Biu–Mandara languages
Appearance
| Biu–Mandara | |
|---|---|
| Central Chadic | |
| Geographic distribution | Nigeria, Chad, Cameroon |
| Linguistic classification | Afro-Asiatic
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | bium1280 |
The Biu–Mandara or Central Chadic languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon. The most widely spoken is Kamwe, with 300,000 speakers.
Languages
Gravina (2014)
Gravina (2014) classifies Central Chadic as follows, as part of a reconstruction of the proto-language. Letters and numbers in parentheses correspond to branches in previous classifications. The greatest changes are breaking up and reassigning the languages of the old Mafa branch (A.5) and Mandage (Kotoko) branch (B.1).[1]
- South
- Hurza
- North
- Margi–Mandara–Mofu
- Margi (A.2)
- Mandara (A.4):
- Mofu (part of South A.5 Mafa)
- Tokombere: Ouldeme, Mada, Muyang, Molokwo
- Meri: Zulgo, Gemzek, Merey, Dugwor
- Mofu Proper: Mofu North, Mofu-Gudur
- Maroua
- Maroua (part of South A.5 Mafa (c)): Giziga North, Giziga South, Mbazla
- Lamang
- Higi
- Higi (A.3): Bana, Hya, Psikyɛ, Kamwe, Kirya-Konzel
- Musgum – North Kotoko
- Kotoko Centre
- Kotoko South
- Gidar
- Margi–Mandara–Mofu
Jilbe was not classified, as no sources were available.
Blench (2006)
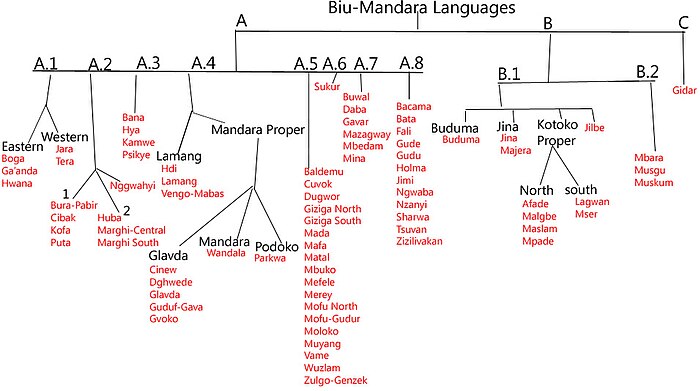
The branches of Biu–Mandara traditionally go by either names or letters and numbers in an outline format. Blench (2006) organizes them as follows:[3]
- Tera (A.1): Tera, Pidlimdi (Hinna), Jara, Ga'anda, Gabin, Boga, Ngwaba, Hwana
- Bura–Higi
- Bura (A.2): Bura-Pabir (Bura), Cibak (Kyibaku), Nggwahyi, Huba (Kilba), Putai (Marghi West), Marghi Central (Margi, Margi Babal), Marghi South
- ? Kofa
- Higi (A.3): Kamwə (Psikyɛ, Higi), Bana, Hya, ? Kirya-Konzəl
- Wandala–Mafa
- Wandala (Mandara) (A.4)
- Mafa (A.5)
- Northeast Mafa: Vame (Pəlasla), Mbuko, Gaduwa
- Matal (Muktele)
- South Mafa
- (a) Wuzlam (Ouldémé), Muyang, Maɗa, Məlokwo
- (b) Zəlgwa-Minew, Gemzek, Ɗugwor, Mikere, Merey
- (c) North Giziga, South Giziga, North Mofu, Mofu-Gudur (South Mofu), Baldemu (Mbazlam)
- (d) Cuvok, Mafa, Mefele, Shügule
- Daba (A.7)
- Bata (Gbwata) (A.8): Bacama, Bata (Gbwata), Sharwa, Tsuvan, Gude, Fali of Mubi, Zizilivakan (Ulan Mazhilvən, Fali of Jilbu), Jimi (Jimjimən), Gudu, Holma (†), Nzanyi
- Mandage (Kotoko) (B.1)
- Buduma (Yedina)
- East–Central
Newman (1977)
Central Chadic classification per Newman (1977):
Notes
- ^ Gravina, R. (2014). The phonology of Proto-Central Chadic: the reconstruction of the phonology and lexicon of Proto-Central Chadic, and the linguistic history of the Central Chadic languages (Doctoral dissertation, LOT: Utrecht).
- ^ Languages are closer to each other than are those of the northern branch
- ^ Blench, 2006. The Afro-Asiatic Languages: Classification and Reference List (ms)
References
- Central Chadic resources at africanlanguages.org