Svyataya Anna
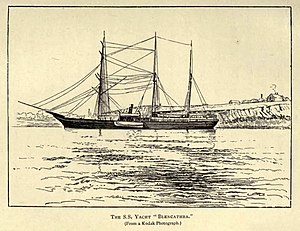 Svyataya Anna in her incarnation as the yacht Blencathra, from Helen Peel's Polar Gleams[1]
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | HMS Newport |
| Ordered | 5 March 1860 |
| Builder | Pembroke Dockyard |
| Laid down |
|
| Launched | 20 July 1867 |
| Commissioned | April 1868 |
| Fate | Sold to Sir Allen Young in May 1881 |
| Name | Pandora II |
| Name | Blencathra |
| Owner |
|
| Name |
|
| Fate | Presumed crushed by ice and lost 1914 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Philomel-class wooden screw gunvessel |
| Displacement | 570 tons |
| Length | |
| Beam | 25 ft 4 in (7.7 m) |
| Depth of hold | 13 ft (3.96 m) |
| Installed power | 325 ihp (242 kW) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed | 9.25 knots (17.13 km/h; 10.64 mph) |
| Complement | 60 |
| Armament |
|
The Philomel-class gunvessel HMS Newport was launched in Wales in 1867. Having become the first ship to pass through the Suez Canal, she was sold in 1881 and renamed Pandora II.[2] She was purchased again in about 1890 and renamed Blencathra,[2] taking part in expeditions to the north coast of Russia. She was bought in 1912 by Georgy Brusilov for use in his ill-fated 1912 Arctic expedition to explore the Northern Sea Route, and was named Svyataya Anna (Russian: Святая Анна), after Saint Anne. The ship became firmly trapped in ice; only two members of the expedition, Valerian Albanov and Alexander Konrad, survived. The ship has never been found.
Design
[edit]The Philomel-class gunvessels were an enlargement of the earlier Algerine-class gunboat of 1856. The first six of the class were ordered by the UK Admiralty from the naval dockyards between April 1857 and April 1859. Another twelve were ordered on 14 June 1859 to be constructed by contract in private yards, receiving their names on 24 September the same year; these were then fitted out at naval dockyards. The last eight of the class, of which Newport was the first, were ordered on 5 March 1860 for construction in naval dockyards, although six of them were later cancelled.[2]
Construction
[edit]Newport was laid down at Pembroke Dockyard in Wales on 17 September 1860. She and Alban were suspended in 1862, and six of the uncompleted vessels, including Alban were cancelled in 1863. Newport was finally launched on 20 July 1867. She was fitted with a Laird Brothers two-cylinder horizontal single-expansion steam engine driving a single screw and developing 325 indicated horsepower (242 kW).[2]
She was armed with a 68-pounder 95 cwt muzzle-loading smooth-bore gun, two 24-pounder howitzers and two 20-pounder breech-loading guns. All ships of the class later had the 68-pounder replaced by a 7-inch/110-pounder breech-loading gun. The class were fitted with a barque-rigged sail plan.[2]
Survey ship
[edit]
She was commissioned in April 1868 under Commander George Strong Nares, and employed in survey work in the Mediterranean.[3]
In 1869 during the opening ceremony and first passage of ships through the Suez Canal, although the French Imperial yacht L'Aigle was officially the first vessel to pass through the canal, Newport, commanded by Nares, actually passed through it first. On the night before the canal was due to open, Nares navigated his vessel, in total darkness and without lights, through the mass of waiting ships until it was in front of L'Aigle. When dawn broke, the French were horrified to find that the Royal Navy was now first in line and that it would be impossible to pass them. Captain Nares received both an official reprimand and an unofficial vote of thanks from the Admiralty for his actions in promoting British interests and for demonstrating superb seamanship.[4][5]
Pandora II
[edit]She was sold to Sir Allen Young in May 1881. He had previously owned another former Philomel-class gun vessel, HMS Pandora, and he named his new ship Pandora II after her.
