Epigravettian
 | |
| Alternative names | Tardigravettian |
|---|---|
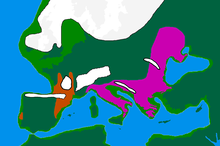
| Geographical range | Southern and Eastern Europe |
| Period | Late Upper Paleolithic |
| Dates | ~21,000 – 10,000 cal. BP[1] |
| Type site | None (because likely a continuation of the Gravettian) |
| Major sites | Paglicci, Arene Candide, Riparo Tagliente, Dolní Věstonice |
| Preceded by | Gravettian |
| Followed by | Magdalenian, Mesolithic cultures |
| Defined by | Georges Laplace, 1958 (broader-than-modern meaning)[2] Broglio, Laplace et al., 1963 (modern meaning, as “Tardigravettiano”)[3] |
| The Paleolithic |
|---|
| ↑ Pliocene (before Homo) |
| ↓ Mesolithic |
The Epigravettian (Greek: epi "above, on top of", and Gravettian) was one of the last archaeological industries and cultures of the European Upper Paleolithic. It emerged after the Last Glacial Maximum around ~21,000 cal. BP or 19,050 BC. It succeeds the Gravettian culture in Italy. Initially named Tardigravettian (Late Gravettian) in 1964 by Georges Laplace in reference to several lithic industries found in Italy,[4] it was later renamed in order to better emphasize its independent character.
Three subphases, the Early Epigravettian (20,000 to 16,000 BP), the Evolved Epigravettian (16,000 to 14,000 BP) and the Final Epigravettian (14,000 to 8,000 BP), have been established, that were further subdivided and reclassified.[5][6][7] In this sense, the Epigravettian is simply the Gravettian after ~21,000 BP,[is this date calibrated?] when the Solutrean had replaced the Gravettian in most of France and Spain.
Several Epigravettian cultural centers have developed contemporaneously after 22,000 years BP in Europe. These range across southern, central and most of eastern Europe, including southwestern France, Italy, Southeast Europe, the Caucasus, Ukraine and Western Russia to the banks of the Volga River.
Its lithic complex was first documented at numerous sites in Italy. Great geographical and local variability of the facies is present, however all sites are characterized by the predominance of microliths, such as backed blades, backed points, and bladelets with retouched end.[8]
The Epigravettian is the last stage of the Upper Paleolithic succeeded by Mesolithic cultures after 10,000 BP.[9]
In a genetic study published in Nature in May 2016, the remains of an Epigravettian male from Ripari Villabruna in Italy were examined. He carried the paternal haplogroup R1b1 and the maternal haplogroup U5b. An Epigravettian from the Satsurblia Cave in Georgia, who was examined in a previous study, has been found to be carrying the paternal haplogroup J1 and the maternal haplogroup K3.[10]
Analysis of Epigravettian producing individuals in Italy indicates that they not closely related to earlier Gravettian-producing inhabitants of the peninsula, and instead belong to the Villabruna genetic cluster. This group is more closely related to ancient and modern peoples in the Middle East and the Caucasus than earlier European Cro-Magnons. Epigravettian peoples belonging to the Western Hunter Gatherer genetic cluster expanded across Western Europe at the end of the Pleistocene, largely replacing the producers of the Magdalenian culture that previously dominated the region.[11]
-
Epigravettian artefacts, maybe 24 000 - 18 000 BP. Anthropos Pavilon, Brno
-
Epigravettian artefact, extremely stylized sculpture, Anthropos, Brno.
-
Epigravettian ceramic figurine of a horse or deer, Vela Spila, Croatia, dated to 15,400-14,600 BP.[12]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Cyril Montoya. "Apport de l'analyse technique à la compréhension de l'évolution des groupes humains épigravettiens d'Italie Nord Orientale: la production lithique de l'US 15a-65 du Riparo Dalmeri" (PDF). Université de Provence. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 7, 2019. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- ^ G. Laplace. "Recherches sur l'origine et l'évolution des complexes leptolithiques. Le problème des Périgordiens I et II et l'hypothèse du synthétotype aurignaco-gravettien. Essai de typologie analytique". Quaternaria (in French). 4: 133–164.
