Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein
| MTTP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | MTTP, ABL, MTP, Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 157147; MGI: 106926; HomoloGene: 212; GeneCards: MTTP; OMA:MTTP - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein large subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTTP, also known as MTP, gene.[5][6]
MTTP encodes the large subunit of the heterodimeric microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) completes the heterodimeric MTP, which has been shown to play a central role in lipoprotein assembly. Mutations in MTTP can cause abetalipoproteinemia.[6]
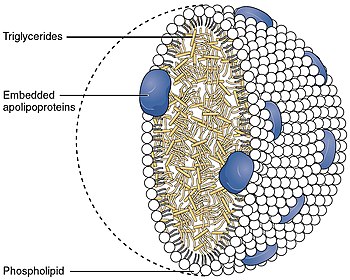
Apolipoprotein B48 on chylomicra and Apolipoprotein B100 on LDL, IDL, and VLDL are important for MTP binding.[citation needed]
MTP adds triglycerides to nascent chylomicrons in the intestine, and to VLDL in the liver.[7]
Structure
[edit]The large subunit of MTP, also known as the alpha subunit, contains an N-terminal half beta barrel, an alpha helix and a C-terminal lipid binding site that lies between two beta pleated sheets. It is a member of the large lipid transfer protein family, like apolipoprotein B (apo B), with which it interacts, but unlike apo B, it is not secreted. The heterodimer is instead retained in the endoplasmic reticulum due to the presence of a C-terminal KDEL motif on the PDI beta subunit.[8]
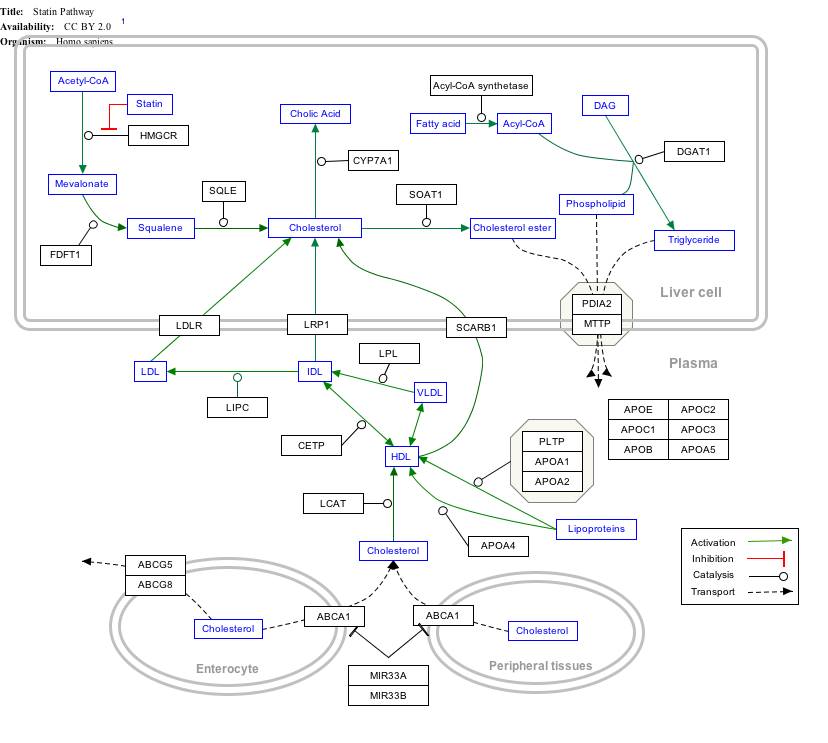
Interactive pathway map
[edit]Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "Statin_Pathway_WP430".
Pharmacology
[edit]Drugs that inhibit MTTP prevent the assembly of apo B-containing lipoproteins thus inhibiting the synthesis of chylomicrons and VLDL and leading to decrease in plasma levels of LDL-C.
- Lomitapide (Juxtapid) was approved by the US FDA for adjunctive treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
- Dirlotapide (Slentrol) and mitratapide (Yarvitan) are veterinary drugs for the management of obesity in dogs.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000138823 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000028158 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Shoulders CC, Brett DJ, Bayliss JD, Narcisi TM, Jarmuz A, Grantham TT, Leoni PR, Bhattacharya S, Pease RJ, Cullen PM, et al. (Mar 1994). "Abetalipoproteinemia is caused by defects of the gene encoding the 97 kDa subunit of a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein". Hum Mol Genet. 2 (12): 2109–16. doi:10.1093/hmg/2.12.2109. PMID 8111381.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: MTTP microsomal triglyceride transfer protein".
