Community Church of New York
| Church of the Messiah I | |
|---|---|
 1826–37, Mercer and Prince Streets | |
| General information | |
| Architectural style | Greek Revival |
| Location | Manhattan, New York City |
| Coordinates | 40°43′46″N 73°59′35″W / 40.72940°N 73.99313°W |
| Opened | 1826 |
| Demolished | 1837 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Josiah R. Brady |
| Church of the Messiah II | |
|---|---|
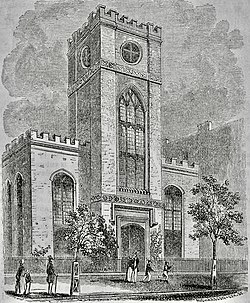 1839–65, Broadway at Waverly Place | |
| General information | |
| Architectural style | Romanesque Revival |
| Location | Manhattan, New York City |
| Coordinates | 40°43′29″N 73°59′55″W / 40.72486°N 73.99866°W |
| Opened | 1839 |
| Demolished | 1865 |
| Church of the Messiah III | |
|---|---|
 1867–1930, 34th Street and Park Avenue | |
| General information | |
| Architectural style | Romanesque Revival |
| Location | Manhattan, New York City |
| Coordinates | 40°44′51″N 73°58′54″W / 40.74753°N 73.98160°W |
| Opened | 1867 |
| Demolished | 1930 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Carl Pfeiffer |
The Second Congregational Church in New York, organized in 1825, was a Unitarian congregation which had three permanent homes in Manhattan, New York City, the second of which became a theater after they left it. In 1919 the congregation joined the Community Church Movement and changed its name to Community Church of New York.[1] The same year, its church building on 34th Street was damaged by fire.[2] From 1948 until 2022, the congregation was housed at 40 East 35th Street.[3][4]: 49 As of 2024, the church offices are located on East 35th Street and services are held at the neighboring Church of the Incarnation. The Community Church of New York is a member of the Unitarian Universalist Association.
Origins
[edit]The first Unitarian Society in New York was founded May 24, 1819, and incorporated on November 15 under the name "First Congregational Church in the City of New York" (later "Unitarian Church of All Souls"), although there had been between three and five Congregational churches in the city before that.[5]: 369 On January 20, 1821, the congregation dedicated a newly built church on Chambers Street, west of Church Street.[5][4]: 12,B60
By 1825, the church had become crowded, and many of the pew holders lived above Canal Street. On March 19, a meeting was held of persons disposed to unite in building a church there for Unitarian worship, and "The Second Congregational Unitarian Society" was formed. They built a church on the northwest corner of Prince and Mercer Streets, opening on December 7, 1826. William Ellery Channing preached a sermon[6] and William Cullen Bryant, a member of the congregation, wrote a hymn for the occasion. Designed by Josiah R. Brady, the edifice was one of the earliest Greek Revival buildings in New York.[5][3][4]: 48,E86
Orville Dewey became pastor in 1835, a position he held until 1848. During his tenure, on November 26, 1837, the church building was completely destroyed by fire. The congregation took temporary quarters until May 2, 1839, when their new church, which they called Church of the Messiah, opened for worship at 728–30 Broadway, opposite Waverly Place.[7][5][8]
In January 1865, that church was sold to department store magnate A. T. Stewart and converted into a theater, which subsequently operated under a series of names, including Globe Theatre, and ending with New Theatre Comique. It burned down in 1884.[9][5][4]: 48
34th Street
[edit]The congregation's third church, located on 34th Street at the northwest corner of Fourth (now Park) Avenue, was inaugurated in 1867. It was designed in Victorian Romanesque style by Carl Pfeiffer.[4]: 48
In 1906, the church called John Haynes Holmes as its minister.[3] At just 27 years old, Holmes was installed in the winter of 1907, beginning a tenure that would profoundly shape the church's identity and mission. Under Holmes' leadership, the church embarked on a path of increased social activism and racial integration.
In 1909, Holmes accepted an invitation from W.E.B. DuBois to join the founding circle of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). The following year, the church welcomed its first Black congregant, Mr. Horace Dudley, whom Holmes invited to become an usher. This marked the beginning of the church's commitment to racial diversity and inclusion.
In 1919, the congregation underwent a significant transformation, renaming itself the Community Church of New York. This change was part of a broader reform led by Rev. Holmes, which included removing pew ownership, granting the minister Freedom of the Pulpit, leaving the Unitarian denomination, and joining the Community Church movement. The church also declared itself pacifist, opposing war and violence in all forms.
On May 25, 1919, Rev. Holmes announced the church's change of name to Community Church of New York. He explained:
I have left Unitarianism, cut myself off from all denominational connections of every kind, that I may preach a universal, humanistic religion which knows no bounds of any kind, not even Christianity. We have … placed the support of the church on the … basis of free voluntary subscriptions. We have rewritten our covenant, eliminating every last vestige of theology, thus relegating all matters of belief to private individual opinion. … [Any person] is welcome to our church, whether he be rich or poor, black or white, Christian, Jew, Hindu, or Parsee.[1]
Mid-20th Century Developments
[edit]A new building on 35th Street was constructed in the late 1940s and dedicated in 1948, envisioned as a permanent home for the Community Church of New York. The dedication ceremony was attended by numerous dignitaries, including Jawaharlal Nehru, Governor Dewey, and Rabbi Stephen Wise.

In 1949, John Haynes Holmes officially retired, succeeded by Donald Szantho Harrington as Senior Minister. The church continued its commitment to social justice, with dozens of congregants participating in the 1962 March on Washington and with Rev. Harrington stepping forward to serve as a prominent activist in favor of civil rights and equality for African Americans. In 1965, Reverend Harrington, along with other liberal religious leaders, spent 17 days in Alabama supporting the Selma marchers.
In 1960, the Community Church of New York hosted a debate between Malcolm X and Bayard Rustin, showcasing the two civil rights leaders’ differing visions for the path to equality and justice between Black and white people in the United States.
Late 20th Century and Beyond
[edit]The church maintained its progressive stance throughout the latter half of the 20th century, supporting causes such as the anti-apartheid movement and LGBTQ+ rights. In the 1970s, the American Committee on Africa was formed and hosted with the support of the Community Church, which served as a home base for the organization until the release of leader Nelson Mandela from South African prison. In 1990, Nelson Mandela spoke at the church shortly after his release, thanking American anti-apartheid activists for their support.
In 1982, Donald Harrington stood down as Senior Minister and the congregation called his successor, Reverend Bruce Southworth. Throughout the 1980s, the church and its leadership continued their dedication to fighting against apartheid in South Africa, and Rev. Southworth went on to serve as an election monitor in Soweto, South Africa in 1994.
The Community Church was recognized as an LGBT Welcoming Congregation by the Unitarian Universalist Association in 1997, and witnessed its first same-sex commitment ceremony in 1998.
In 2019, Community Church of New York, called their first woman to the position of Senior Minister, Rev. Peggy Clarke.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Church of Messiah Adopts New Name" (PDF). The New York Times. May 26, 1919.
- ^ "To Restore Burned Church" (PDF). The New York Times. September 13, 1919.
- ^ a b c "The Early Years". The Community Church of New York. Archived from the original on July 31, 2013. Retrieved April 14, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Dunlap, David W. (2004). From Abyssinian to Zion: A Guide to Manhattan's Houses of Worship. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231125437.
- ^ a b c d e Greenleaf, Jonathan (1850). A History of the Churches, of All Denominations, in the City of New York (second ed.). New York: E. French. pp. 369, 373–76.
- ^ Channing, William E. (1846). "Unitarian Christianity Most Favorable to Piety". The Works of William E. Channing, D. D. Vol. III (sixth complete ed.). Boston: James Munroe and Company. p. 163.
- ^ Dewey, Mary E., ed. (1884). Autobiography and Letters of Orville Dewey, D. D. Boston: Roberts Brothers. pp. 75f.
- ^ Perris, William (1854). Maps of the City of New York. Vol. 5. New York: Perris & Browne. Plate 61 (church is mislabeled "Presbyterian").
- ^ Brown, Thomas Allston (1903). A History of the New York Stage: From the First Performance in 1732 to 1901. Vol. II. New York: Dodd, Mead and Company. pp. 376–98.
External links
[edit] Media related to Church of the Messiah (Manhattan) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Church of the Messiah (Manhattan) at Wikimedia Commons- Official website

- Churches in Manhattan
- Building and structure fires in New York City
- Church fires in the United States
- Demolished churches in New York City
- Demolished buildings and structures in Manhattan
- Churches completed in 1826
- Churches completed in 1839
- Churches completed in 1867
- 1864 disestablishments in New York (state)
- West Village
- SoHo, Manhattan
- Murray Hill, Manhattan
- Gothic Revival church buildings in New York City
- Greek Revival church buildings in New York City
- Romanesque Revival church buildings in New York City
- Victorian architecture in New York City
- Broadway (Manhattan)
- 1825 establishments in New York (state)
