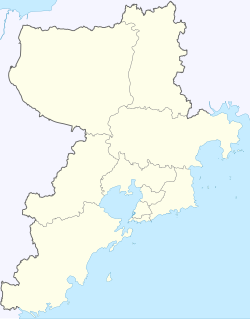
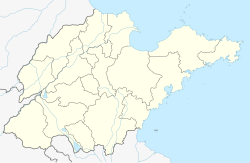
Huangdao, Qingdao
Huangdao District / West Coast New Area
黄岛区 / 西海岸新区 | |
|---|---|
| Huangdao District / West Coast New Area | |
 | |
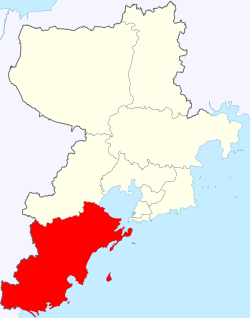 Huangdao / West Coast New Area in Qingdao | |
| Coordinates: 35°52′22″N 120°02′46″E / 35.8727°N 120.0462°E | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Shandong |
| Sub-provincial city | Qingdao |
| Township-level divisions | 12 subdistricts 10 towns |
| District seat | Yinzhu Subdistrict (隐珠街道) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,220.10 km2 (857.19 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 25 m (83 ft) |
| Population (2019) | |
| • Total | 1,608,200 |
| • Density | 720/km2 (1,900/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+08:00 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 266400, 266500 |
| Area code | 0532 |
| Website | HuangDao.gov.cn |
| Huangdao District | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 黃島區 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 黄岛区 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | Yellow Island District | ||||||
| |||||||
| West Coast New Area | |||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 西海岸新區 | ||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 西海岸新区 | ||||||
| |||||||
Huangdao District (Chinese: 黄岛区; lit. 'Yellow Island District') and West Coast New Area[1] (Chinese: 西海岸新区), is a district and a state-level new area of Qingdao, Shandong, China, located south-west and west of the main urban area of the city on the western shore of Jiaozhou Bay. It was identical to Qingdao Economic and Technological Development Zone (QETDZ, simplified Chinese: 青岛经济技术开发区; traditional Chinese: 青島經濟技術開發區; pinyin: Qīngdǎo Jīngjì Jìshù Kāifā Qū), which was launched in 1985 after the zone was merged with Huangdao District and set up the Free Trade Zone in 1992. In December 2012, Jiaonan, a county-level city in Qingdao was merged into Huangdao District.[2]
The pillar industries engaged in the zone include electronics, household electric appliances, building materials, petrochemicals, machinery and pharmaceutical drugs.[3][4] It is connected via Qingdao Jiaozhou Bay Bridge.
In mid 2018, the Ministry of Civil Affairs approved the consolidation of Huangdao District Government and West Coast New Area Government into a single governing body, which became the fourth administrative state-level new areas after Pudong of Shanghai; Binhai of Tianjin; and Nansha of Guangzhou. The population was 1.71 million in 2014.
Administrative divisions
[edit]
Huangdao District is the earliest key area of Qingdao's opening-up to the outside world. In 1985, the Qingdao Economic and Technological Development Zone was built in Huangdao District. In 1992, with the approval of the Shandong Provincial Party Committee and Government, the total area of Qingdao Economic and Technological Development Zone and Huangdao District was expanded to 217.33 square kilometers after the integration of the two district systems. In 2004, the original renovation system of Hongshiya Town in Jiaonan City was transferred to Huangdao District, and the area was further expanded to 274.1 square kilometers. Huangdao is divided into 12 subdistricts and 10 more rural towns; the latter half of the current subdistricts and all towns were ceded from Jiaonan City.[5][6]
- Subdistricts
|
|
- Towns
|
Transport
[edit]There is the Jiaohuang Railway in the area, with a total length of 43 kilometers, which is connected to the Jiaoji Railway from Qingdao to Jinan and has been put into operation. The Jiaozhou Bay Ring Expressway from Huangdao to Qingdao urban area has a total length of 66 kilometers.The Jiaozhou Bay Bridge in Qingdao has a total length of 36.48 kilometers and is the world's longest cross sea bridge, connecting Huangdao, Qingdao, and Hongdao. The Qingdao Jiaozhou Bay Underwater Tunnel is the longest underwater tunnel in China, with a length of 3950 meters in the underwater section. It connects the two cities and operates 8 tunnel buses, making the transportation between Qingdao and Huangdao more convenient. There are dual purpose sea ferries and sea passenger express ships between Huangdao and Qingdao urban area. The roads in the area are crisscrossing and extending in all directions. The coastal high-speed railway from Qingdao to Lianyungang to Shanghai will be opened and constructed, passing through Huangdao District.
