Upper East Region
This article needs to be updated. (January 2020) |
Upper East Region, Dagbon | |
|---|---|
 Rock formation in the Tongo Hills near Gorogo | |
 Location of Upper East Region in Ghana | |
| Country | Ghana |
| Capital | Bolgatanga |
| Districts | 10 |
| Government | |
| • Regional Minister | Stephen Yakubu[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,842 km2 (3,414 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 9th |
| Population (2021 Census)[3] | |
• Total | 1,301,226 |
| • Rank | Ranked 9th |
| • Density | 150/km2 (380/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | |
| • Year | 2013 |
| • Per capita | $5,150 |
| GDP (Nominal) | |
| • Year | 2013 |
| • Per capita | $2,500 |
| Time zone | GMT |
| Area code | 039 |
| ISO 3166 code | GH-UE |
| HDI (2017) | 0.520[4] low · 8th |
The Upper East Region is located in northern part of Ghana[5] and it is the third smallest of the 16 administrative regions in Ghana. It occupies a total land surface of 8,842 square kilometers or 2.7% of the total land area of Ghana. The regional capital is Bolgatanga, which is sometimes referred to as Bolga. Other major towns in the region include Navrongo, Paga, Sandema, Bawku, and Zebilla, Tempane, Pusiga, Garu, Pwalugu, Widana[6]
Geography
[edit]Location and size
[edit]The Upper East Region is located in the north-eastern corner of Ghana and bordered by Burkina Faso to the north and Togo to the east. It lies between longitude 0° and 1° West, and latitudes 10° 30′N and 11°N. The region shares boundaries with Burkina Faso to the north, Togo to the east, Upper West Region to the west, and the Northern Region to the south. The Upper East Region is divided into 15 districts, each headed by a district chief executive.
Tourism
[edit]Recreation areas
[edit]- Tongo rocks
- Bongo Rocks
- Tono Dam
Historic sites
[edit]- Navrongo's mud-built church
- Pikworo Slave camp
- Naa Gbewa Shrine in PUSIGA
Festivals
[edit]The region plays host to many festivals throughout the year, most of which are either to bring a good planting season or celebrate the harvest.
- Samanpiid festival
- Gologo Festival
- Fao Festival
- Feok festival builsa
- Zekula festival, By Bissa people
- Boaram Festival[7]
- Tengana festival, By the people of Balungu, Winkongo and Pwalugu
- Ndaakoya festival, by the Frafra, Talensi and Nabdam speaking Communities.
Languages
[edit]Official language of the region is English. There are more than 8 languages and major dialects, including Gurunie (frafra), Nankani, kassem, Taleni, Nadam, Kusal, Buili and Bisah. The major ethnic groups in the region are[8]
- Gurusi (frafra)-Bolgatanga
- Kassena- Nankani- Navrongo/Paga, Mirigu, Sirigu
- Kusasi/Bisah-Bawku, Zebilla, Garu, Pusiga
- Bonsi-Bongo
- Talensi- Tongo
- Nadams-Nangodi
- Builisa-Sandema, Fumbis
Other tourist attractions
[edit]- Upper East Regional Museum
- Sirigu Pottery and Arts Center
- Bolga market - a market for farmers and livestock, held twice weekly.
- Bolgatanga Craft Village
- Paga crocrodile pond
Demographics
[edit]Population
[edit]The center of population of the Upper East Region is located in its capital of Bolgatanga.
The population is primarily rural (79%) and scattered in dispersed settlements. The rural population was 87.1 percent in 1984 and 84.3% in 2000. There was, thus, a 2.8 percentage point reduction in the rural share of the population between 1984 and 2000 and a further 5.3 percent reduction between 2000 and 2010.[3]
With only 21 per cent of the population living in urban areas, the region is the least urbanized in Ghana. In fact, together with Upper West, they are the two regions with a less than 20 per cent urban population.
Ghanaian citizen by birth, childhood or parenthood constitute 92.5 percent of the population of the Upper East region. Naturalized Ghanaian citizen constitute 5.3 percent.
Upper East Region has a total population of 1,301,221 in the 2021 Population and Housing Census (PHC) conducted by the Ghana Statistical Service indicate that the Upper East Region representing 4.2 percent of Ghana’s population.
The region shows a total of 631,963 males and 669,963 representing 48.5 and 51.5 percentages respectively[9]
Transportation
[edit]Three national highways – N2, N10, and N11 – and a few Regional highways such as the R113, R114, R116 and R181, serve the region.
The N10 originates from Yemoransa in the Central Region and connects through Kumasi in the Ashanti Region and terminates at Paga in the Upper East Region. The national capital of Accra is also connected to the region by the N2 which terminates in Kulungugu in the Upper East Region. Both these national routes are connected by the N11 which links the regional capital of Bolgatanga to Bimpiela, also in the region.
