Hakone Tozan Line
| Hakone Tozan Line | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Hakone Tozan Railway 1000 series trainset "Bernina" at Gōra Station | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native name | 箱根登山鉄道線 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | Odakyu Group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stations | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | Odakyu Hakone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depot(s) | Iriuda | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | 1 June 1919 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 15.0 km (9.3 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of tracks | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | partly 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge and 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum radius | 555 ft (169 m) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 750 V and 1,500 V DC (Overhead catenary) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Signalling | Automatic closed block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Train protection system | D-ATS-P | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation | 553 m (1,814 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum incline | 8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

The Hakone Tozan Line (箱根登山鉄道線, Hakone Tozan Tetsudō-sen, lit. Hakone Mountain-Climbing Railroad Line) is a mountain railway in Japan operated by Odakyu Hakone, an Odakyu Group company that also owns the Hakone Tozan Cable Car.
The section of the line from Odawara Station to Hakone-Yumoto Station began operating in 1919, with the current terminus of Gōra being reached in 1930. Since 2006, only Odakyū Odawara Line trains run on the section from Odawara Station to Hakone-Yumoto Station, as that section was converted from dual-gauge (standard and narrow) to just narrow-gauge. From Gora, travelers can continue up the mountain on the Hakone Tozan Cable Car.
The railway is capable of climbing one meter vertically for every 12.5 metres (41 feet) of horizontal distance, with a maximum gradient of 8%. The line traverses Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park, so the line was carefully designed to limit the impact on the scenery. Due to the difficult topography, the line has three switchbacks used to ascend particularly steep sections.
The section of the line between Hakone-Yumoto and Gora was suspended in October 2019 due to heavy damage caused by Typhoon Hagibis.[1] On 9 July 2020, after repairs had been completed, test trains began running over the line and full service was restored two weeks later on 23 July.[2][3]
Description
[edit]

- Length: 15.0 km (9.3 mi)
- Gauge:
- Odawara - Iriuda: 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in)
- Iriuda - Hakone-Yumoto: 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in)/1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) (dual gauge)
- Hakone-Yumoto - Gōra: 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in)
- Stations: 11 (including termini)
- Track: single
- Power:
- Odawara - Hakone-Yumoto: 1,500 V DC overhead supply
- Hakone-Yumoto - Gōra: 750 V DC overhead supply
- Block system: Automatic (cab signal/digital) (CTC)
Stations
[edit]All stations are in Kanagawa.
- Trains: "S" = All stop, "|" = All pass.
| No. | Stations/ Signal Stations |
Japanese | Distance | Elevation | Stops | Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limited Express |
Local | Local | |||||||
| OH47 | Odawara | 小田原 | 0.0 km (0 mi) | 26 m (85 ft) | S | S | Odawara | ||
| OH48 | Hakone-Itabashi | 箱根板橋 | 1.7 km (1.1 mi) | 1.7 km (1.1 mi) | 27 m (89 ft) | | | S | ||
| OH49 | Kazamatsuri | 風祭 | 1.5 km (0.93 mi) | 3.2 km (2.0 mi) | 48 m (157 ft) | | | S | ||
| OH50 | Iriuda | 入生田 | 1.0 km (0.62 mi) | 4.2 km (2.6 mi) | 66 m (217 ft) | | | S | (terminus) | |
| OH51 | Hakone-Yumoto | 箱根湯本 | 1.9 km (1.2 mi) | 6.1 km (3.8 mi) | 108 m (354 ft) | S | S | S | Hakone, Ashigarashimo District |
| OH52 | Tōnosawa | 塔ノ沢 | 1.0 km (0.62 mi) | 7.1 km (4.4 mi) | 165 m (541 ft) | (terminus, from/to Shinjuku (some from/to Kita-Senju)) |
(terminus, from/to Shin-Matsuda) |
S | |
| – | Deyama Switchback | 出山信号場 | 1.2 km (0.75 mi) | 8.3 km (5.2 mi) | 234 m (768 ft) | No passengers | |||
| OH53 | Ōhiradai | 大平台 | 1.6 km (0.99 mi) | 9.9 km (6.2 mi) | 349 m (1,145 ft) | S | |||
| – | Kami-Ōhiradai Switchback | 上大平台信号場 | 0.5 km (0.31 mi) | 10.4 km (6.5 mi) | 359 m (1,178 ft) | No passengers | |||
| – | Sennindai Signal Stop | 仙人台信号場 | 0.8 km (0.50 mi) | 11.2 km (7.0 mi) | 410 m (1,350 ft) | No passengers | |||
| OH54 | Miyanoshita | 宮ノ下 | 0.9 km (0.56 mi) | 12.1 km (7.5 mi) | 448 m (1,470 ft) | S | |||
| OH55 | Kowakidani | 小涌谷 | 1.3 km (0.81 mi) | 13.4 km (8.3 mi) | 535 m (1,755 ft) | S | |||
| OH56 | Chōkoku-no-Mori | 彫刻の森 | 0.9 km (0.56 mi) | 14.3 km (8.9 mi) | 551 m (1,808 ft) | S | |||
| OH57 | Gōra | 強羅 | 0.7 km (0.43 mi) | 15.0 km (9.3 mi) | 553 m (1,814 ft) | S | |||
- Transfers:
- At Odawara Station:
- At Gōra Station:
- Hakone-Yumoto Station is the terminus for all Hakone Tozan Line trains.
