officials
- List of National Football League officials
- Super Bowl officials
- Art McNally Award
- American football rules
- 2012 NFL referee labor dispute
Notes
[edit]- ^ ESPN says the center judge was used for six games, while Football Zebras says it was used for five games.
- ^ The traditional term head linesman is being phased out in favor of head line-judge in high school and youth football
- ^ In 2017, NFL switched from head linesman to down judge as to the gender-neutral term following Sarah Thomas moving from line judge to the position. The CFL did the same the following year.
References
[edit]- ^ Markbreit, Jerry (November 23, 2005). "Jerry Markbreit's answers: The former NFL referee answers readers' questions each week throughout the season". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on October 19, 2006.
- ^ Pascoe, Bruce (August 14, 2006). "Grad of CDO finds fame as NFL referee". Arizona Daily Star. Tucson. Archived from the original on January 8, 2007.
- ^ Zimmerman, Lisa (July 10, 2001). "Replay booth: Positively no visitors". NFL.com. Archived from the original on 2007-07-17. Retrieved 2007-03-10.
- ^ "SFFOA Oritentation Guide". South Florida Football Officials Association. April 1, 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-19.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Uni Watch: How the zebra got its stripes Archived 2010-01-16 at the Wayback Machine, Slate.com
- ^ a b Roberts, Rich (October 24, 1985). "AN NFL UMPIRE'S . . . LIFE IN THE WAR ZONE - For His Own Protection, This Official Must Read Defenses and Offenses; Draw Plays Are Murder". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on October 2, 2011. Retrieved 2009-09-02.
- ^ "Fashion statement: NFL refs to sport new uniforms". ESPN. 4 August 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-07-12.
- ^ "NFL 2013 Rulebook" (PDF). NFL. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 9, 2013. Retrieved December 2, 2013.
Rule 15-2-1: [The referee] is the final authority for the score, and the number of a down in case of a disagreement. His decisions upon all matters not specifically placed under the jurisdiction of other officials, either by rule or the officials' manual, are to be final
- ^ "NFL 2013 Rulebook" (PDF). NFL. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 9, 2013. Retrieved December 2, 2013.
Rule 15-1-6: All officials are responsible for any decision involving the application of a rule, its interpretation or enforcement ... if there is a disagreement, the Referee's decision will be the deciding factor
- ^ "Canadian Football League Rulebook" (PDF). 2012-05-11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-05-11. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ "NFL experimenting with putting umpire in offensive backfield". CBC. August 4, 2001. Archived from the original on September 9, 2010. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
- ^ Mortensen, Chris (March 22, 2010). "NFL moves umpires for safety's sake". ESPN. Archived from the original on March 26, 2010. Retrieved 2010-03-23.
- ^ Schultz, Mark (10 August 2023). "New umpire mechanic on field goals and extra points is the old mechanic". footballzebras.com. Retrieved 7 September 2023.
- ^ a b Austro, Ben (June 16, 2017). "NFL has a new name for the head linesman position: down judge". Football Zebras. Archived from the original on June 19, 2017. Retrieved June 16, 2017.
- ^ Football Officiating Manual for a Crew of 7 or 8. Collegiate Commissioners Association. 2021. pp. 38 et al. ISBN 978-1-58208-500-5.
- ^ GHSA Football Officials Manual 2019. Georgia High School Association. 2019. p. 36.
- ^ a b "Football so fast, complex: NFL adding sixth official". Spokesman-Review. Spokane, Washington. Associated Press. July 25, 1965. p. 3, sports.
- ^ a b c d Strickler, George (February 20, 1965). "Sixth N.F.L. official to watch scramblers, clock". Chicago Tribune. p. 1, sec. 2. Archived from the original on October 8, 2015.
- ^ GHSA Football Officials Manual 2009 (PDF). Georgia High School Association. p. 60. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-03-31.
- ^ "2009 FOOTBALL MANUAL For IOA Officials, Observers, Athletic Directors, and Coaches" (PDF). Intercollegiate Officiating Association. p. 12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 26 February 2010.
