John 21
| John 21 | |
|---|---|
Acts 1 → | |
 John 21:11–14, 22–24 in Papyrus 122 (4th/5th century) | |
| Book | Gospel of John |
| Category | Gospel |
| Christian Bible part | New Testament |
| Order in the Christian part | 4 |
| Part of a series of articles on |
| John in the Bible |
|---|
 |
| Johannine literature |
| Authorship |
| Related literature |
| See also |
John 21 is the twenty-first and final chapter of the Gospel of John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It contains an account of a post-crucifixion appearance in Galilee, which the text describes as the third time Jesus had appeared to his disciples. In the course of this chapter, there is a miraculous catch of 153 fish, the confirmation of Peter's love for Jesus, a foretelling of Peter's death, and a comment about the beloved disciple's future.
Text
[edit]The original text was written in Koine Greek. This chapter is divided into 25 verses.
Textual witnesses
[edit]Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter are:[1]
- Papyrus 66 (c. AD 200; extant verses 1–9, 12, 17)[2]
- Papyrus 109 (3rd century; extant verses 18–20, 23–25)[3]
- Codex Vaticanus (325–350)
- Codex Sinaiticus (330–360; complete)
- Papyrus 122 (4th/5th century; extant verses 11–14, 22–24)[4]
- Codex Bezae (c. 400)
- Codex Alexandrinus (400–440)
- Codex Ephraemi Rescriptus (c. 450; complete)[5][6]
- Papyrus 59 (7th century; extant verses 7, 12–13, 15, 17–20, 23)[7]
Later addition?
[edit]Scholarly discussions
[edit]According to Helmut Koester (2000), similar to the Pericope Adulterae, John 21:1–25, though present in all extant manuscripts, is also widely recognized as a later addition. A redactor is thought by some to have later added some text to the original author's work.[8] Arguments in favour of this hypothesis include:
- John 20:30–31 could be 'the original ending of the gospel, which is repeated in an exaggerated version in John 21:25.'[8] 20:30–31 summarizes the many signs which Jesus performed for his followers, not all of which could be recorded in the Gospel.
- The Restoration of Peter (John 21:3–19) emphasises the ecclesiastical leadership of Peter, which may indicate that this addition was intended to take a side in 'a later discussion on competing claims of apostolic authorities', especially in John 21:15–17, in which Jesus instructs Peter to 'Tend my sheep!', meaning to lead the flock (=lay people) as a pastor (literally 'shepherd').[8]
- The part about the disciple whom Jesus loved (John 21:20–24) 'underlines the authority of the special tradition of this gospel as the report of an eyewitness.'[8] In particular, 21:24 shows a close resemblance to the earlier comment about the reliability of the eyewitness in John 19:35.[8] This assertion to the credibility of the gospel, with the claim that it is based on an eyewitness account, seems to be at odds with the climax of the original gospel, where, after Doubting Thomas comes to believe in Jesus's resurrection, those who believe without having seen are blessed above those who need evidence in order to believe (John 20:24–29).[8]
Scholars opposing a later addition by another author have argued the following:
- No existing manuscript of the Gospel of John omits chapter 21.[8][9]
- Westcott proposed a theory that the author simply decided to add an additional incident at some time after writing the book, but before final publication. In this view, the redactor and the original author are the same person.[citation needed]
- Donald Guthrie commented: 'It is unlikely that another author wrote this section since there are several points of contact in it with the style and language of previous chapters.'[10]
- Paul N. Anderson and Ben Witherington III argue that the appendix was added after the disciple whom Jesus loved had died, at which point the gospel reached its final form.[11]
Manuscript evidence
[edit]The Nestle-Aland Novum Testamentum Graece (27th ed.) as well as major translations of the New Testament (e.g. KJV, NASB, NIV, RSV, NRSV) retain this chapter in their editions as original.
In an essay contributed on behalf of scholars unconvinced of any decisive sense of "originality" to John 21 (published in 2007), Jesuit author Felix Just wrote: "We (unfortunately!) do not possess any ancient manuscript of John that actually ends at 20:31."[12] In other words, ancient manuscripts that contain the end of John 20 also contain text from John 21. So if John 21 is an addition, it was so early (which is not in doubt: part of John 21 appears in P66) and so widespread, that no evidence of the prior form has survived.