Administrative divisions
[edit]The political administration of the region is through the local government system. Under this administration system, the region is divided into 15 MMDA's (made up of 0 Metropolitan, 4 Municipal and 15 Ordinary Assemblies).[10] Each District, Municipal or Metropolitan Assembly, is administered by a Chief Executive, who represents the central government but deriving authority from an Assembly headed by a presiding member elected from among the members themselves. The current list is as follows:
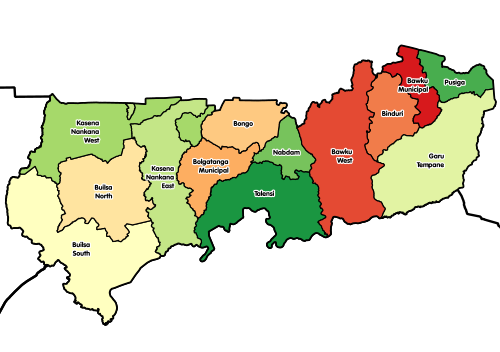
| # | MMDA Name | Capital | MMDA Type | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bawku | Bawku | Municipal | |
| 2 | Bawku West | Zebilla | Ordinary | |
| 3 | Binduri | Binduri[12] | Ordinary | |
| 4 | Bolgatanga | Bolgatanga | Municipal | |
| 5 | Bolgatanga East | Zuarungu | Ordinary | |
| 6 | Bongo | Bongo | Ordinary | |
| 7 | Builsa North | Sandema | Municipal | |
| 8 | Builsa South | Fumbisi[13] | Ordinary | |
| 9 | Garu | Garu | Ordinary | |
| 10 | Kassena Nankana East | Navrongo | Municipal | |
| 11 | Kassena-Nankana West | Paga | Ordinary | |
| 12 | Nabdam | Nangodi | Ordinary | |
| 13 | Pusiga | Pusiga[14] | Ordinary | |
| 14 | Talensi | Tongo | Ordinary | |
| 15 | Tempane | Tempane | Ordinary |
Education
[edit]Senior high schools
[edit]- Bolga Girls Senior High School
- Awe Senior High/Tech School
- Bawku Senior High/Tech School
- Bolgatanga Senior High School
- Bongo Senior High School
- Chiana Senior High School
- Fumbisi Senior High School
- Gowrie Senior High Tech School
- Gambigo Day Community SHS
- Garu Day Community SHS
- Kongo Senior High School
- Kusanaba Senior High School
- Navrongo Senior High School
- Nabango Senior High
- Notre Dame Sem/ Senior High School
- Mirigu Community Day SHS
- O. L. L. Girls Senior High School
- Paga Senior High School
- Queen Of Peace Senior High School
- Sandema Senior High/Tech School
- Sandema Senior High School
- Sirigu Senior High School
- St John's Integrated Senior High/Tech
- Tempane Senior High School
- Zamse Senior High/Tech School
- Zebilla Senior High/Tech School
- Zorkor Senior High School
- St John's Integrated SHTS
- Zuarungu Senior High School
- Bawku Senior High School
- Bawku Technical School[15]
Tertiary Institutions 1). Bolgatanga Technical University 2). St. John Bosco's College of Education 3). Gbewaa College of Education, Pusiga 4). C.K.Tedam University of Technology &r Applied Sciences.
Notable native citizens
[edit]| Notable native citizens of Upper East region | ||
|---|---|---|
| # | Citizen | Settlement |
| 1 | Joseph Kofi Adda | Navrongo |
| 2 | Roland Agambire | Sirigu |
| 3 | Roger A. Agana | Soe |
| 4 | David Atanga | Namoo |
| 5 | Theresa Lardi Awuni | Winkongo |
| 6 | Adam Kwarasey | Navrongo |
| 7 | Abedi Pele | Paga |
| 8 | Mark Woyongo | Navrongo |
| 9 | Hawa Yakubu | PUSIGA |
| 10 | Stephen Yakubu | Binduri |
| 11 | Adabere Adabre Donald | Bolgatanga |
| 12 | John Kapribo Ndebugri | Bawku West |
| 13 | Cletus Apul Avoka | Bawku west |
| 14 | Mahama Ayariga | Bawku East |
| 15 | Awini Emmanuel Ayonde | Bawku East |
| 16 | Laadi Ayamga | PUSIGA |
| 16 | ||
| 17 | Rev.Professor John Azumah | PUSIGA |
| 18 | Simon Atingban Akunye | PUSIGA |
| 18 | Dr.Kingley Akurugu | Bawku West |
References
[edit]- ^ http://www.ghana.gov.gh/index.php/governance/regional-ministers [dead link]
- ^ "Upper East Region". Ghanadistricts.com. Archived from the original on 2011-07-11. Retrieved 2010-10-15.
- ^ a b "Upper East Region – Population" (PDF). statsghana.gov.gh. Retrieved 2013-01-20.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- ^ "Upper East Region: Group pushes for sex education to reduce teenage pregnancies". Citinewsroom - Comprehensive News in Ghana. 2021-05-18. Retrieved 2021-05-18.
- ^ "Directory of Cities and Towns in Upper East". www.fallingrain.com. Retrieved 2024-07-13.
- ^ "Festivals in the Upper East Region - Ghana Embassy Berlin". Ghanaemberlin Germany. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ "About the Region: Upper East Region of Ghana". The Ghana Times. Retrieved 25 December 2024.
- ^ "2021 PHC results: Upper East constitutes 4.2% of Ghana's population - A1 Radio Bolgatanga". Radionline. 2021-09-22. Retrieved 2023-09-16.
- ^ "Upper East". GhanaDistricts. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2013.
- ^ Upper East Region – Districts
- ^ "Ghana Districts - A repository of all districts in the republic of Ghana". GhanaDistricts. Archived from the original on 2012-10-18.
- ^ "Ghana Districts - A repository of all districts in the republic of Ghana". GhanaDistricts. Archived from the original on 2012-10-18.
- ^ "Ghana Districts - A repository of all districts in the republic of Ghana". GhanaDistricts. Archived from the original on 2012-10-18.
- ^ "Senior High Schools in Upper East Region of Ghana". schoolsInGh. Retrieved 2024-07-13.
https://www.modernghana.com/author/AbongoMashoodAjene

