'Abd Allah II ibn 'Ali 'Abd ash-Shakur
| 'Abd Allah II Ibn 'Ali 'Abd-Ash Shakur الأمير عبدالله الثاني إبن علي عبدالشكور Amir Abdullahi | |
|---|---|
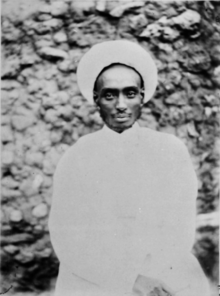 Amir Hajji Abdallah II of Harar | |
| 18th and last Emir of Harar | |
| Reign | 1884–1887 |
| Predecessor | Muhammad ibn 'Ali 'Abd ash-Shakur |
| Born | 1850s Harar, Emirate of Harar |
| Died | 1930 Harar, Ethiopian Empire |
| Dynasty | Dawud Dynasty |
| Religion | Sunni Islam |
Amir Abdullahi, formally Abd Allah II ibn 'Ali 'Abd ash-Shakur or Amir Hajji 'Abdu'llahi II ibn 'Ali 'Abdu's Shakur (c. 1850s – 1930), was the last Emir of Harar and ruled from late 1884 to 26 January 1887, when the state was terminated, following the defeat of the Harari troops at the Battle of Chelenqo on 9 January.
According to R. A. Caulk, Amir Abdullahi was the son of Muhammad ibn `Ali `Abd ash-Shakur by Kadija, the daughter of Emir `Abd al-Karim ibn Muhammad.[1] To secure his hold on the emirate of Harar, his father had married Abdullahi to the daughter of Ahmad III ibn Abu Bakr, his predecessor. Abdullahi was a student of and an Islamic fundamentalist.[2][3]
Egypt had occupied Harar since 1875, but the local commander reported that maintaining that occupation was costly and logistically challenging,[4] so the Egyptians withdrew leaving Amir Abdullahi with the Khedive's firman to rule Harar.[5] He was given "a few hundred soldiers trained by one of the British officers, 300 to 400 rifles, some cannon, and munitions, a force hardly sufficient to garrison Harar and Jaldessa, let alone police the trade routes and ensure the security of the state."[6] During his brief tenure Abdullahi expanded the Jami Mosque.[7]
Amir Abdullahi sought to make Harar a theocratic state. According to the Italian traveller Alberto Pogliano, he destroyed the old Egyptian barracks, which he had little use of for his small army, and turned them into mosques. At the same time he sought an alliance with the Issa Somalis, who controlled the trade route to Zeila, and fought against their traditional enemies the Oromos whom he stigmatized as infidels. Insistent on re-establishing Islamic principles he ordered anyone coming to him in quest of justice to pray and recite verses from the Quran in his presence. At the same time he issued a decree against drunkenness, which the Egyptians had on the whole regarded with a tolerant eye, and proclaimed his subjects' freedom to engage in the slave trade which had been officially prohibited by Egypt.[8]
Amir Abdullahi grew anxious about the growing Ethiopian threat to his domain, and accused the resident Europeans of co-operating with Menelik II. His situation had deteriorated by July 1885, according to historian Harold Marcus, with a population that had grown "uncontrollable, European traders [who] became virtual prisoners in their homes and shops, and the adjacent Oromos [who] raided the town."[9] In response, the Amir introduced a new currency which impoverished the local population.[10] The neighboring Oromo and Somali deserted Harar's markets and the town's economy collapsed. Amir Abdullahi ordered all non-citizens in the town to either convert to Islam or leave.[11]
Hearing of an Italian trade mission headed to Harar, he ordered troops to intercept them and to turn them back or kill them. The Italians were killed at Jildessa.[11] This gave Menelik II a casus belli, based on protecting trade, with the added impetus to prevent the Italian takeover of the city.[12][13]