- ^ a b c "CFL Guide & Record Book 2017 Edition" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-12-03. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ a b "NFL revises rules to promote points". Milwaukee Journal. UPI and AP. March 15, 1978. p. 18, part 2.
- ^ "National League officials to work in crews of six (five)". Milwaukee Journal. Associated Press. August 19, 1947. p. 6, part 2.
- ^ "Why the ACC will use an eighth official called the 'center judge' in all conference games this season". syracuse. 2014-07-08. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ a b "Inside Slant: Using Microsoft tablets for replay and more preseason experiments". ESPN.com. 2015-08-18. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ a b c d Austro, Ben (2019-08-16). "NFL taking another look at adding an 8th official in preseason test". Football Zebras. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ Dodd, Dennis (July 22, 2013). "Big 12 adds eighth official just to keep up with up-tempo offenses". CBS Sports. Archived from the original on December 4, 2013. Retrieved December 7, 2013.
- ^ "XFL Rules". www.xfl.com. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ "Canadian Football League Ruleboook" (PDF). 2012-05-11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-05-11. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ "XFL Q&A: Oliver Luck on lessons learned, Colin Kaepernick and sports betting". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ Shapiro, Michael (15 November 2018). "CFL adds eighth official to monitor hits to helmet". Sports Illustrated. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ "NFL experimenting with 8th on-field official". August 25, 2011. Retrieved August 25, 2011.[dead link]
- ^ "Thomas will become first female referee in top tier of college football". ESPN. Associated Press. September 14, 2007. Archived from the original on August 14, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ "Thomas on field for Little Caesars Bowl". Yahoo! Sports. Associated Press. December 27, 2009. Archived from the original on November 8, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ Reiter, Bill (September 6, 2011). "Female ref Conti still chases NFL dream". Fox Sports. Archived from the original on August 7, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ "NFL makes Sarah Thomas first full-time female official". NFL.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2017. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ^ "Sarah Thomas, NFL's 1st Full-Time Female Ref, Gets 2015 Season Assignment". yahoo.com. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 5 May 2018.
- ^ a b c Regan, Brett (2020-01-16). "Meet Sarah Thomas: The Only Female Official in NFL Playoff History". FanBuzz - Sports News - NFL | NCAA | NBA | WWE. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ Conway, Tyler. "Sarah Thomas Becomes 1st Woman to Officiate NFL Playoff Game". Bleacher Report. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ "UFL hires first female official in pro football". Newsday. October 6, 2009. Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ "United Football League Announces Officials And Explains Rules Differences For 2010 Season". OurSportsCentral.com. 2010-07-29. Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2010-07-29.
- ^ a b c Filipe, Cameron; Austro, Ben (2020-01-28). "XFL breaks new ground by having a woman on every officiating crew". Football Zebras. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ a b Austro, Ben (2020-01-28). "Officiating crews for the 2020 XFL season". Football Zebras. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ Farmer, Sam (July 20, 2012). "Former officials are at odds with the NFL, too". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on July 29, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
One of them is Shannon Eastin, who has been a referee in the Mid-Eastern Athletic Conference and other leagues. The NFL has never had a woman work as an on-field game official
- ^ "NFL's replacement officials would include first female ref". ProFootballTalk. July 22, 2012. Archived from the original on July 28, 2012. Retrieved August 6, 2012.
- ^ "Football referee Shannon Eastin a pioneer, but also a pawn". Los Angeles Times. August 8, 2012. Archived from the original on August 8, 2012. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
- ^ a b c Lewis, Josh (2020-02-05). "XFL makes history again by opening doors to LGBTQ officials". Football Zebras. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
- ^ Austro, Ben (2019-02-08). "Officiating crews for the 2019 AAF season". Football Zebras. Retrieved 2020-02-23.
External links
[edit]- NFL Rulebook - digest of rules, updated 2023
- football.refs.org - officiating rules and mechanics for college and high school football.