Maritime transportation
[edit]- Qianwan Port: The seventh largest port in the world, with 75 berths/15.52 million TEUs (2013), and navigation to over 450 ports in over 150 countries and regions
- Dongjiakou Port: Located in the southern wing of Qingdao City, Langya Taiwan in Huangdao District, under the jurisdiction of Boli Town, has an average natural water depth of -15 meters near the coast, and a water depth of up to -20 meters from the shore at a distance of 1000 meters. It is a rare and excellent natural deep-water port.
Air transport
[edit]208 domestic and international passenger routes have been opened, with a total of 17 freight routes opened. More than 50 domestic and foreign airlines have been gathered, connecting 130 domestic and foreign cities, and the total number of domestic destinations has reached 102 as of 2023.
China Railway
[edit]- Qingdao West railway station
- West Coast Bus Terminal
Qingdao Metro
[edit]Climate
[edit]| Climate data for Huangdao (Zhuhai Subdistrict) (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.2 (59.4) |
19.7 (67.5) |
24.8 (76.6) |
35.9 (96.6) |
35.0 (95.0) |
36.6 (97.9) |
41.0 (105.8) |
35.8 (96.4) |
38.0 (100.4) |
30.5 (86.9) |
25.6 (78.1) |
18.6 (65.5) |
41.0 (105.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 4.3 (39.7) |
6.7 (44.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
17.5 (63.5) |
23.0 (73.4) |
25.9 (78.6) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
26.4 (79.5) |
21.0 (69.8) |
13.6 (56.5) |
6.7 (44.1) |
17.9 (64.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.5 (31.1) |
1.8 (35.2) |
6.6 (43.9) |
12.5 (54.5) |
18.1 (64.6) |
21.8 (71.2) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.0 (78.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.0 (60.8) |
8.6 (47.5) |
1.9 (35.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.1 (24.6) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
2.4 (36.3) |
8.2 (46.8) |
13.9 (57.0) |
18.7 (65.7) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.2 (73.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
11.6 (52.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
9.7 (49.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −16.2 (2.8) |
−15.1 (4.8) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
3.4 (38.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
14.8 (58.6) |
6.6 (43.9) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
−16.2 (2.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.9 (0.43) |
17.7 (0.70) |
20.4 (0.80) |
34.8 (1.37) |
72.8 (2.87) |
76.9 (3.03) |
156.3 (6.15) |
192.4 (7.57) |
90.3 (3.56) |
37.4 (1.47) |
37.2 (1.46) |
14.9 (0.59) |
762 (30) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 11.7 | 11.5 | 7.2 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 3.6 | 79.1 |
| Average snowy days | 3.6 | 3.0 | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 11.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 63 | 64 | 63 | 64 | 69 | 79 | 84 | 82 | 73 | 67 | 67 | 63 | 70 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 166.7 | 165.8 | 212.1 | 224.8 | 239.5 | 199.2 | 178.4 | 193.4 | 202.2 | 199.8 | 170.1 | 166.9 | 2,318.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 54 | 54 | 57 | 57 | 55 | 46 | 41 | 47 | 55 | 58 | 56 | 55 | 53 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[7][8] | |||||||||||||
References
[edit]- ^ "QINGDAO WEST COAST NEW AREA". Archived from the original on 2024-05-02. Retrieved 2024-05-02.
- ^ "青岛部分行政区划调整-中国青年报" [Some Administrative Regions in Qingdao-China Youth Daily]. zqb.cyol.com. 2012-12-03. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- ^ Introduction to Qingdao Economic & Technical Development Zone Archived 2012-08-05 at archive.today Qingdao Government
- ^ Qingdao Economic and Technological Development Zone chinadaily.com.cn 2006-04-19
- ^ 2011年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:黄岛区 (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Archived from the original on 2013-01-07. Retrieved 2013-01-06.
- ^ 2011年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:胶南市 (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Archived from the original on 2013-01-07. Retrieved 2013-01-06.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.