Benzenesulfonic acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
Benzene sulphonic acid; Benzenesulphonic acid; Phenylsulfonic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.399 | ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6O3S | |||
| Molar mass | 158.17 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 (47 °C) | ||
| Melting point | * 44 °C (hydrate)
| ||
| Boiling point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) | ||
| Soluble | |||
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in alcohol, insoluble in non-polar solvents | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | -2.8[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Corrosive | ||
| Flash point | >113 °C | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Benzenesulfonic acid is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SO3H. It is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It forms colorless deliquescent sheet crystals or a white waxy solid that is soluble in water and ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene and insoluble in carbon disulfide and diethyl ether. It is often stored in the form of alkali metal salts. Its aqueous solution is strongly acidic.
Preparation
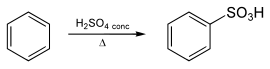
Benzenesulfonic acid is prepared from the sulfonation of benzene using concentrated sulfuric acid:
This conversion illustrates aromatic sulfonation, which has been called "one of the most important reactions in industrial organic chemistry."[3]
Reactions
Benzenesulfonic acid exhibits the reactions typical of other aromatic sulfonic acids, forming sulfonamides, sulfonyl chloride, and esters. The sulfonation is reversed above 220 °C. Dehydration with phosphorus pentoxide gives benzenesulfonic acid anhydride ((C6H5SO2)2O). Conversion to the corresponding benzenesulfonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) is effected with phosphorus pentachloride.
It is a strong acid, being dissociated in water.
Applications
The alkali metal salt of benzenesulfonic acid was once widely used in the production of phenol:
- C6H5SO3Na + 2 NaOH → C6H5ONa + Na2SO3
- C6H5ONa + HCl → C6H5OH + NaCl
The process has been largely displaced by the Hock process, which generates less waste. Benzenesulfonic acid is mainly consumed by conversion to other specialty chemicals. A variety of pharmaceutical drugs are prepared as salts of benzenesulfonic acid and are known as besylates or besilates.
References
- ^ Benzenesulfonic acid, Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Guthrie, J. P. Hydrolysis of esters of oxy acids: pKa values for strong acids. Can. J. Chem. 1978, 56, 2342-2354.
- ^ Otto Lindner, Lars Rodefeld "Benzenesulfonic Acids and Their Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03 507