At around the end of 1886 Menelik II ordered his troops to march eastwards towards Harar. He seems to have hoped for a time to make Amir Abdullahi accept his suzerainty without battle, but the chief proved obdurate. Tradition states that when his advisers warned him of the size of the Shewan army, and suggested that he should temporize by handing over some weapons, he proudly retorted, "I did not ask you how much power Menelik possesses; I asked you a simple question, ‘Will the book allow us to give up arms to a kafir?’" The Amir is said to have thereupon imprisoned his courtiers, and prepared to embark on a jihad, or holy war.[14][15]
Amir Abdullahi responded to the advance force led by Walda Gabryiel, decisively defeating them at the Battle of Hirna. When the Negus Menelik personally led a second attack a few months later, the Amir misjudged the quality of these troops and attempted to repeat his earlier success with a second night attack. "Had he allowed the enemy to attack the walled city, where his few Krupp cannon might have been effective, the Shewans might have suffered a defeat with serious political consequences," Marcus notes. However, the Battle of Chelenqo destroyed the Amir's army, the Amir fled, with his wives and children, into the desert country east of Harar. He left his uncle Ali Abu Barka to submit to Menelik and ask clemency for the people of Harar.[10][12]
Abdullahi later returned to Harar to live as a Sufi religious scholar. He died there in 1930.[16]
See also
[edit]Notes and references
[edit]- ^ Caulk, Richard A. (1977). "Harär Town and Its Neighbours in the Nineteenth Century". Journal of African History. 18 (3): 369–386, page 384. JSTOR 180638.
- ^ Tesfai, Yacob (2010). Holy Warriors, Infidels, and Peacemakers in Africa. New York: Palgrave Macmillan. p. 93. ISBN 978-0-230-10427-3.
- ^ Marcus, Harold G. (2002). A History of Ethiopia. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-520-22479-7.
- ^ Kavas, Ahmet (2013). Osmanlı-Afrika İlişkileri (in Turkish) (third ed.). Istanbul: Kitabevi Yayınları. p. 138. ISBN 9786055397029.
- ^ Pankhurst, E. Sylvia (1958). "Harar under Egyptian rule" (PDF). Ethiopian Observer. Vol. 2, no. 2. pp. 56–58. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 January 2022. Retrieved 1 January 2022.
- ^ Marcus, Harold G. (1995). The Life and Times of Menelik II: Ethiopia 1844-1913. Lawrence, Kansas: Red Sea Press. pp. 89–92. ISBN 978-1-56902-010-4.
- ^ Insoll, Timothy; Zekaria, Ahmed (2019). "The Mosques of Harar: An Archaeological and Historical Study". Journal of Islamic Archaeology. 6 (1): 81–107, page 88. doi:10.1558/jia.39522. hdl:10871/39031.
- ^ Pankhurst, Richard (1982). History Of Ethiopian Towns. p. 190. ISBN 9783515032049.
- ^ Marcus 1995, p. 90
- ^ a b Marcus 2002, p. 84
- ^ a b Baynes-Rock, Marcus (2015). "Chapter 1: Past Finding Around Harar". Among the Bone Eaters: Encounters with Hyenas in Harar. University Park, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State University Press. ISBN 978-0-271-06720-9.
- ^ a b Marcus 1995, pp. 91–92
- ^ Bahru, Zewde (2002). A History of Modern Ethiopia, 1855–1991. Athens, Ohio: Ohio University Press. p. 86. ISBN 978-0-85255-786-0.
- ^ Caulk, Richard A. (1971). "The Occupation of Harar: January 1887". Journal of Ethiopian Studies. 9 (2). Institute of Ethiopian Studies: 1–20. JSTOR 41967469.
- ^ Pankhurst, Richard (1982). History Of Ethiopian Towns. p. 254. ISBN 9783515032049.
- ^ Waldron, Sidney R. (1981). "The political economy of Harari-Oromo relationships (1554-1975)". Refugee Studies Centre. p. 23. Archived from the original on 31 October 2010., republished in revised form as Waldron, Sidney R. (1984). "The political economy of Harari-Oromo relationships (1554-1975)". Northeast African Studies. 6 (1/2): 23–39. JSTOR 43663302.