Novum Testamentum Graece (NA28) and the United Bible Societies (UBS5) provide the critical text for John 21.[13]
In 2006, following the discovery of a 4th-century Sahidic papyrus manuscript (Bodleian MS. Copt.e.150(P)) some scholars speculated that such text may end at 20:31,[14] but this is not conclusive due to its fragmentary state.[15]
Contents
[edit]
Breakfast by the Sea of Tiberias (verses 1–14)
[edit]Verses 1–2
[edit]- After these things, Jesus revealed himself again to the disciples at the sea of Tiberias. He revealed himself this way.[16]
- Simon Peter, Thomas called the Twin, Nathanael of Cana in Galilee, the sons of Zebedee, and two others of His disciples were together.[17]
Of these seven disciples, the last two remain unnamed. Ernst Hengstenberg suggests they may have been Andrew and Philip, whereas Heinrich Meyer suggests they were non-apostolic disciples from the wider group of those who followed Jesus.[18]
Verse 4
[edit]- But when the morning had now come, Jesus stood on the shore; yet the disciples did not know that it was Jesus.[19]
The setting was in the "early morning",[20] or at dawn.[21] Alfred Plummer notes that a better translation is "Jesus came and stood on the beach.[21]
Verse 11
[edit]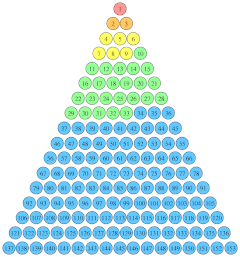
- So Simon Peter went aboard and hauled the net ashore, full of large fish, 153 of them. And although there were so many, the net was not torn.[22]
Two points about the catch of fish are emphasized here:[23]
- there were 153 large fish in the net.
- even with so many, the net was not torn.
Both are the kind of thing that would remain in the mind of a person who had witnessed them firsthand.[23]
The number 153 is the 17th triangular number, as well as the sum of the first five positive factorials, and is associated with the geometric shape known as the Vesica Piscis (literally, "bladder of a fish") or Mandorla, which Archimedes, in his Measurement of a Circle, referred to in the ratio 153/265 as constituting the "measure of the fish", being an imperfect representation of 1/√3.[24] Augustine of Hippo argued the significance of 153 being the sum of the first 17 integers is that 17 represents the combination of divine grace (the seven gifts of the Holy Spirit) and law (the Ten Commandments).[25][26]
Verse 14
[edit]- This was now the third time that Jesus was revealed to the disciples after he was raised from the dead.[27]
Irish Archbishop John McEvilly suggests the count is based on Jesus' appearances to his disciples "collectively".[28]
Jesus restores Peter (verses 15–19)
[edit]Jesus restores Peter to fellowship after Peter had previously denied him, and tells Peter to feed Jesus' sheep. This restoration of Peter occurs in verses 21:15–19.
The Disciple whom Jesus loved (verses 20–23)
[edit]
The description of the "beloved disciple's" (normally assumed to be John the Apostle) fate is presented as an aside to Peter. Jesus says that it is not Peter's concern, even if Jesus should wish that that disciple remain alive until the end of time. The following verse clarifies that Jesus did not say "This disciple will not die", but that it was not for Peter to know.
The last appearance of the 'Disciple whom Jesus loved' in this Gospel, together with his first appearance in chapter 1 form a literary "inclusio of eyewitness testimony" to privilege this witness (in the Gospel of John 21:24) over Peter's, not to denigrate Peter's authority, but rather to claim a distinct qualification as an 'ideal witness' to Christ, because he survives Peter and bears his witness after Peter.[29][30] Bauckham notes the occurrence of at least two specific words in the narratives of both the first and the last appearance of this disciple: "to follow" (Greek: ἀκολουθέω 'akoloutheó') and "to remain/stay" (Greek: μένω 'menó').[31] In the first chapter verse 1:38 it is stated that "Jesus turned, and seeing them following ('akolouthountas'), said to them, "What do you seek?"", then in verse 1:39 they "remained ('emeinan') with Him that day".[31] In John 21, the last appearance of the 'Disciple whom Jesus loved' is indicated using similar words: in verse 21:20 it is written that "Peter, turning around, saw the disciple whom Jesus loved following ('akolouthounta')", then in verse 21:22 "Jesus said to him [Peter], "If I will that he remain ('menein') till I come, what is that to you?"[31] The appearances are also close to Peter's, as the first one, along with Andrew, happened just before Peter's, who was then given the name 'Cephas' (alluding to Peter's role after Jesus' departure), and the last one, just after Jesus' dialogue with Peter, acknowledging the significance of Peter's testimony within "the Petrine's inclusio", which is also found in the Gospel of Mark and Luke (see Luke 8 under "The Women who sustained Jesus").[32]
Conclusion (verses 24–25)
[edit]The chapter and the whole book are closed by two verses referring to the author of the gospel in the third person ("We know that his testimony is true"):
Verse 24
[edit]- This is the disciple who is bearing witness about these things, and who has written these things, and we know that his testimony is true.[33]
Verse 25
[edit]- And there are also many other things that Jesus did, which if they were written one by one, I suppose that even the world itself could not contain the books that would be written. Amen.[34]
Although ever since the 2nd century some people have taken verse 24 to mean that the author of the Gospel of John himself was the eyewitness (namely the disciple whom Jesus loved), other scholars point out that this verse indicates that the author is someone other than this disciple, because he is speaking about himself in the first person plural ('we know') and the disciple in the third person ('the disciple... who has written all these things'). Therefore, the author merely claims to have used an earlier written report, allegedly from this disciple, as a source for writing the Fourth Gospel.[35]: 4:37
See also
[edit]- 153 (number)
- Overview of resurrection appearances in the Gospels and Paul
- Pericope Adulterae
- Related Bible parts: Mark 16, Luke 24, John 1
References
[edit]- ^ Papyri and Manuscripts related to the Gospel and Epistles of John in The Johannine Literature Web at Catholic-Resources.org.
