Loft conversions in the United Kingdom
This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2013) |

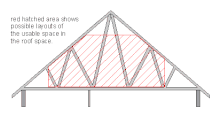
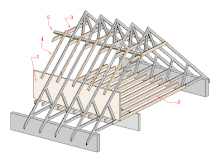
A loft conversion or an attic conversion is the process of transforming an empty attic space or loft into a functional room, typically used as a bedroom, office space, a gym, or storage space. Loft conversions are one of the most popular forms of home improvement in the United Kingdom as a result of their numerous perceived benefits.
Another type of loft conversion is converting non-residential spaces (most commonly warehouses, docks, former factories or water towers) into habitable homes. This form of loft conversion has its origins in the USA during the 1960s. Artists created living spaces on the upper levels of obsolete industrial buildings, sometimes located in the heart of the city.
Feasibility
[edit]The first stage of any loft conversion is a close inspection of the loft space to find out its exact dimensions and whether conversion is feasible. On entering the loft one needs to establish if there is adequate room under the ridge of the roof. A measurement of 2.3 metres is required to allow enough headroom, although you may find that you can still get a useful room from as little as 7 feet (2.1 metres), and there must be at least 2 metres clearance above the position of the access stairs.
Due to the slope of the roof and the required access headroom, the feasibility of a loft conversion is dependent upon a minimum height of approximately 2.2 m (7 ft 6 in) measured from the joist to the apex. Providing that this requirement is met, most properties will likely possess the potential to have the loft space converted.
Types
[edit]2015 saw a surge in demand for loft conversions by homeowners in the UK as a result of the new and simplified planning regulations. There are different types of loft conversions chosen because of price, space available, aesthetic appeal, property style, the height of the roof, and the planning permission required.[1] In London, there are many types of loft conversions, and the most popular of these is, Dormer conversion, Mansard conversion, Hip, to Gable conversion, Velux, or Roof window conversion. The least popular choices are Gambrel conversions and Hipped Roof conversion.
Roof window conversion
[edit]Roof windows are often an attractive option for homeowners due to their ability to fit into the line of the roof; thus not necessitating any restructuring of the roof itself. The installation of such windows will provide the loft space with substantial light. In the UK, a roof window conversion can often be completed under permitted development rights and will not require planning permission, although they will always require building regulation approval.
Dormer conversion
[edit]A dormer is a window-featured extension of the roof, usually installed to provide more space and headroom within the loft, in addition to improved staircase access. The dormer conversion is constructed in a way that it projects from the plane of a sloping roof. It is built with vertical walls and a horizontal ceiling, providing a more spacious room for your house. For a cohesive look, the dormer should match the existing roof. Dormers are also popular due to the aesthetic enhancement to a property that they provide. In the UK, the installation of a dormer is subject to planning permission requirements from the local authorities only when certain rules aren't met. Most dormer conversions come under permitted development.
-
Mobilisation to site, start of dormer extension
-
Start of dormer conversion. Tiles and felt stripped off
-
Tiles, felt and wood battens stripped off from inside
-
Dormer extension with tiles and felt stripped off and wood battens removed
-
Wood structure progress from inside
-
Window frame structure complete
-
Dormer extension almost complete from outside
-
Dormer extension plastered from inside
Mansard loft conversion
[edit]This loft conversion pays tribute to the famous French Architect of the 17th century, Francois Mansard by picking his name. This type of conversion is constructed by raising roof's sloping side to an almost vertical side. It is similar to the flat dormer since it has a flat roof, although the windows are housed in a smaller dormer. The mansard loft extension is a more appealing option to the dormer conversion as it gives the house a better look. The challenge to this type of loft conversion is that it requires planning permission due to the enormous changes to the shape and structure of the house. This loft conversion is a common choice as it maximizes space to create an additional room with the loft built at the rear end of the house with a flat roof and back wall sloping at a 72-degree angle, and windows housed in small dormers that extend from the roof.