- On the Odawara - Hakone-Yumoto section, Limited Express "Romancecar" and Local trains run through to and from the Odakyu Odawara Line.
- Odakyu LE, Super Hakone, Hakone and Homeway services run from/to Shinjuku Station.
- Odakyu LE Metro Hakone runs between Hakone-Yumoto and Kita-Senju Station, on Tokyo Metro Chiyoda Line at weekends only.
- Local trains runs between Odawara and Hakone-Yumoto, partly from/to Shin-Matsuda Station using 4-car Odakyu EMUs.
- Section between Hakone-Yumoto and Gōra is operated by local trains only, using Hakone Tozan 2/3-car EMUs.
- Trains stop at three signal stops which have no passenger platforms.
- There are three switchbacks: Deyama, Ōhiradai, and Kami-Ōhiradai.
- Journey time between Odawara - Hakone-Yumoto is approximately 15 minutes, Hakone-Yumoto - Gōra is approximately 40 minutes, Shinjuku - Hakone-Yumoto is approximately an hour and 25–35 minutes by limited express.
Signal stops
[edit]There are three signal stops on the Hakone Tozan Line in addition to the regular passenger stations. All of them have a siding track and two of them have switchbacks.
Deyama Switchback
[edit]Signal stop with a switchback. 234 m AMSL. 35°13′57″N 139°05′14″E / 35.232402°N 139.087167°E
Kami-Ōhiradai Switchback
[edit]Signal stop with a switchback near Ōhiradai station which also has a switchback. 359 m AMSL. 35°14′08″N 139°04′32″E / 35.235604°N 139.075444°E
Sennindai Signal Stop
[edit]Signal stop without a switchback. 410 m AMSL. 35°14′18″N 139°04′09″E / 35.238215°N 139.069042°E
-
Deyama switchback
-
Kami-Ōhiradai switchback
-
Sennindai signal stop
Rolling stock
[edit]Hakone Tozan Railway (Hakone-Yumoto - Gōra)
[edit]
- MoHa 1 (formerly ChiKi 1, since 1919)
- MoHa 2 (formerly ChiKi 2, since 1927)
- 1000 series ("Bernina", named after the Rhätische Bahn railway of the same name in Switzerland)
- 2000 series ("St. Moritz", after the Swiss resort town and Bernina Railway terminus)
- 3000 series (since November 2014)[4]
- 3100 series two-car EMU (since May 2017)[5]
- MoNi 1 (non-revenue car, since 1975)
All trains are based at Iriuda Depot.
Former
[edit]
- MoHa 3 (withdrawn in 1997)
- Mu 1 (goods wagon, withdrawn in 1952/1992)
- Yu 1 (goods wagon, withdrawn in 1976)
Odakyu Electric Railway (Shinjuku - Odawara - Hakone-Yumoto)
[edit]Romancecar EMUs
[edit]- Odakyu 7000 series LSE
- Odakyu 10000 series HiSE
- Odakyu 20000 series RSE
- Odakyu 30000 series EXE
- Odakyu 50000 series VSE
- Odakyu 60000 series MSE (also from Kita-Senju)
Commuter EMUs
[edit]History
[edit]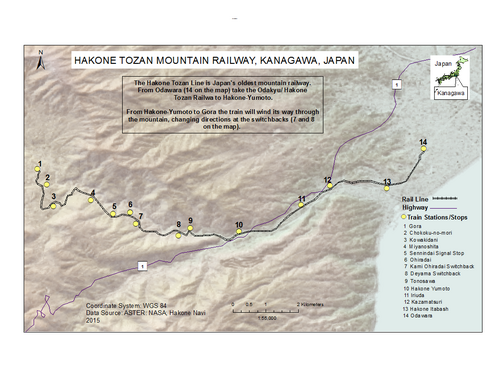
- October 1, 1888: Odawara Horse-drawn Railway opens from Kōzu Station via Odawara Station, to Hakone-Yumoto Station.