- ^ Victor Martin, Papyrus Bodmer II: Evangile de Jean chap. 1–14 (Cologny-Geneva: Bibliotheca Bodmeriana, 1956), 15-18.
- ^ Comfort, P. W., & Barrett, D. P. (2001). The text of the earliest New Testament Greek manuscripts, p. 653
- ^ "Liste Handschriften". Münster: Institute for New Testament Textual Research. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ^ Gallica, Bibliothèque nationale de France. Département des Manuscrits. Grec 9 (2012). "Codex Ephræmi Syri rescriptus". Folios 85r and 85v.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ WWU, Institut für Neutestamentliche Textforschung (INTF) /Eng. "Institute for New Testament Textual Research". "New Testament Virtual Manuscript Room - Workspace Doc ID 20004". Folios 1350 (85r) and 1360 (85v).
- ^ Aland, Kurt; Aland, Barbara (1995). The Text of the New Testament: An Introduction to the Critical Editions and to the Theory and Practice of Modern Textual Criticism. Erroll F. Rhodes (trans.). Grand Rapids: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company. pp. 99–100. ISBN 978-0-8028-4098-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g Koester, Helmut (2000). Introduction to the New Testament. Vol. 2. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. p. 192. ISBN 978-3-11014970-8. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ Chris Keith, The Pericope Adulterae, the Gospel of John, and the Literacy of Jesus (Brill 2009 ISBN 978-9-00417394-1), p. 258
- ^ IVP New Bible Commentary.
- ^ John, Jesus, and History, Volume 2, p. 210 p. 245
- ^ Felix Just, 'Combining Key Methodologies in Johannine Studies', in Tom Thatcher (ed), What We Have Heard from the Beginning: The Past, Present, and Future of Johannine Studies, (Baylor University Press, 2007), p. 356.
- ^ "Read the Bible text :: academic-bible.com". www.academic-bible.com.
- ^ Gesa Schenke, 'Das Erscheinen Jesu vor den Jüngern und der ungläubige Thomas: Johannes 20, 19–31' in Louis Painchaud and Paul-Hubert Poirier, eds, Coptica – Gnostica – Manichaica: Mélanges offerts à Wolf-Peter Funk (Les presses de l'Université Laval / Peeters, 2006) pp. 893–904.
- ^ Kok, Michael J. (2017). The Beloved Apostle?: The Transformation of the Apostle John into the Fourth Evangelist. Wipf and Stock Publishers. p. 32. ISBN 9781532610219.
- ^ John 21:1: NKJV
- ^ John 21:2: NKJV
- ^ Meyer, H. A. W., Meyer's NT Commentary on John 21, accessed 7 December 2020
- ^ John 21:4: NKJV
- ^ Nicoll, W. R., Expositor's Greek Testament on John 21, accessed 10 September 2022
- ^ a b Plummer, A., (1902), Cambridge Bible for Schools and Colleges on John 21, accessed 10 September 2022
- ^ John 21:11: English Standard Version (ESV)
- ^ a b Note [b] on John 21:11 in ESV
- ^ Heath, Thomas Little (1897), The Works of Archimedes, Cambridge University: Cambridge University Press., pp. lxxvii , 50, retrieved 2010-01-30
- ^ Jason Byassee, Praise Seeking Understanding: Reading the Psalms with Augustine, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2007, p. 130, ISBN 0-8028-4012-4.
- ^ John E. Rotelle (ed) and Edmund Hill (tr), The works of Saint Augustine: A Translation for the 21st Century, Part 3, Volume 7 (Sermons: On the Liturgical Seasons), p. 112, ISBN 1-56548-059-7.
- ^ John 21:14: ESV}}
- ^ McEvilly, J. (1879), An Exposition Of The Gospels by The Most Rev. John Macevilly D.D.: John 21, accessed 26 January 2024
- ^ Bauckham 2017, pp. 128–129.
- ^ Bauckham, R. "The Beloved Disciple as Ideal Author," JNST 49 (1993) 21-44; reprinted in S. E. Porter and C. A. Evans, eds., The Johannine Writings (Biblical Seminar 32; Sheffield: Sheffield Academic, 1995) 46-68; apud Bauckham 2017, p. 128
- ^ a b c Bauckham 2017, p. 128.
- ^ Bauckham 2017, pp. 129.
- ^ John 21:24: ESV
- ^ John 21:25: NKJV
- ^ Bart D. Ehrman (2002). "5: The Birth of the Gospels". The New Testament. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
Further reading
[edit]- Bauckham, Richard (2017). Jesus and the Eyewitnesses (2nd ed.). Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. ISBN 9780802874313.
External links
[edit]- John 21 King James Bible - Wikisource
- English Translation with Parallel Latin Vulgate Archived 2020-09-25 at the Wayback Machine
- Online Bible at GospelHall.org (ESV, KJV, Darby, American Standard Version, Bible in Basic English)
- Multiple bible versions at Bible Gateway (NKJV, NIV, NRSV etc.)
| Preceded by John 20 |
Chapters of the Bible Gospel of John |
Succeeded by Acts of the Apostles 1 |