Hip-to-gable loft conversion
[edit]With the United Kingdom having the smallest room sizes when compared to Ireland and other European countries[citation needed], and with space getting smaller with new builds, the hip-to-gable loft conversion has become a popular choice as the spaces have small internal volume. It is the most innovative way to maximize small spaces. This conversion requires planning permission as it means structural alterations to the roof. The size of the room is increased and allows for more headroom by extending the roof's ridgeline from its existing hips to the end of the vertical wall and altering the side of the house that's into a flat end gable.
Hipped-roof conversion
[edit]This conversion type got its name from the hipped roof that is a result of changing the side hip into a vertical one because the building has a sloping roof. This conversion increases the size of functional space that was limited by the sloping roof of a house. However, depending on the extent of conversion to be done, this type of conversion falls under permitted development[citation needed].
Gambrel conversion
[edit]The word gambrel is gotten from the Latin word "gamba", and it means horse legs. Initially, for designing domestic roofs and barns in America, this loft conversion design is now used because of its elegant aesthetic and the increased living and storage space. Very similar to a Mansard conversion, this conversion type has two-sided roofs that are symmetrical, and both sides have two slopes, and vertical gable ends. For the two slopes, one has a shallow angle while the other has a steep angle. For most conversion type of this nature, there is planning permission required.
Velux loft conversion
[edit]The design of Velux loft conversion is easily fitted as only one of the present rafters is clipped out for each window. Due to easy design, the existing roof is remained unbroken and results in a shorter build time with slight invasion. You can think of this type of loft conversion if your roof has plenty of available headroom and the cost of Velux loft conversion is very low and the build time period is also minimal.
Regulations
[edit]Building control regulations
[edit]Building control regulations will almost always be required if the loft space is being converted into any usable form of accommodation, subject to the local authority requirements. Planning permission may not be required as many conversions fall within the permitted development rights. In some areas of the United Kingdom, known generally as 'designated areas', permitted development rights are more restricted. For example, a Conservation Area, a National Park, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, a World Heritage Site or the Norfolk or Suffolk Broads. These above will generally have restricted permitted development rights. The local planning authority may have removed some of the permitted development rights with an Article 4 direction, in these cases a planning application will be required. These requirements are in place to ensure that the necessary construction criteria are met and that all health and safety laws, amongst other things, have been satisfied. A professional loft conversion specialist will usually conduct all liaisons with the relevant local authority.[2]
Properties which have had change of use from commercial use into homes may not then be able to develop the property further under household permitted development legislation.[3]
Structural strengthening
[edit]The existing ceiling joists in most houses are only designed to support the weight of a ceiling, therefore additional support will be required to transfer the loads from the new loft floor to the walls of the house, since the alignment of roof supports would generally need to be altered, causing a significant increase in pressure at specific points on the flooring of the property. A common method used is to install I-beams or rolled steel joists (RSJs). These can either be installed in single lengths or in smaller sections which are bolted together. New timber joists are then installed between the RSJs onto which the new floor can be laid. A structural engineer will calculate the size of the RSJs and joists.
Benefits
[edit]Loft conversions yield numerous benefits for homeowners, which may be the reason for their increasing popularity. Often, up to 30% of a property's potential space is located within the loft area. Converting the attic will therefore provide a significant amount of room that may be used for a wide variety of accommodation; often a bedroom, bathroom, office, or entertainment room.
In 2016 it was reported that a loft conversion could increase the value of a home by 20% in the UK by Robert Gardner, Chief Economist at Nationwide.[4]
Many families also choose to convert their loft area as a means of obtaining more space without having to endure the costly and stressful process of moving property.[citation needed]
Key features of former industrial space that makes for attractive use as a loft include high, unfinished ceilings, large windows, exposed brick or cinder block walls and exposed duct work. Many industrial lofts have only partial height walls separating rooms or areas within the space. Some lofts even preserve the industrial-era freight elevators that open into the living space.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Planning Permission". www.planningportal.co.uk. Retrieved 2021-06-15.
- ^ Planning Portal (Department for Communities and Local Government) (2012). "Planning Permission for Loft Conversion". Retrieved 2012-05-05.
- ^ Garrett, James. "Planning Permission". www.planningportal.co.uk. Retrieved 2019-05-27.
- ^ "Home extension or loft conversion 'can add 20% to house value'" (PDF). The Nationwide. Press Association. 2016-03-27. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2019-05-27.








