Taenianotus
| Taenianotus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Scorpaeniformes |
| Family: | Scorpaenidae |
| Tribe: | Scorpaenini |
| Genus: | Taenianotus Lacepède, 1802 |
| Species: | T. triacanthus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Taenianotus triacanthus Lacepède, 1802
| |
| Synonyms[2][3] | |
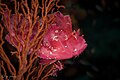
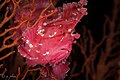
Taenianotus is a monotypic genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. Its only species is Taenianotus triacanthus, the leaf scorpionfish, paperfish, paper scorpionfish, sailfin leaffish or threespine scorpionfish. This taxon has a wide Indo-Pacific distribution.
Taxonomy
[edit]Taenianotus was created as a genus in 1802 by the French naturalist Bernard Germain Étienne de La Ville-sur-Illon, comte de Lacépède when he described Taenianotus triacanthus, with no type locality being given. The type species was designated as Taenianotus triacanthus in 1829 by Cuvier in Cuvier & Valenciennes Histoire naturelle des poissons. Tome quatrième. Livre quatrième. Des acanthoptérygiens à joue cuirassée.[3][4] This genus is classified within the tribe Scorpaenini, in the subfamily Scorpaeninae of the family Scorpaenidae.[5] The genus name is a compound of taenia, meaning a "narrow flat band" and notus, which means "back", an allusion to the long dorsal fin which extends from the head to the tail. The specific name triacanthus is a combination of tri meaning "three" and acanthus, which means "thorn" or "spine", a reference to the three preopercular spines this fish possesses, in fact, it has only two such spines.[6]
Description
[edit]Taenianotus triacanthus is about 10 cm (3.9 in) long fully grown. Their color varies from green, red, pink, brown, ocher and yellowish to a ghostly white. The fish is almost as flat as a leaf and resembles a leaf in many other ways. The head and mouth are large. Through their eyes is a dark line. The large dorsal fin starts just behind the eyes and has 12 spines and eight to 11 soft rays.[2] The anal fin has three spines and five or six soft rays. The venom of the leaf scorpionfish is considerably weaker than that of the lionfish and stonefish. The skin often has blotches that enhance a camouflage effect. This fish has appendages around the mouth, and sometimes real algae and hydroids grow on its skin. This fish molts every 10 to 14 days, and can change colors after the molt.[7]
Behavior
[edit]Taenianotus triacanthus resembles a dead leaf lying in the water. To enhance this camouflage, it even makes gentle sideways movements in its pelvic area which make it resemble a drifting inert object.[2] It is an ambush predator, waiting until suitable prey, a small fish or shrimp, approaches. Then it slowly moves with its pectoral fins close to the victim. When the leaf scorpionfish is close enough, the prey is sucked in by a sudden opening of its mouth. It eats small crustaceans, fishes, and larvae.[2]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Taenianotus triacanthus is widespread from east African coast and the Red Sea to the tropical Indo-Pacific, north to the Galapagos Islands, the Ryukyu Islands, Hawaii, and the coast of New South Wales. This species can be found in tropical waters on coral reefs, from shallow water to a depth of 130 m.[2]
-
T. triacanthus in Vietnam
-
Leaf scorpionfish in Borneo
-
White Leaf scorpionfish on a sandy bottom near Alor Island, Indonesia
-
Pink Leaf scorpionfish at Wakatobi National Park Sulawesi, 2018
-
Front side of Leaf scorpionfish at Wakatobi National Park Sulawesi, 2018
-
Close up of yellow Leaf scorpionfish at Wakatobi National Park Sulawesi, 2018
References
[edit]- ^ Motomura, H.; Matsuura, K. (2016). "Taenianotus triacanthus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T79800214A79800219. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T79800214A79800219.en. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Taenianotus triacanthus". FishBase. August 2021 version.
- ^ a b Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Species in the genus Taenianotus". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron & van der Laan, Richard (eds.). "Genera in the family Scorapenidae". Catalog of Fishes. California Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ J. S. Nelson; T. C. Grande; M. V. H. Wilson (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). Wiley. pp. 468–475. ISBN 978-1-118-34233-6.
- ^ Christopher Scharpf & Kenneth J. Lazara, eds. (2 October 2021). "Order Perciformes (Part 9): Suborder Scorpaenoidei: Family Scorpaenidae". The ETYFish Project Fish Name Etymology Database. Christopher Scharpf and Kenneth J. Lazara. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ "Eight interesting facts about the Leaf Scorpionfish". Retrieved 2010-04-28.
External links
[edit]- Photos of Taenianotus on Sealife Collection
![]() Media related to Taenianotus triacanthus at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Taenianotus triacanthus at Wikimedia Commons
![]() Data related to Taenianotus triacanthus at Wikispecies
Data related to Taenianotus triacanthus at Wikispecies