Portal:Capitalism
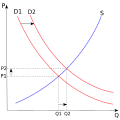
The Capitalism PortalCapitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. The defining characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price systems, private property, recognition of property rights, self-interest, economic freedom, meritocracy, work ethic, consumer sovereignty, economic efficiency, limited role of government, profit motive, a financial infrastructure of money and investment that makes possible credit and debt, entrepreneurship, commodification, voluntary exchange, wage labor, production of commodities and services, and a strong emphasis on innovation and economic growth. In a market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by owners of wealth, property, or ability to maneuver capital or production ability in capital and financial markets—whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets. Economists, historians, political economists, and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include laissez-faire or free-market capitalism, anarcho-capitalism, state capitalism, and welfare capitalism. Different forms of capitalism feature varying degrees of free markets, public ownership, obstacles to free competition, and state-sanctioned social policies. The degree of competition in markets and the role of intervention and regulation, as well as the scope of state ownership, vary across different models of capitalism. The extent to which different markets are free and the rules defining private property are matters of politics and policy. Most of the existing capitalist economies are mixed economies that combine elements of free markets with state intervention and in some cases economic planning. Capitalism in its modern form emerged from agrarianism in England, as well as mercantilist practices by European countries between the 16th and 18th centuries. The Industrial Revolution of the 18th century established capitalism as a dominant mode of production, characterized by factory work and a complex division of labor. Through the process of globalization, capitalism spread across the world in the 19th and 20th centuries, especially before World War I and after the end of the Cold War. During the 19th century, capitalism was largely unregulated by the state, but became more regulated in the post–World War II period through Keynesianism, followed by a return of more unregulated capitalism starting in the 1980s through neoliberalism. The existence of market economies has been observed under many forms of government and across a vast array of historical periods, geographical locations, and cultural contexts. The modern industrial capitalist societies that exist today developed in Western Europe as a result of the Industrial Revolution. The accumulation of capital is the primary mechanism through which capitalist economies promote economic growth. However, it is a characteristic of such economies that they experience a business cycle of economic growth followed by recessions. (Full article...) Selected article
The slate industry in Wales began during the Roman period when slate was used to roof the fort at Segontium, modern Caernarfon. The slate industry grew slowly until the early 18th century, from when it expanded rapidly and reached its peak output in the late 19th century, at which time the most important slate producing areas were in north-west Wales. These included the Penrhyn Quarry near Bethesda, the Dinorwig Quarry near Llanberis, the Nantlle Valley quarries and Blaenau Ffestiniog, where the slate was mined rather than quarried. Penrhyn and Dinorwig were the two largest slate quarries in the world, and the Oakeley mine at Blaenau Ffestiniog was the largest slate mine in the world. The Great Depression and the Second World War led to the closure of many smaller quarries, and competition from other roofing materials, particularly tiles, resulted in the closure of most of the larger quarries in the 1960s and 1970s. Slate production continues on a much reduced scale. (Full article...)
Selected biographyKarl Hess (born Carl Hess III; May 25, 1923 – April 22, 1994) was an American speechwriter and author. He was also a political philosopher, editor, welder, motorcycle racer, tax resister, and libertarian activist. His career included stints on the Republican right and the New Left before embracing a mix of left-libertarianism and laissez-faire anarcho-capitalism, a term which is attested earliest in his 1969 essay "The Death of Politics". Later in life, he summed up his role in the economy by remarking "I am by occupation a free marketer (crafts and ideas, woodworking, welding, and writing)." (Full article...) Selected quote
General imagesThe following are images from various capitalism-related articles on Wikipedia.
Did you know
CategoriesRelated portalsCapitalism topicsCapitalism .. Private property .. Economic freedom .. Laissez-faire .. British Agricultural Revolution .. Industrial Revolution .. Klondike Gold Rush .. Marketplace .. Money .. Wage .. Taxes .. Patent .. Capitalist mode of production .. Criticisms of socialism .. Adam Smith .. Milton Friedman .. Ludwig Von Mises .. Murray N. Rothbard .. The Wealth of Nations .. The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism .. Capital and Interest .. Capitalism and Freedom .. American capitalism .. Corporate capitalism .. Democratic capitalism .. Anarcho-capitalism .. State capitalism .. Welfare capitalism .. Ronald Reagan Things you can do Improve this portal! Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |