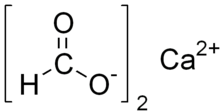
Calcium formate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Calcium diformate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.058 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E238 (preservatives) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ca(HCO2)2 | |
| Molar mass | 130.113 g/mol |
| Appearance | white-to-yellow crystals or crystalline powder[1] |
| Odor | smells slightly like acetic acid[2] |
| Density | 2.02 g/cm3[3] |
| Melting point | decomposes at 300 °C[3] |
| 16.1 g/100 g (0 °C) 18.4 g/100 g (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | insoluble in ethanol[3] methanol: 0.27 g/100 g (15 °C) 0.23 g/100 g (66 °C)[4] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H318 | |
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310, P337+P313 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
rats: 2640 mg/kg (oral), 154 mg/kg (IV)[4] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Calcium acetate |
Other cations
|
Sodium formate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Calcium formate is the calcium salt of formic acid. It is also known as E238. Under this E number it is used as an animal feed preservative within EU, but not in foods intended for people.[5]
Calcium formate is stable at room temperature,[5] is flammable and forms orthorhombic crystals.[2] The mineral form is very rare and called formicaite, and is known from a few boron deposits.
Uses
[edit]Calcium formate is used within EU as an animal feed preservative. It acidifies the feed thus preventing microbe growth and increasing shelf life. About 15 g of calcium formate addition per kg of feed lowers its pH by one. 15 g/kg is the maximum recommended feed concentration within EU – this level is thought to be safe for pigs, chickens, fish and ruminants. The compound is not environmentally harmful in feed use at these levels. Calcium formate prevents the growth of bacteria such as E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus hirae in growth mediums. It also prevents the growth of fungi like Aspergillus niger and Candida albicans. However, the relevance of these experimental observations to feed preservation is not known.[5]
Calcium formate is used as a masking agent in the chrome tanning of leather. Calcium formate in tannage formulation promotes faster, more efficient leather penetration of the chrome. Calcium formate can also be used as a replacement for formic acid in the pickling operation.[4]
As a grout and cement additive, calcium formate imparts a number of desirable properties in the final product, e.g. increased hardness and decreased setting time. Its addition is desirable for work at low temperature and for inhibition of corrosion of metal substrates within cement/grout. It is also effective in the prevention of efflorescence. In drywall (gypsum board), calcium formate can function as a fire retardant.[4]
Calcium formate and urea mixtures are effective deicers, and tend to cause less corrosion of steel and cement surfaces relative to some other deicers.[4]
Research
[edit]Calcium formate seems to be safe as a calcium supplement for people with one time doses of 3.9 g (1200 of calcium) per day.[6] Increases in blood formate concentration have been observed with such doses, but in healthy subjects the formate does not accumulate, and is quickly metabolized. Calcium formate is shown to be more readily absorbed form of calcium than calcium carbonate and calcium citrate.[7] No optic nerve damage has been observed with calcium formate supplementation – along with formaldehyde, formate is a major metabolic product of methanol, which can cause blindness upon ingestion.[8]
Calcium formate could be used to remove environmentally harmful (see acid rain) sulfur oxides (SOX) from fossil fuel exhausts of e.g. power plants. Calcium formate is added to wet calcium carbonate to promote the formation of gypsum when exhaust is run through it. This process is called wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGS). Gypsum binds sulfur oxides thus reducing their release to the environment via exhaust. Calcium formate seems to be more effective than or almost equally as effective as some other industrially used WFGS agents.[9]
Production
[edit]Calcium formate is formed as a co-product during trimethylolpropane production. Hydrated lime (calcium hydroxide) is used as the source of calcium. Butyraldehyde and formaldehyde react in a water solution in the presence of a basic catalyst, forming an unstable intermediate product, dimethylol butyraldehyde (DIMBA). DIMBA reacts further with formaldehyde to give trimethylolpropane and calcium formate. Calcium formate is separated from the solution, heat treated to remove formaldehyde and then dried.[5]
Calcium formate can also be made from calcium hydroxide and carbon monoxide at high pressure and temperature[2] – e.g., at 180 °C and 35 atm.[10] It may also be made from calcium chloride and formic acid.[2]
Safety
[edit]Pure calcium formate powder irritates eyes severely, but causes no skin irritation. Powder inhalation can be dangerous.[5] The compound has a stinging taste. Ingesting liquids with high calcium formate concentrations cause severe gastrointestinal lesions.[11]
References
[edit]- ^ "ICSC 1634 – Calcium formate". www.ilo.org. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ a b c d The Merck index. S Budavari, M O'Neil, A Smith (12th ed.). Chapman & Hall Electronic Pub. Division. 2000. p. 1675. ISBN 9781584881292.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b c Haynes, William M. (2014). "4". CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. Haynes, WM (95th ed.). p. 55. ISBN 9781482208689.
- ^ a b c d e "Calcium Formate Product Data" (PDF). GEO Specialty Chemicals. 2015. Retrieved 2019-02-11.
- ^ a b c d e "Scientific Opinion on the safety and efficacy of calcium formate when used as a technological additive for all animal species". EFSA Journal. 12 (11). 2014. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3898. ISSN 1831-4732.
- ^ Hanzlik, RP; Fowler, SC; Eells, JT (2005). "Absorption and elimination of formate following oral administration of calcium formate in female human subjects". Drug Metabolism and Disposition. 33 (2): 282–286. doi:10.1124/dmd.104.001289. hdl:1808/5937. ISSN 0090-9556. PMID 15547050. S2CID 5956107.
- ^ Hanzlik, RP; Fowler, SC; Fisher, DH (2005). "Relative bioavailability of calcium from calcium formate, calcium citrate, and calcium carbonate". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 313 (3): 1217–1222. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.081893. hdl:1808/5936. ISSN 0022-3565. PMID 15734899. S2CID 4976426.
- ^ MM Altaweel; et al. (2009). "Ocular and systemic safety evaluation of calcium formate as a dietary supplement" (PDF). Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 25 (3): 223–230. doi:10.1089/jop.2008.0128. hdl:1808/8319. ISSN 1557-7732. PMID 19456257.
- ^ Z Li; et al. (2017). "Effect of calcium formate as an additive on desulfurization in power plants". Journal of Environmental Sciences. 67: 89–95. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2017.06.023. PMID 29778177.
- ^ US patent 1920851A, "Process for producing formates of alkaline earth metals"
- ^ Scott, DJ; van Wijk, N (2000). "Comparison in dairy cattle of mucosal toxicity of calcium formate and calcium chloride in oil". New Zealand Veterinary Journal. 48 (1): 24–26. doi:10.1080/00480169.2000.36153. ISSN 0048-0169. PMID 16032113. S2CID 42365225.