- October 31, 1896: Operating company name is changed to Odawara Electric Railway.
- March 21, 1900: Line is electrified (as a tram, 600 V DC).
- June 1, 1919: Line opens between Hakone-Yumoto and Gōra as an electrified (600 V DC) funicular railway.
- December 16, 1920: Tram line closes between Kōzu - Odawara, and connected with the JGR (now JR) Tōkaidō Main Line at Odawara.
- August 16, 1928: Hakone Tozan Railway is founded.
- October 1, 1935: Mainline railway is extended from Hakone-Yumoto to Odawara. Tram line remains between Odawara - Hakone-Itabashi, and is renamed the "Odawara Town Line".
- December 20, 1940: Tram section is renamed "Odawara City Line".
- June 1, 1948: Hakone Tozan Railway becomes part of the Odakyu Group.
- August 1, 1950: Odakyu Electric Railway begins operating Limited Express and Express trains from Shinjuku to Hakone-Yumoto. The line voltage is changed to 1,500 V DC for the dual gauge section between Odawara and Hakone-Yumoto.
- June 1, 1956: Odawara City Line (tram) is abandoned.
- July 14, 1993: Hakone-Yumoto - Gōra section is uprated from 600 to 750 V DC. Operations start using 3-car EMUs.
- March 18, 2006: Hakone Tozan Railway discontinues operation using its own units between Odawara and Hakone-Yumoto. Dual-gauge section reduced to Iriuda - Hakone-Yumoto.
- March 15, 2008: New Odakyu "Romancecar" through service starts from Kita-Senju Station.
- October 12, 2019: The section between Hakone-Yumoto and Gora closed due to severe damage caused by Typhoon Hagibis. The heavy rains caused landslides over the tracks and washed away ballast.[1] In November 2019, the railway announced that repairs would keep the line closed until the fall of 2020.[7]
- On July 9, 2020, test trains began running on the fixed line with services scheduled to begin on July 23.[2]
- On April 1, 2024, the name of the operator company was changed from Hakone Tozan Railway Co., Ltd. to Odakyu Hakone Co., Ltd.[8]
Microsoft Train Simulator
[edit]This route appears in Microsoft Train Simulator complete with scenarios simulating prototypical operation (Only from Odawara to Hakone-Yumoto).
References
[edit]- ^ a b Kinoshita, Shotaro (18 October 2019). "Famous Japan mountain railway to take months to recover after Typhoon Hagibis: operator". mainichi.jp. The Mainichi. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ^ a b Murano, Eiichi (9 July 2020). "Test runs begin to resume trains along Hakone mountain route". asahi.com. The Asahi Shimbun. Retrieved 9 July 2020.
- ^ "Traversing Hakone's "Golden Course" by Land, Air, and Water". nippon.com. 2020-08-14. Retrieved 2023-09-17.
- ^ 箱根登山鉄道3000形を導入 [Hakone Tozan Railway to introduce 3000 series]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 6 June 2013. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ^ 箱根登山鉄道,3100形を導入 [Hakone Tozan Railway to introduce 3100 series]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 6 December 2016. Archived from the original on 6 December 2016. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ^ "地下鉄に乗り入れなくなった関東大手私鉄車両 想定しながら乗り入れてない車両まで6選" [6 major private railway vehicles in Kanto that can no longer enter the subway]. Traffic News (in Japanese). 2021-03-20. p. 1. Retrieved 2022-04-12.
- ^ "箱根湯本駅-強羅駅間の運転再開の見込みについて" [Expected Resumption of Operation between Hakone-Yumoto Station and Gora Station] (PDF) (Press release) (in Japanese). Hakone Tozan Railway. 22 November 2019. Retrieved 25 November 2019.
- ^ Odakyu Hakone Holdings Co., Ltd. (24 January 2024). "小田急箱根グループの組織再編に関するお知らせ" [Notice regarding reorganization of Odakyu Hakone Group] (PDF) (in Japanese).
External links
[edit]- Hakone Tozan Railway Official Site
- Hakone Navi (Odakyu official sightseeing guide, in English)