Blencathra
[edit]The ship was sold in about 1890 to the wealthy F. W. Leyborne-Popham, who intended to use her as a yacht, and had an interest in Arctic waters. The vessel was specially adapted at the Richmond Dry Dock in Appledore, where an ice-ram was fitted and her quarter-deck extended.[6] Leybourne-Popham appointed Joseph Wiggins as captain of Blencathra for an 1893 voyage to the Kara Sea and into the Yenisey River, thus taking the ship to the furthest reaches of Siberia. To combine business with pleasure, he formed a syndicate to exploit the commercial opportunities offered by the carriage of cargo to the far north. As plans were being finalised, Wiggins received an urgent request from the Russians to carry rails for the Trans-Siberian Railway up the Yenisey to Krasnoyarsk. A 2,500-ton steamer, Orestes, was chartered and four Russian river vessels were provided for the final stages of transport in the Yenisey. With the river vessels embarked in Orestes, and Blencathra in company, the group left Vardø on 22 August 1893, reaching the mouth of the Yenisey on 3 September. Blencathra and Orestes returned to England via Arkhangelsk, while Wiggins stayed with the Russian river vessels, reaching Yeniseysk on 23 October.[7]
Among the party was Miss Helen Peel, granddaughter of Sir Robert Peel, who wrote a book about her experiences titled Polar Gleams.[1]
Leyborne-Popham sold his yacht to Major Andrew Coats, and in company with William Speirs Bruce, Coats made a long hunting voyage to the Arctic waters around Novaya Zemlya and Spitsbergen.[8] Bruce joined Blencathra at Tromsø, Norway in May 1898, and the cruise explored the Barents Sea, the dual islands of Novaya Zemlya and Kolguyev, before a retreat to Vardø to re-provision for the voyage to Spitsbergen. In a letter Bruce reported, "This is a pure yachting cruise and life is luxurious". Nevertheless, the scientific purpose of the voyage was not forgotten; measurement of temperature and salinity and meteorological observations went on day and night.[9]
1912 Arctic expedition
[edit]The ship was lost in 1914 during the disastrous Arctic expedition captained by Georgy Brusilov, when it was hopelessly locked in the ice. Svyataya Anna was last seen by the party led by the second-in-command Valerian Albanov who abandoned the ship to try and reach safety. Only two members of the expedition survived, Albanov included. Svyataya Anna, Brusilov and the rest of the crew were never seen again.
A geological feature in the Arctic Ocean basin, the St. Anna or Svyataya Anna Trough, located east of Franz Josef Land, with a depth of 620 m, has been named in memory of this ill-fated ship.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Peel, Helen (1894). Polar Gleams. London: Edward Arnold. Retrieved 25 June 2010.
- ^ a b c d e Winfield, p.222
- ^ "HMS Newport at William Loney RN website". Retrieved 24 June 2010.
- ^ "The People: Captain Nares". HMS Challenger. University of California, San Diego. Archived from the original on 9 October 2015. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ "Obituary of Sir George Nares at JSTOR". The Geographical Journal. 45 (3): 255–257. 1915. JSTOR 1779806.
- ^ "Western Morning News". 26 July 1893. pp. 5h.
- ^ "Joseph Wiggins (1832–1905)". Arctic Journal, Vol 47, No.4 (December 1994). p. 405. Retrieved 25 June 2010.
- ^ With the yachts Blencathra and Princesse Alice to the Barents and Greenland seas, Scottish Geographical Magazine, 1899. Vol 15, pp. 113-126.
- ^ Speak, Peter: William Speirs Bruce NMS Publishing, Edinburgh 2003 ISBN 1-901663-71-X
- Albanov, Valerian; Tr. Dubosson, Linda. In the Land of White Death : An Epic Story of Survival in the Siberian Arctic, Modern Library, 2000, ISBN 978-0-679-64100-1
- Remote Sensing of Sea Ice in the Northern Sea Route, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2007 ISBN 978-3-540-24448-6
- Barr, William, Otto Sverdrup to the rescue of the Russian Imperial Navy.