- ^ A. Broglio; G. Laplace; F. Zorzi. "I depositi quaternari di Ponte di Veia. Le industrie". Memorie del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Verona (in Italian). 11: 325–367.
- ^ Laplace, Georges (1964). "Les subdivisions du Leptolithique italien. Étude de typologie analytique". Bullettino di Paletnologia Italiana. 73: 25–63.
- ^ Margherita Mussi (11 April 2006). Earliest Italy: An Overview of the Italian Paleolithic and Mesolithic. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 238–. ISBN 978-0-306-47195-7.
- ^ Giulia Ricci, Margarita Vadillo Conesa, Fabio Martini (2019). "Through diachronic discontinuities and regionalization: The contribution of the analysis of the lithic industries from Grotta della Serratura (Strata 10-9) in the definition of Epigravettian in the southern Italian peninsula". Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports. 24: 175–191. Bibcode:2019JArSR..24..175R. doi:10.1016/j.jasrep.2018.11.038.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Epigravettian". Archaeology Wordsmith. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- ^ Keiko Kitagawa, Marie-Anne Julien, Oleksandra Krotova, Alexander A. Bessudnov, Mikail V. Sablin, Dmytro Kiosak, Natalia Leonova, Boris Plohenko, Marylene Patou-Mathis. "Glacial and post-glacial adaptations of hunter-gatherers: Investigating the late Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic subsistence strategies in the southern steppe of Eastern Europe" (PDF). Unite Histoire Naturelle de l’Homme Prehistorique, Sorbonne Universités. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 7, 2019. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zdenka Nerudova. "ON SITE SETTLEMENT ACTIVITIES: THE EXAMPLE OF THE EPIGRAVETTIAN SITE OF BRNO-ŠTÝŘICE III (CZECH REPUBLIC)" (PDF). Moravian Museum, Anthropos Institute, Brno. Retrieved February 5, 2019.
- ^ Fu 2016.
- ^ Posth, C., Yu, H., Ghalichi, A. (2023). "Palaeogenomics of Upper Palaeolithic to Neolithic European hunter-gatherers". Nature. 615 (2 March 2023): 117–126. Bibcode:2023Natur.615..117P. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-05726-0. hdl:10256/23099. PMID 36859578.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Farbstein, Rebecca; Radić, Dinko; Brajković, Dejana; Miracle, Preston T. (24 July 2012). "First Epigravettian Ceramic Figurines from Europe (Vela Spila, Croatia)". PLOS ONE. 7 (7): e41437. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...741437F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041437. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3404104. PMID 22848495.
Sources
[edit]- Fu, Qiaomei (May 2, 2016). "The genetic history of Ice Age Europe". Nature. 534 (7606). Nature Research: 200–205. Bibcode:2016Natur.534..200F. doi:10.1038/nature17993. PMC 4943878. PMID 27135931.
- Upper Paleolithic cultures of Europe
- Industries (archaeology)
- Archaeological cultures of Europe
- Archaeological cultures in Austria
- Archaeological cultures in Bulgaria
- Archaeological cultures in Croatia
- Archaeological cultures in Italy
- Archaeological cultures in Montenegro
- Archaeological cultures in Romania
- Archaeological cultures in Serbia
- Archaeological cultures in Slovakia
- Archaeological cultures in Ukraine
- Stone Age Austria



![Epigravettian ceramic figurine of a horse or deer, Vela Spila, Croatia, dated to 15,400-14,600 BP.[12]](http://up.wiki.x.io/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2b/Epigravettian_ceramic_figurine_of_a_horse_or_deer%2C_Vela_Spila%2C_Croatia%2C_15400-14600_BP.jpg/200px-Epigravettian_ceramic_figurine_of_a_horse_or_deer%2C_Vela_Spila%2C_Croatia%2C_15400-14600_BP.jpg)