- ^ Katzung BG (2018). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (14th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. p. 638. ISBN 978-1-259-64115-2.
- ^ Biterova EI, Isupov MN, Keegan RM, Lebedev AA, Sohail AA, Liaquat I, Alanen HI, Ruddock LW (2019). "The crystal structure of human microsomal triglyceride transfer protein". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (35): 17251–17260. Bibcode:2019PNAS..11617251B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1903029116. PMC 6717300. PMID 31395737.
Further reading
[edit]- Luz JM, Lennarz WJ (1996). "Protein disulfide isomerase: A multifunctional protein of the endoplasmic reticulum". In Feige U, Yahara I, Morimoto RI, Polla BS (eds.). Stress-Inducible Cellular Responses. Experientia Supplementum. Vol. 77. pp. 97–117. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-9088-5_7. ISBN 978-3-0348-9901-7. PMID 8856971.
- Wetterau JR, Lin MC, Jamil H (1997). "Microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1345 (2): 136–50. doi:10.1016/s0005-2760(96)00168-3. PMID 9106493.
- Gordon DA (1997). "Recent advances in elucidating the role of the microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein in apolipoprotein B lipoprotein assembly". Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 8 (3): 131–7. doi:10.1097/00041433-199706000-00002. PMID 9211060.
- Ye J (2007). "Reliance of Host Cholesterol Metabolic Pathways for the Life Cycle of Hepatitis C Virus". PLOS Pathog. 3 (8): e108. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030108. PMC 1959368. PMID 17784784.
- Wetterau JR, Aggerbeck LP, Bouma ME, et al. (1992). "Absence of microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein in individuals with abetalipoproteinemia". Science. 258 (5084): 999–1001. Bibcode:1992Sci...258..999W. doi:10.1126/science.1439810. PMID 1439810.
- Sharp D, Ricci B, Kienzle B, et al. (1994). "Human microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein large subunit gene structure". Biochemistry. 33 (31): 9057–61. doi:10.1021/bi00197a005. PMID 7545943.
- Shoulders CC, Narcisi TM, Read J, et al. (1995). "The abetalipoproteinemia gene is a member of the vitellogenin family and encodes an alpha-helical domain". Nat. Struct. Biol. 1 (5): 285–6. doi:10.1038/nsb0594-285. PMID 7664034. S2CID 11860468.
- Hagan DL, Kienzle B, Jamil H, Hariharan N (1994). "Transcriptional regulation of human and hamster microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein genes. Cell type-specific expression and response to metabolic regulators". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (46): 28737–44. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)61967-8. PMID 7961826.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Sharp D, Blinderman L, Combs KA, et al. (1993). "Cloning and gene defects in microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein associated with abetalipoproteinaemia". Nature. 365 (6441): 65–9. Bibcode:1993Natur.365...65S. doi:10.1038/365065a0. PMID 8361539. S2CID 4334532.
- Narcisi TM, Shoulders CC, Chester SA, et al. (1996). "Mutations of the Microsomal Triglyceride-Transfer–Protein Gene in Abetalipoproteinemia". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 57 (6): 1298–310. PMC 1801399. PMID 8533758.
- Rehberg EF, Samson-Bouma ME, Kienzle B, et al. (1997). "A novel abetalipoproteinemia genotype. Identification of a missense mutation in the 97-kDa subunit of the microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein that prevents complex formation with protein disulfide isomerase". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (47): 29945–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.47.29945. PMID 8939939.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Linnik KM, Herscovitz H (1998). "Multiple molecular chaperones interact with apolipoprotein B during its maturation. The network of endoplasmic reticulum-resident chaperones (ERp72, GRP94, calreticulin, and BiP) interacts with apolipoprotein b regardless of its lipidation state". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (33): 21368–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.33.21368. PMID 9694898.
- Bradbury P, Mann CJ, Köchl S, et al. (1999). "A common binding site on the microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein for apolipoprotein B and protein disulfide isomerase". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (5): 3159–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.5.3159. PMID 9915855.
- Wang J, Hegele RA (2000). "Microsomal triaglyceride transfer protein (MTP) gene mutations in Canadian subjects with abetalipoproteinemia". Hum. Mutat. 15 (3): 294–5. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200003)15:3<294::AID-HUMU14>3.0.CO;2-E. PMID 10679949.